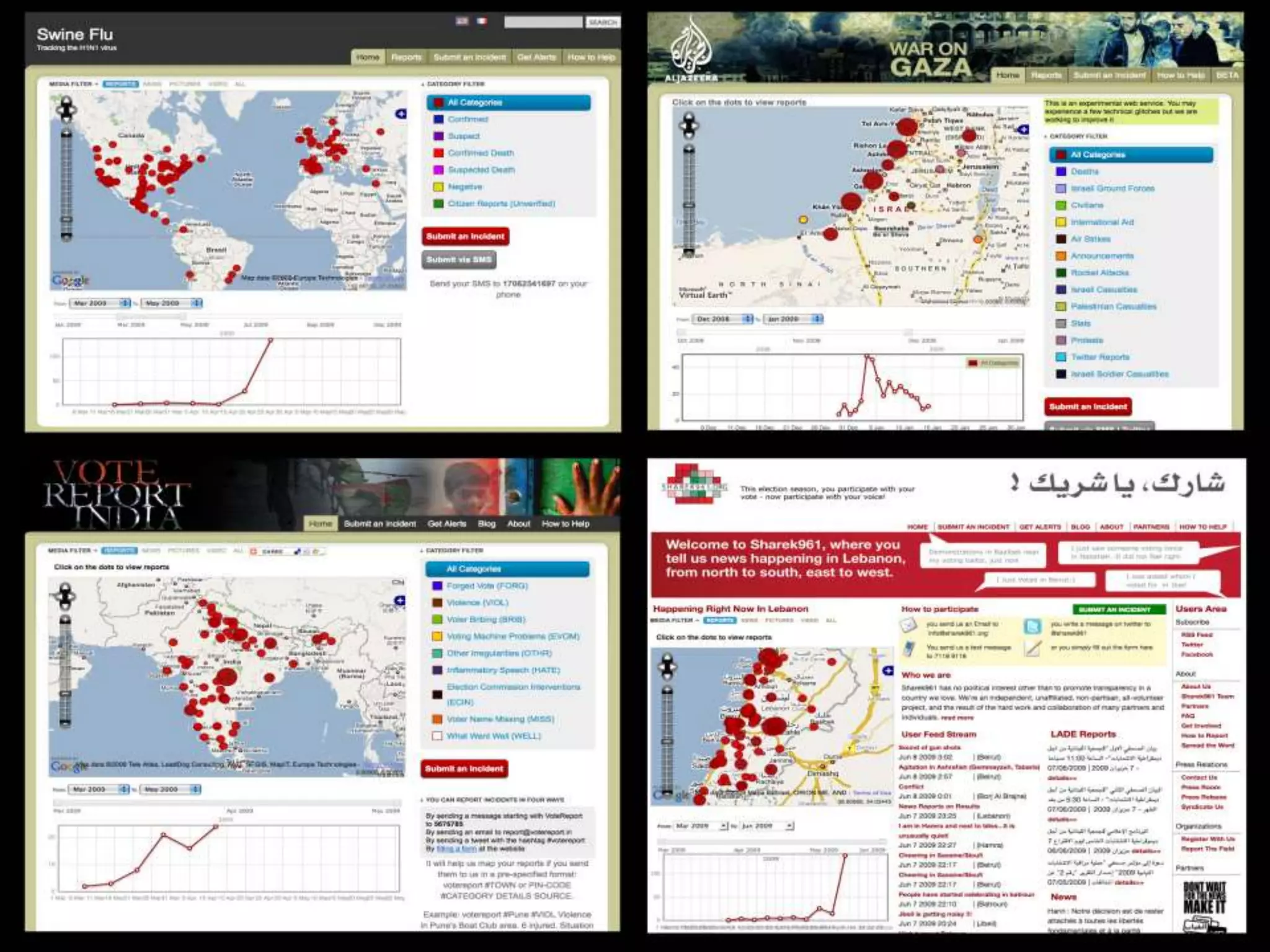
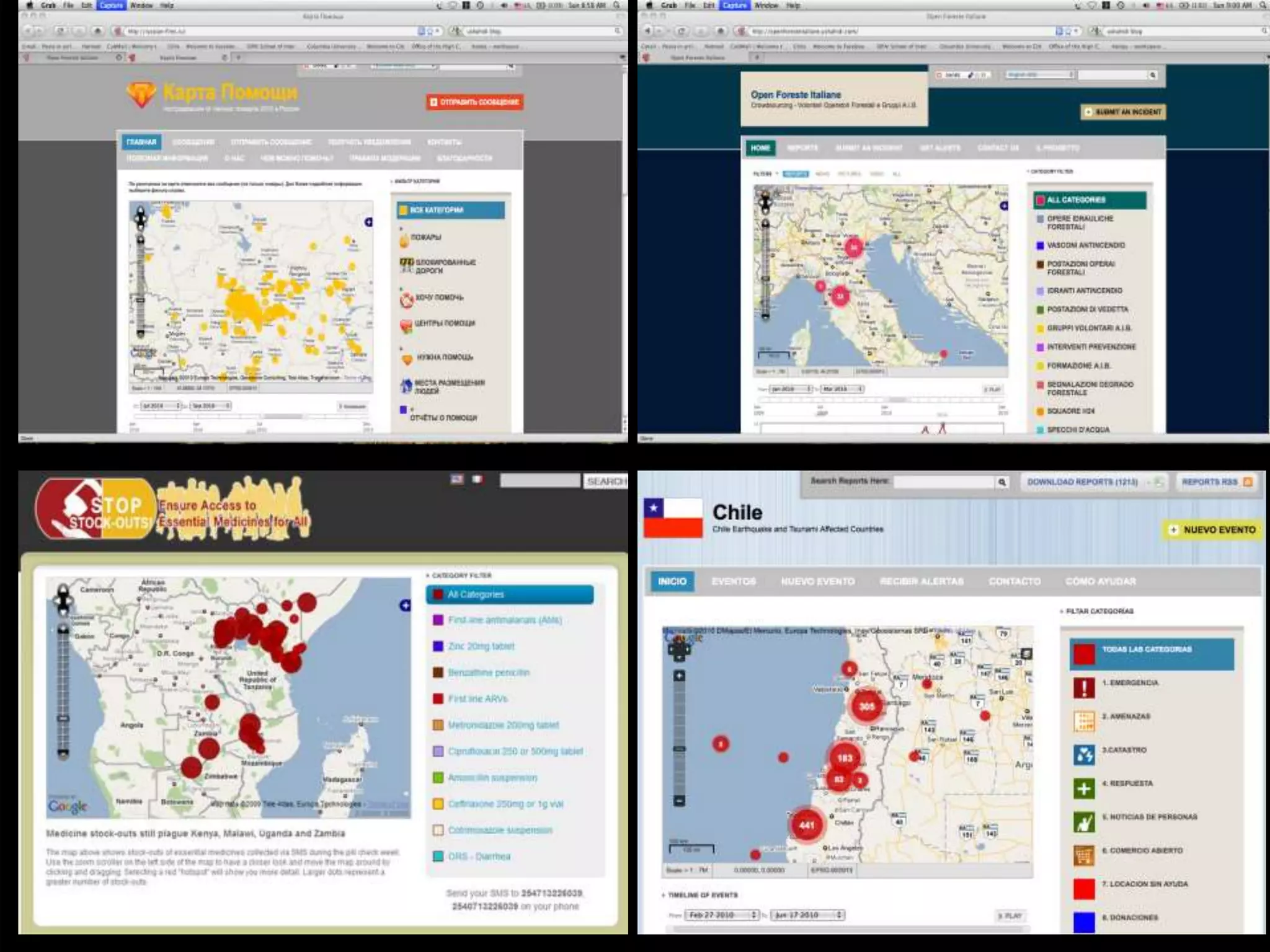
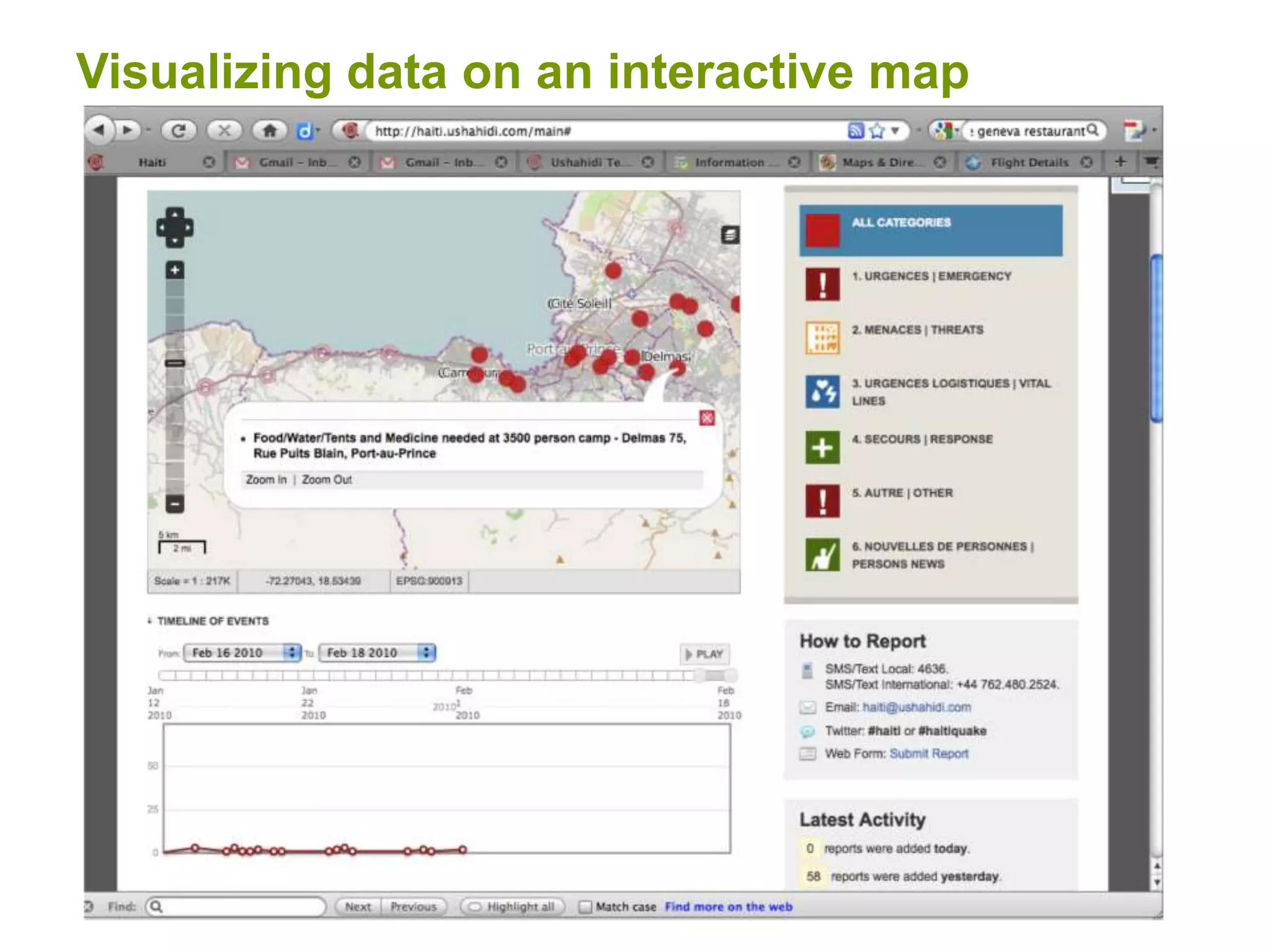
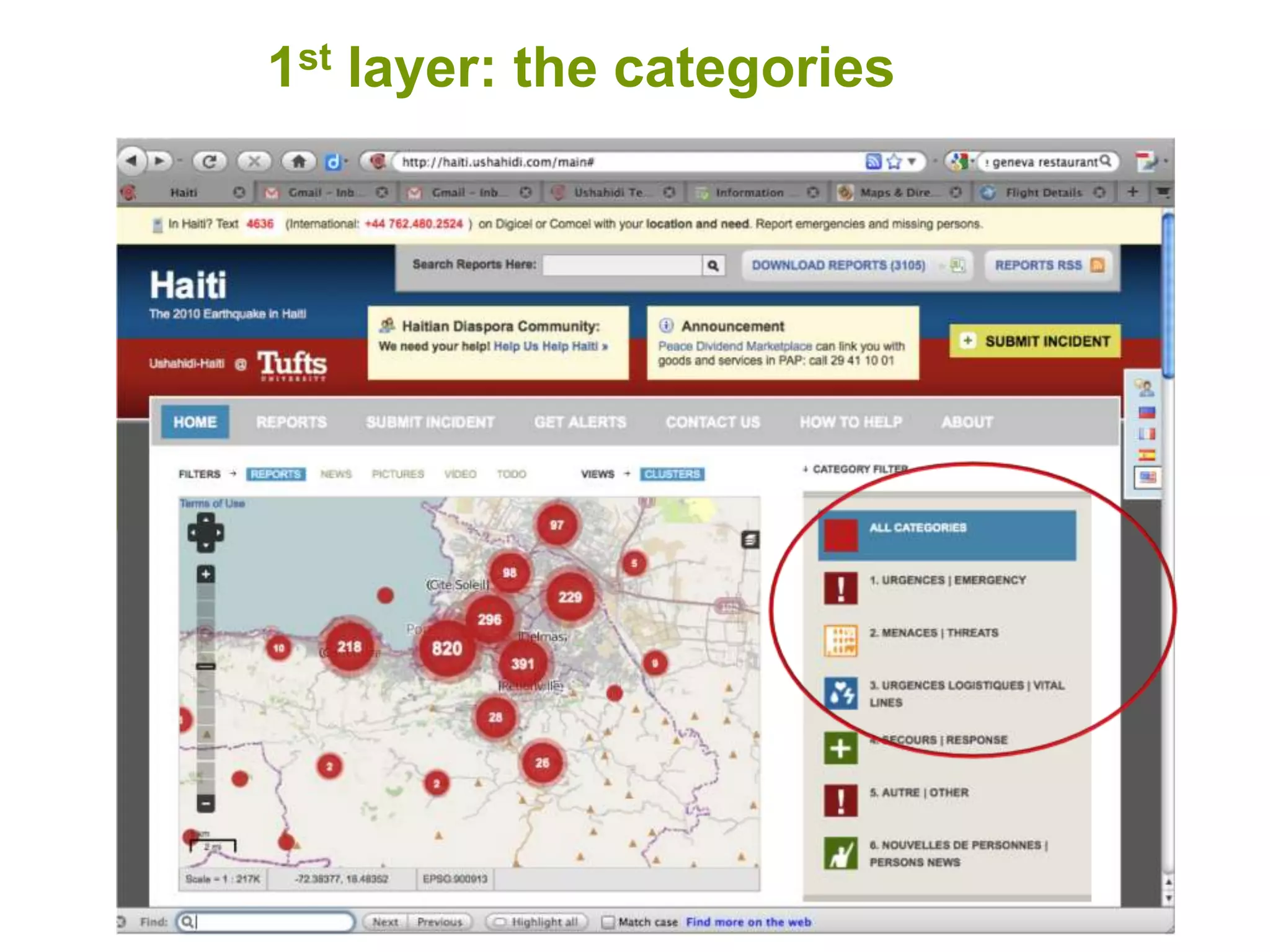
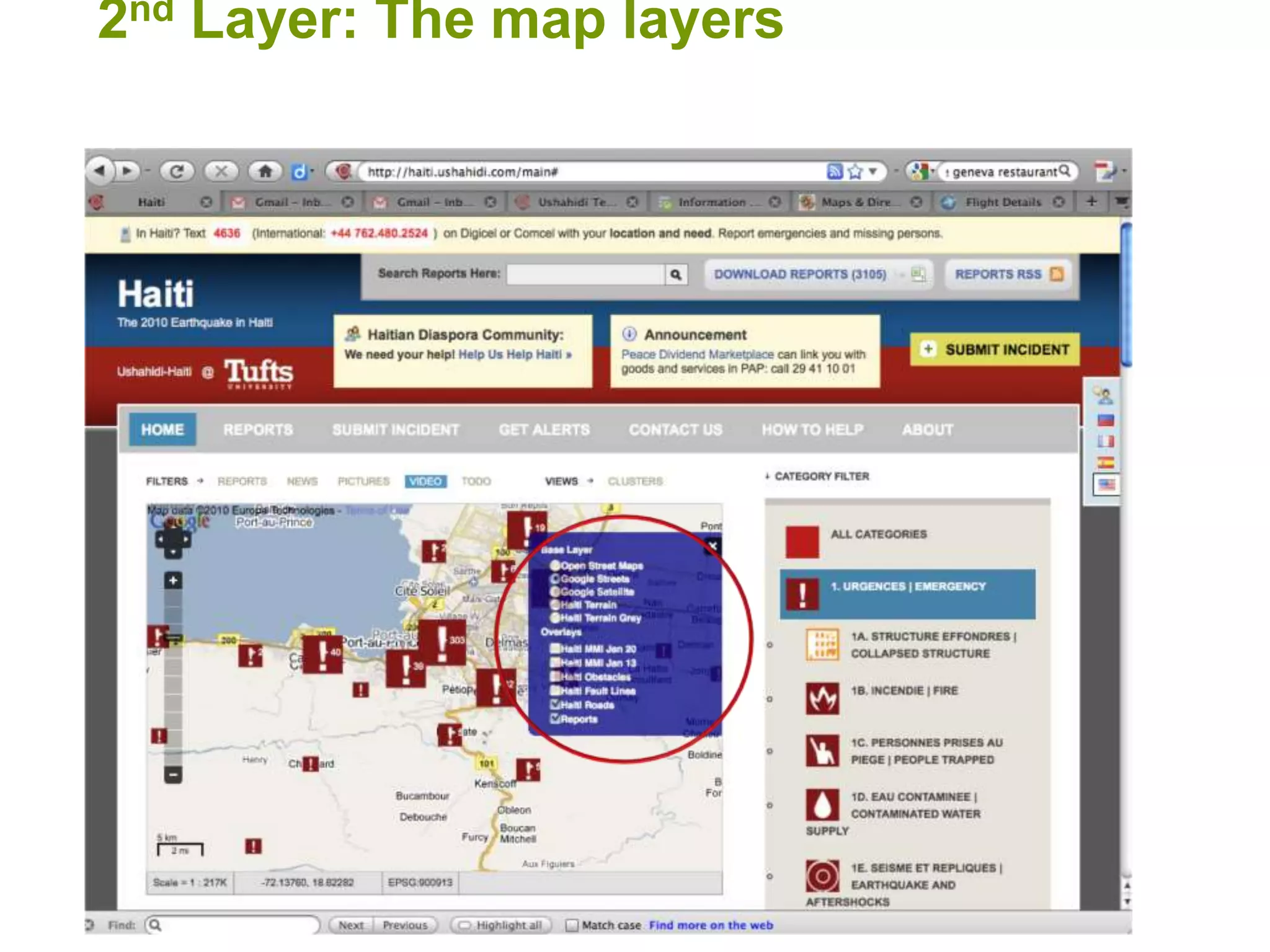
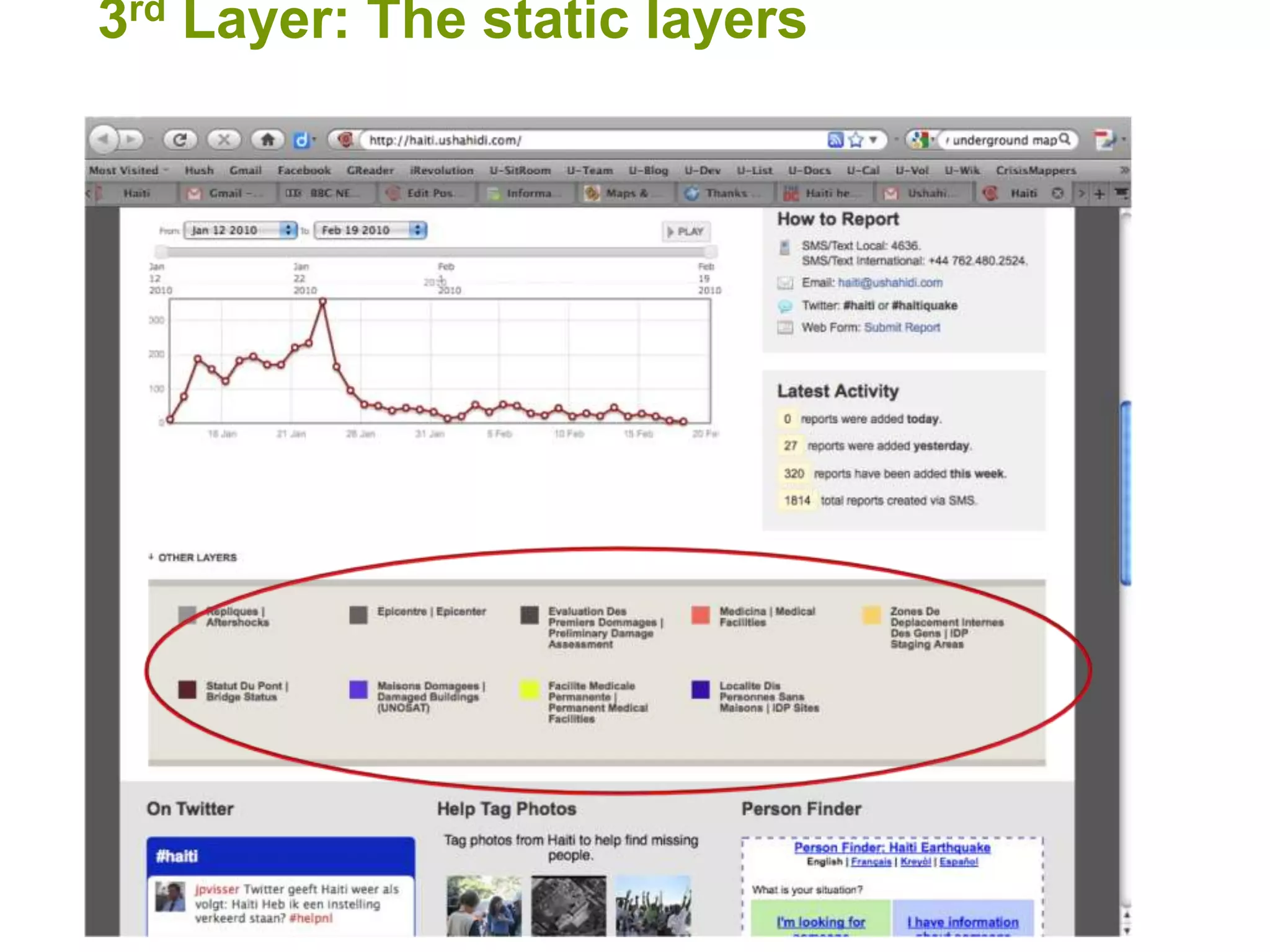
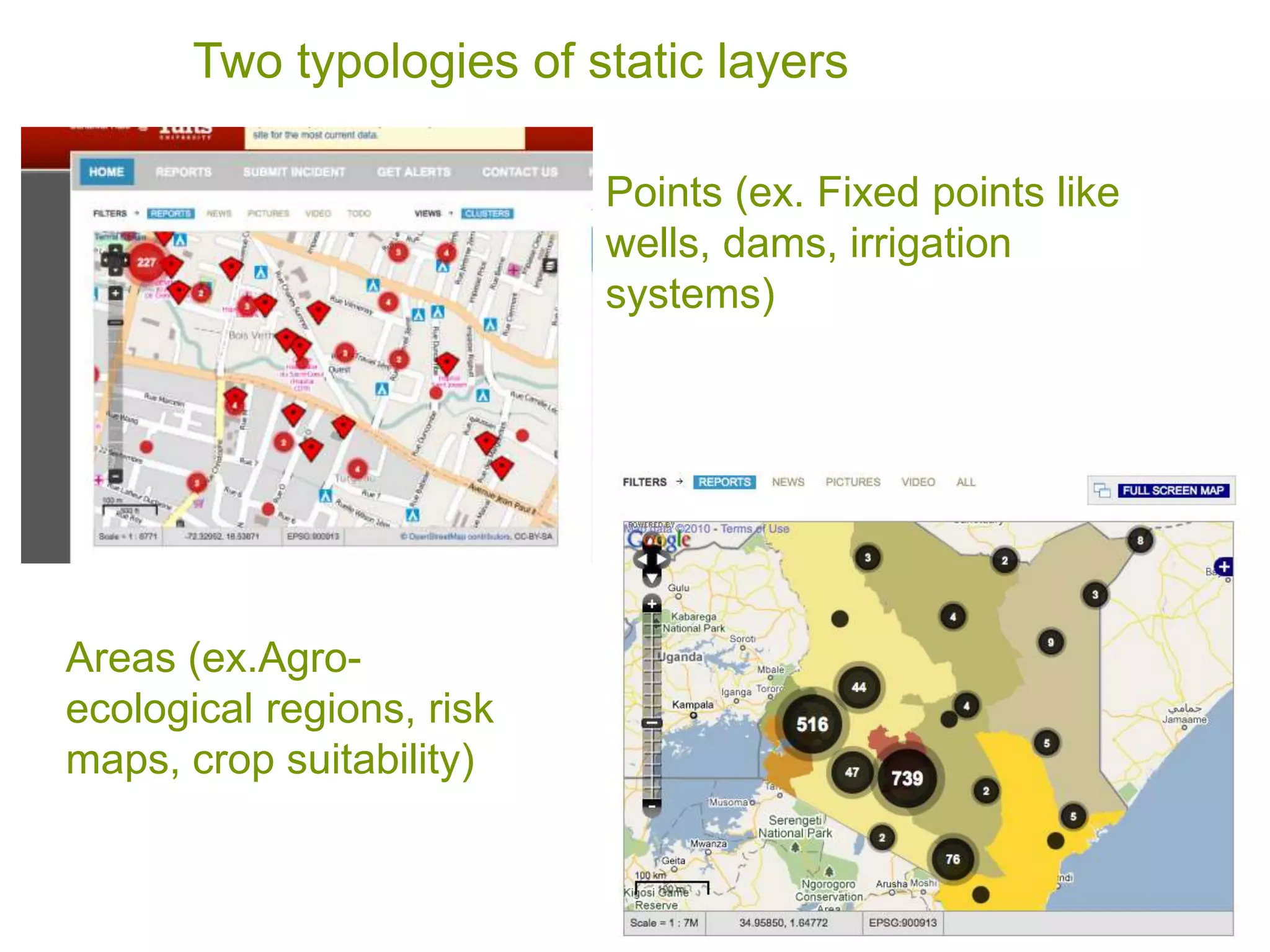
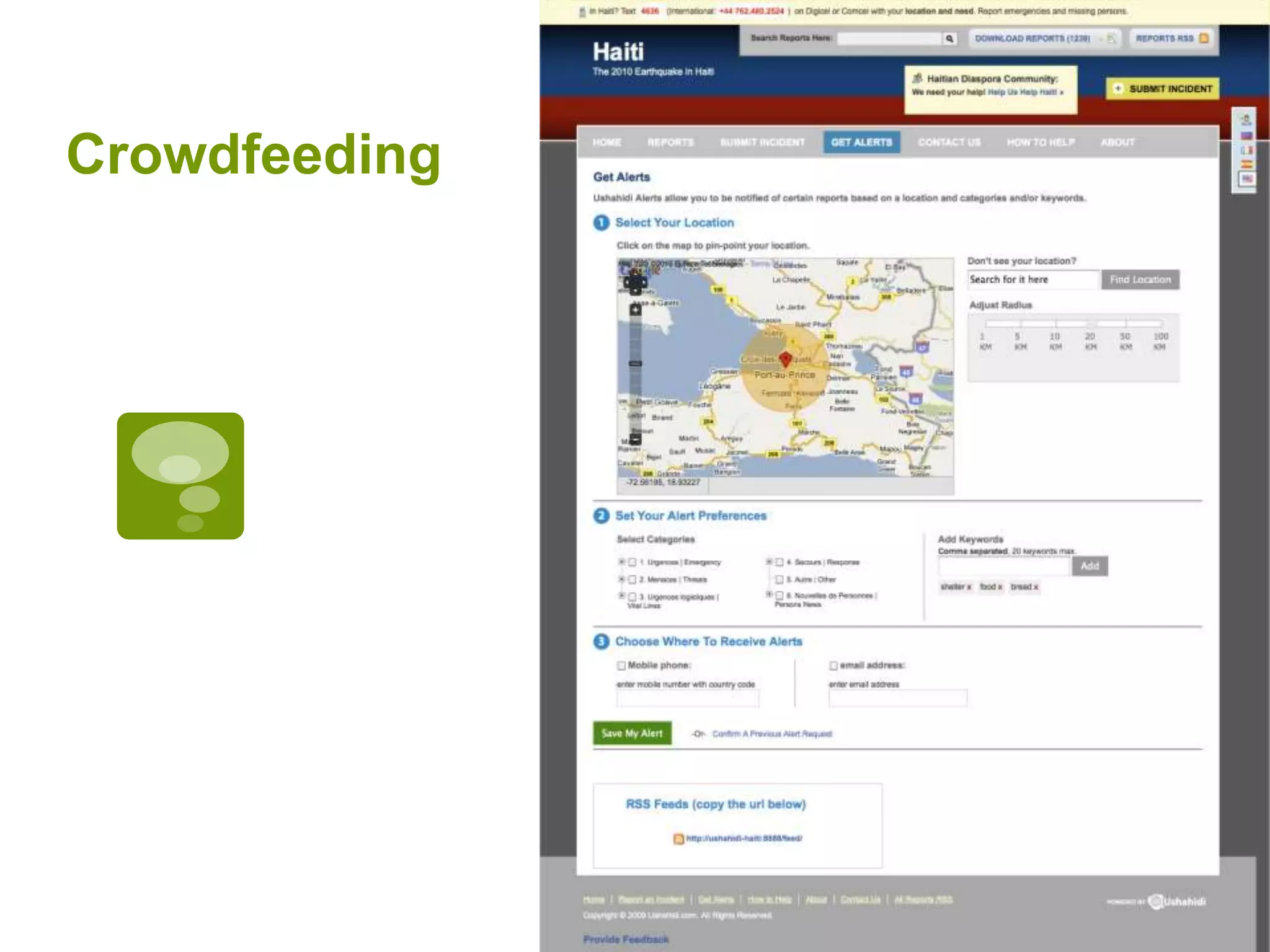
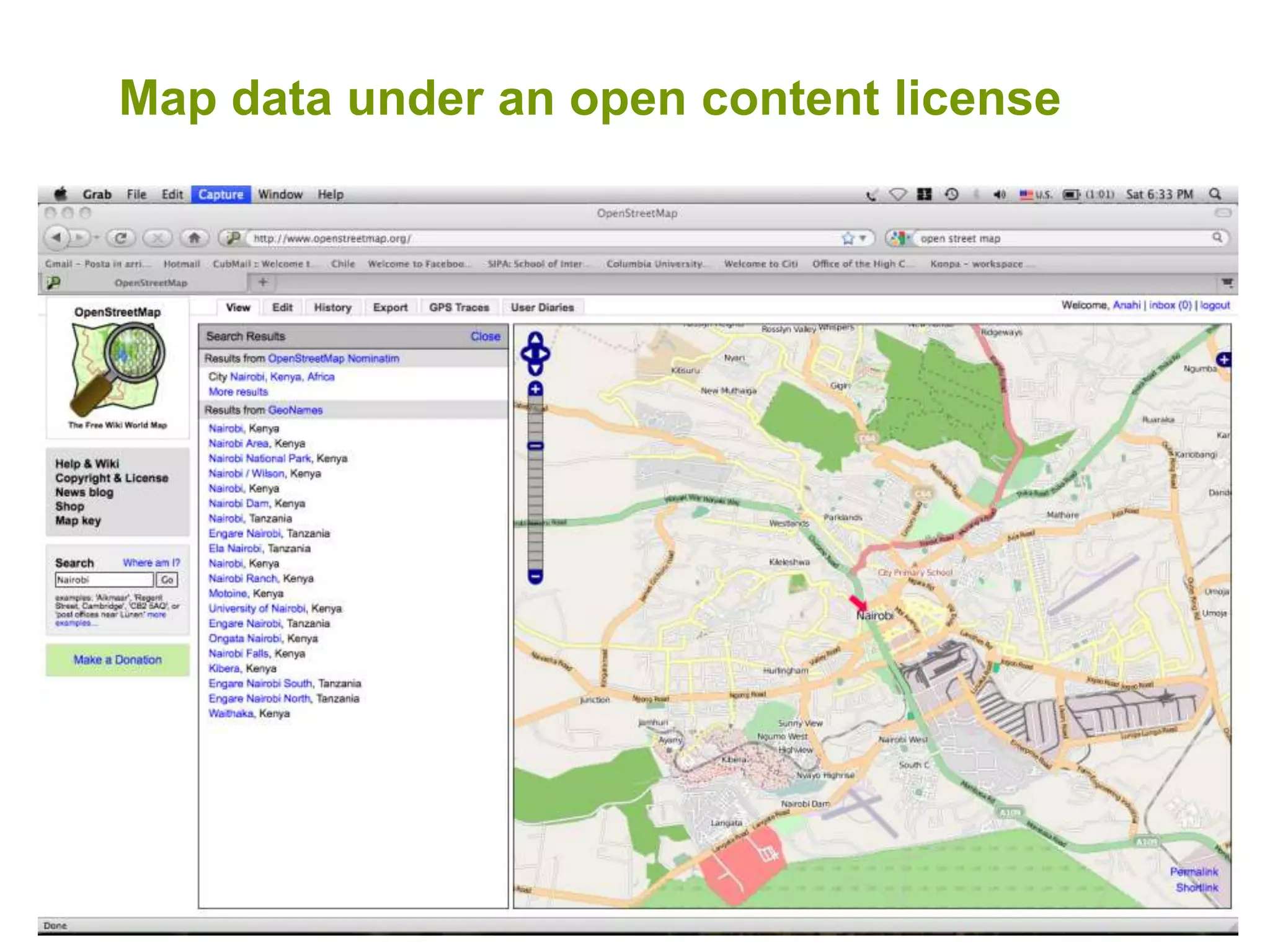
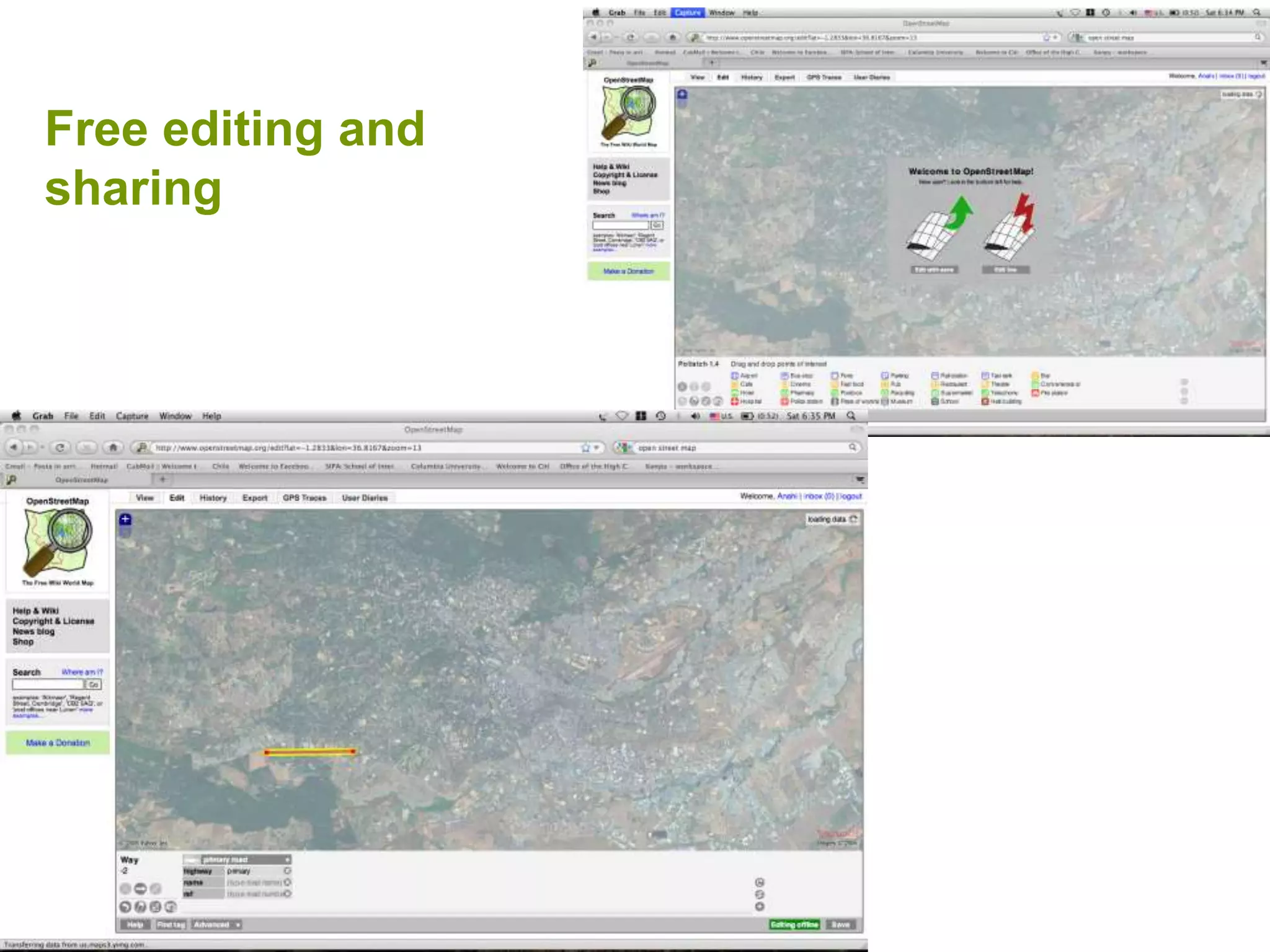
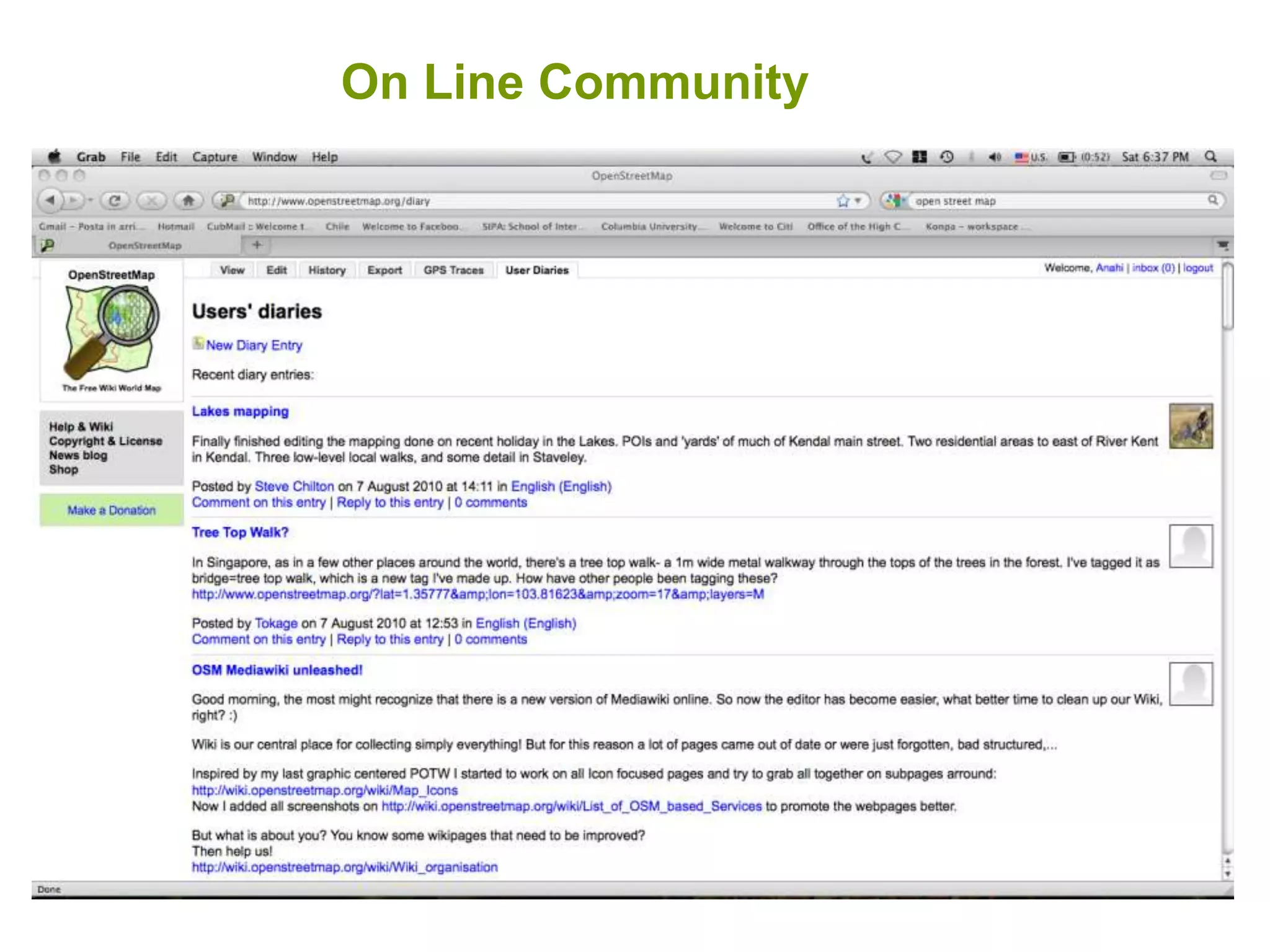
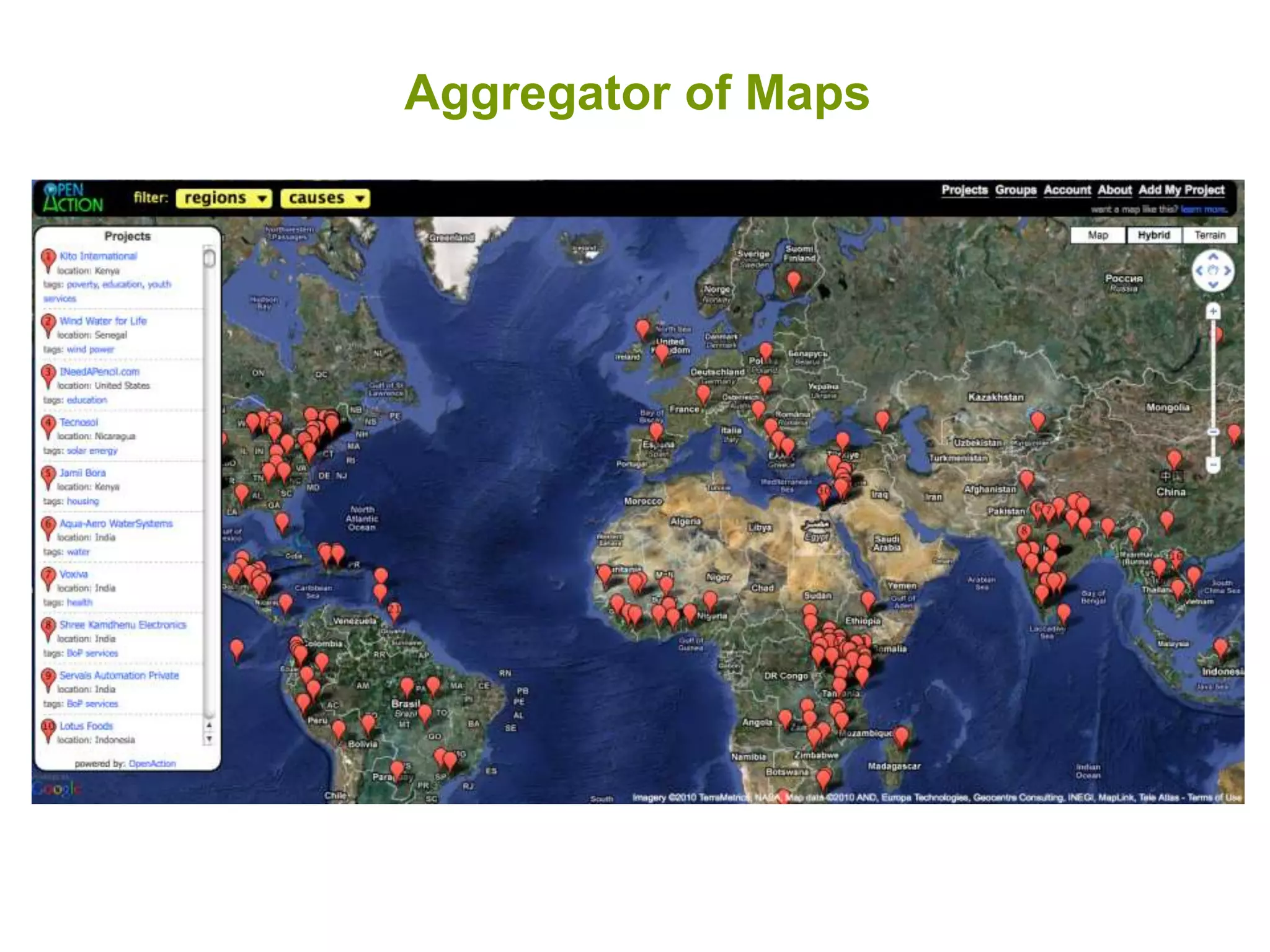
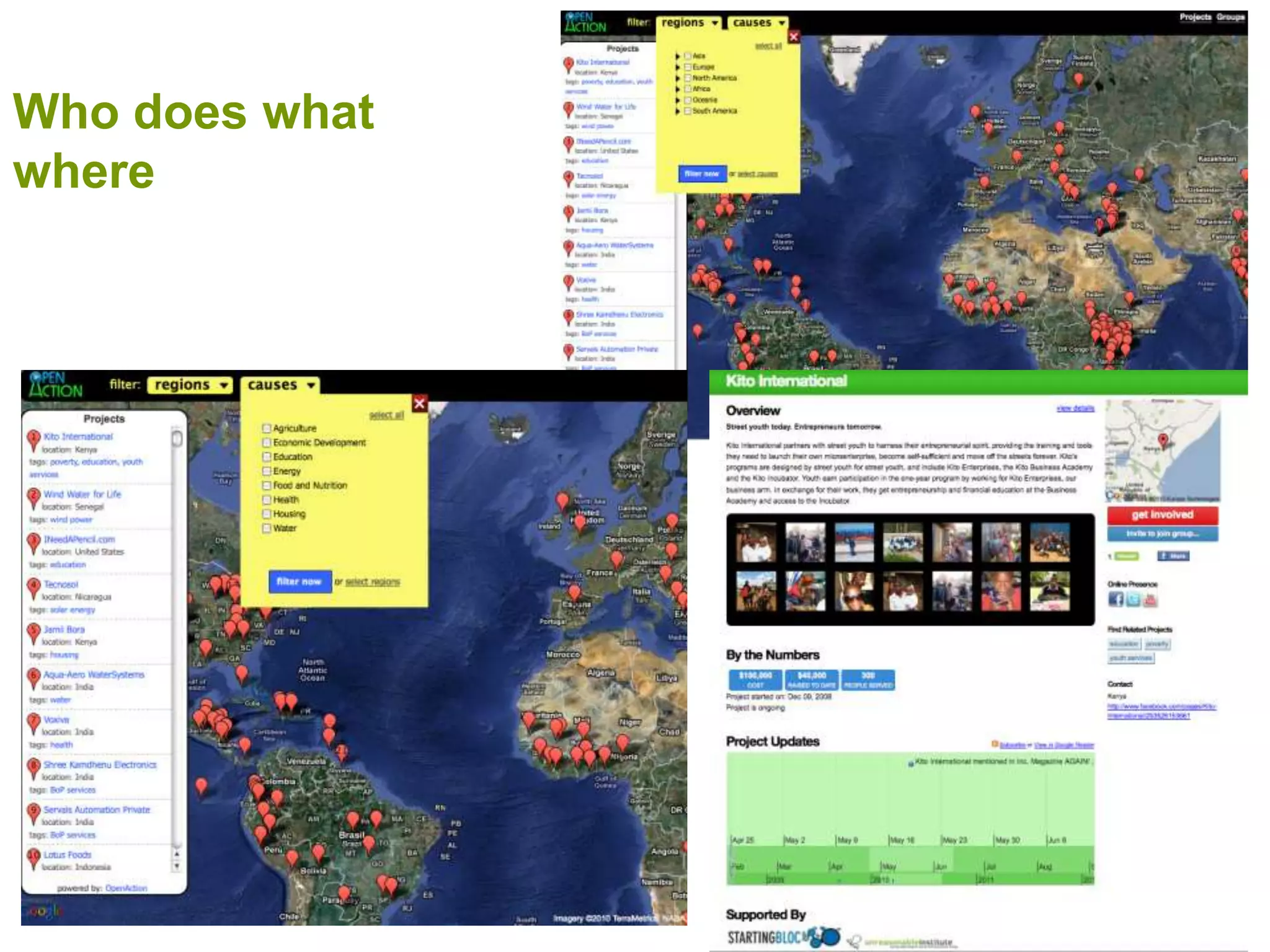
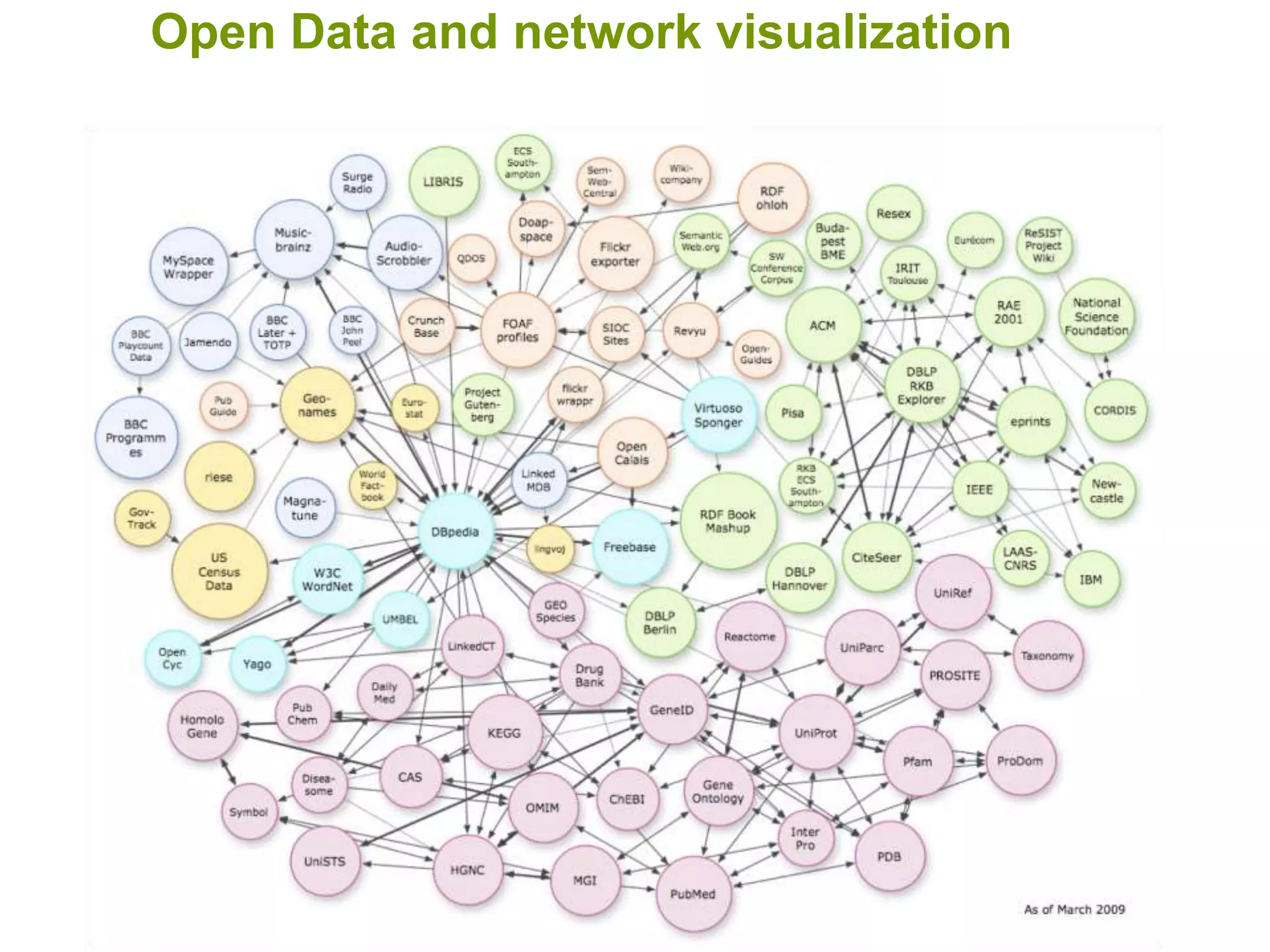
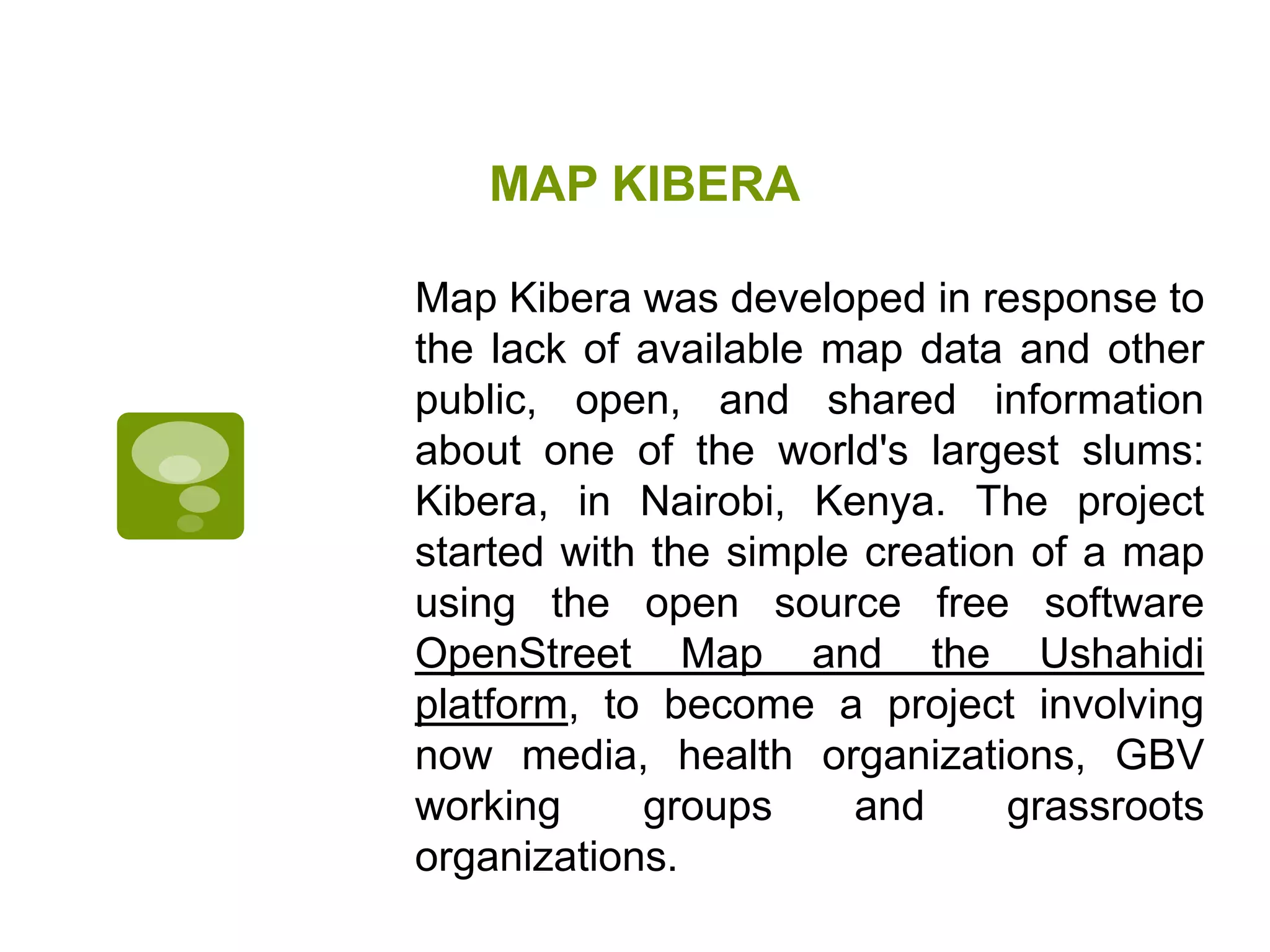
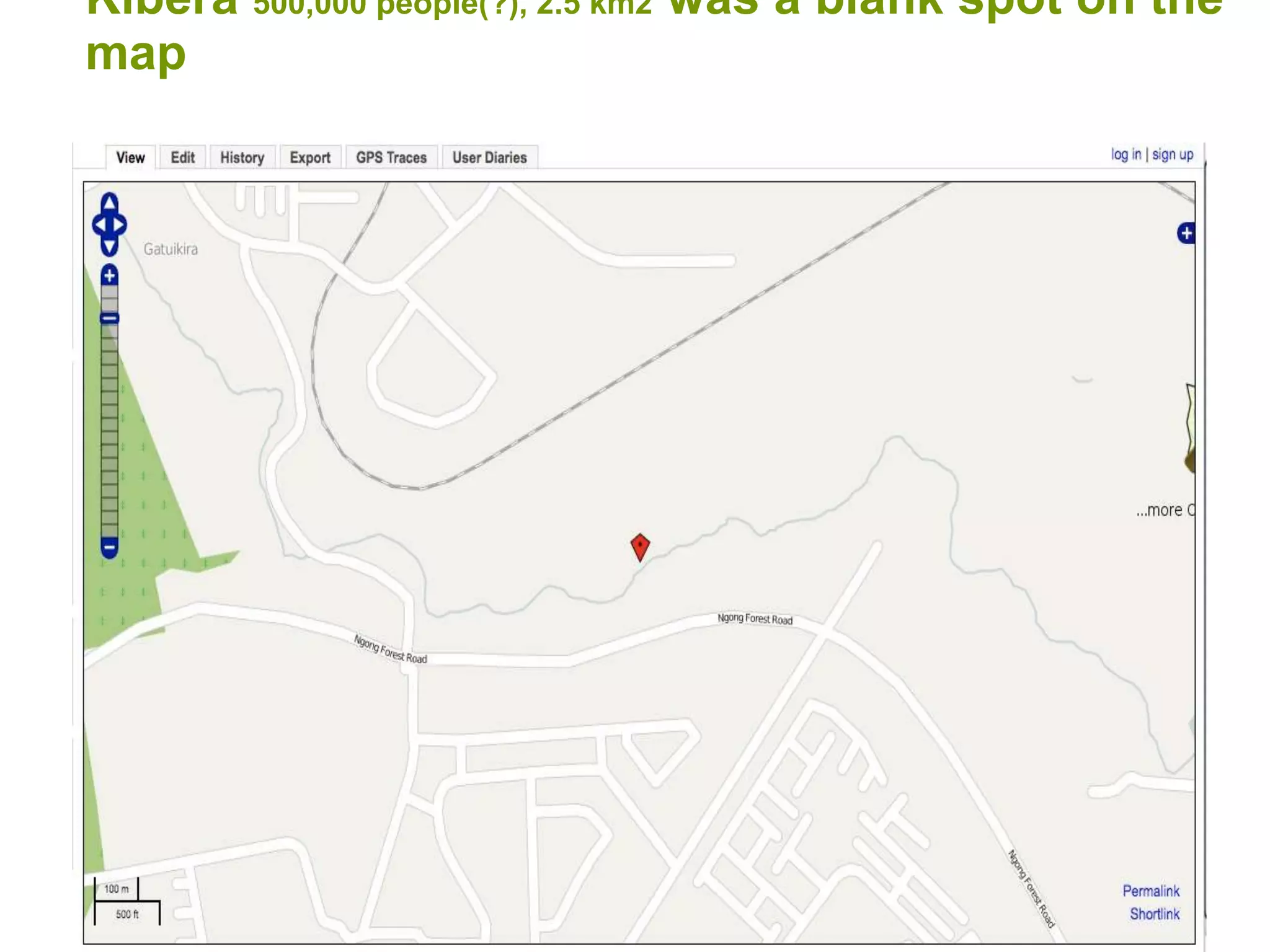
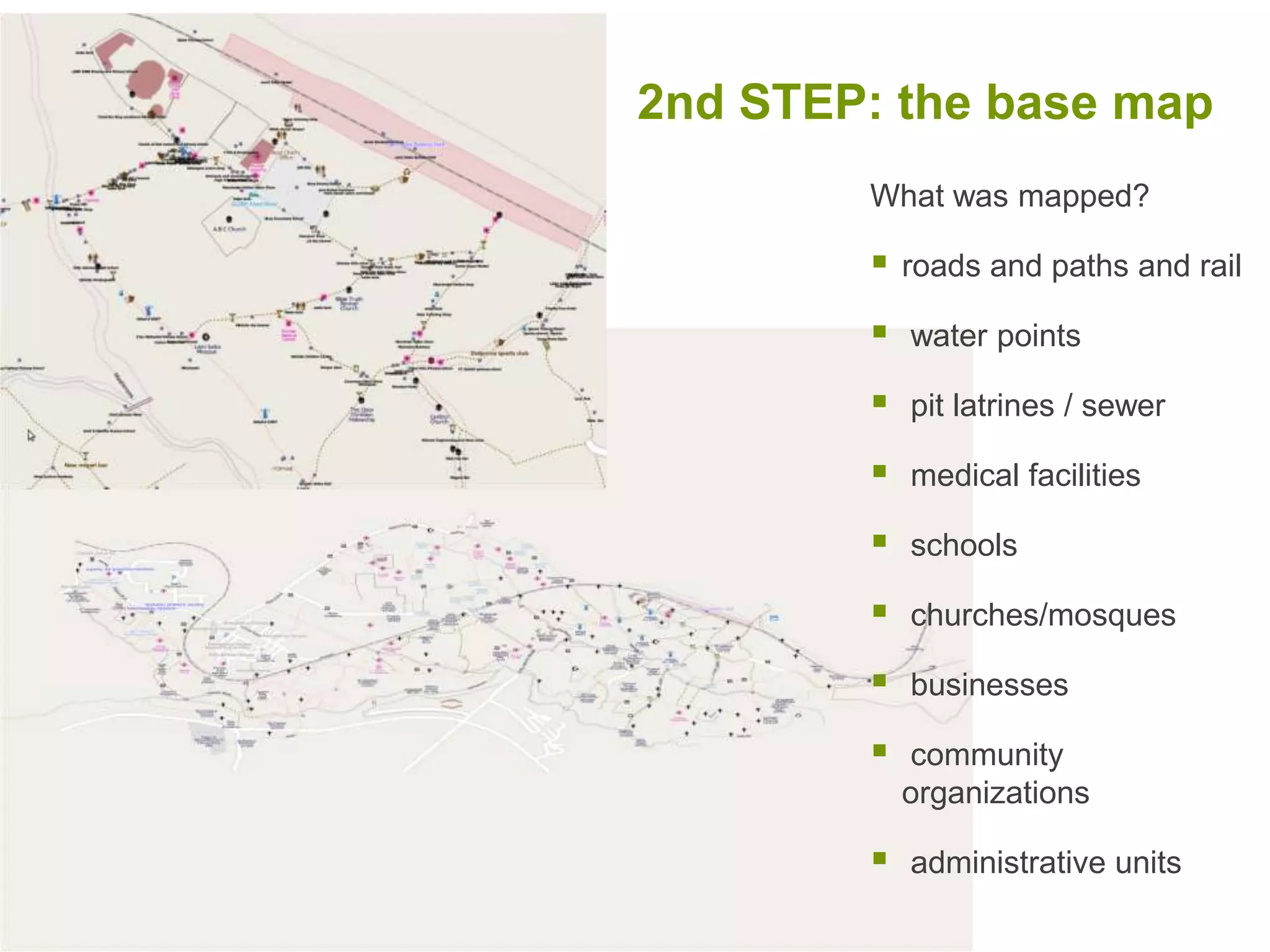
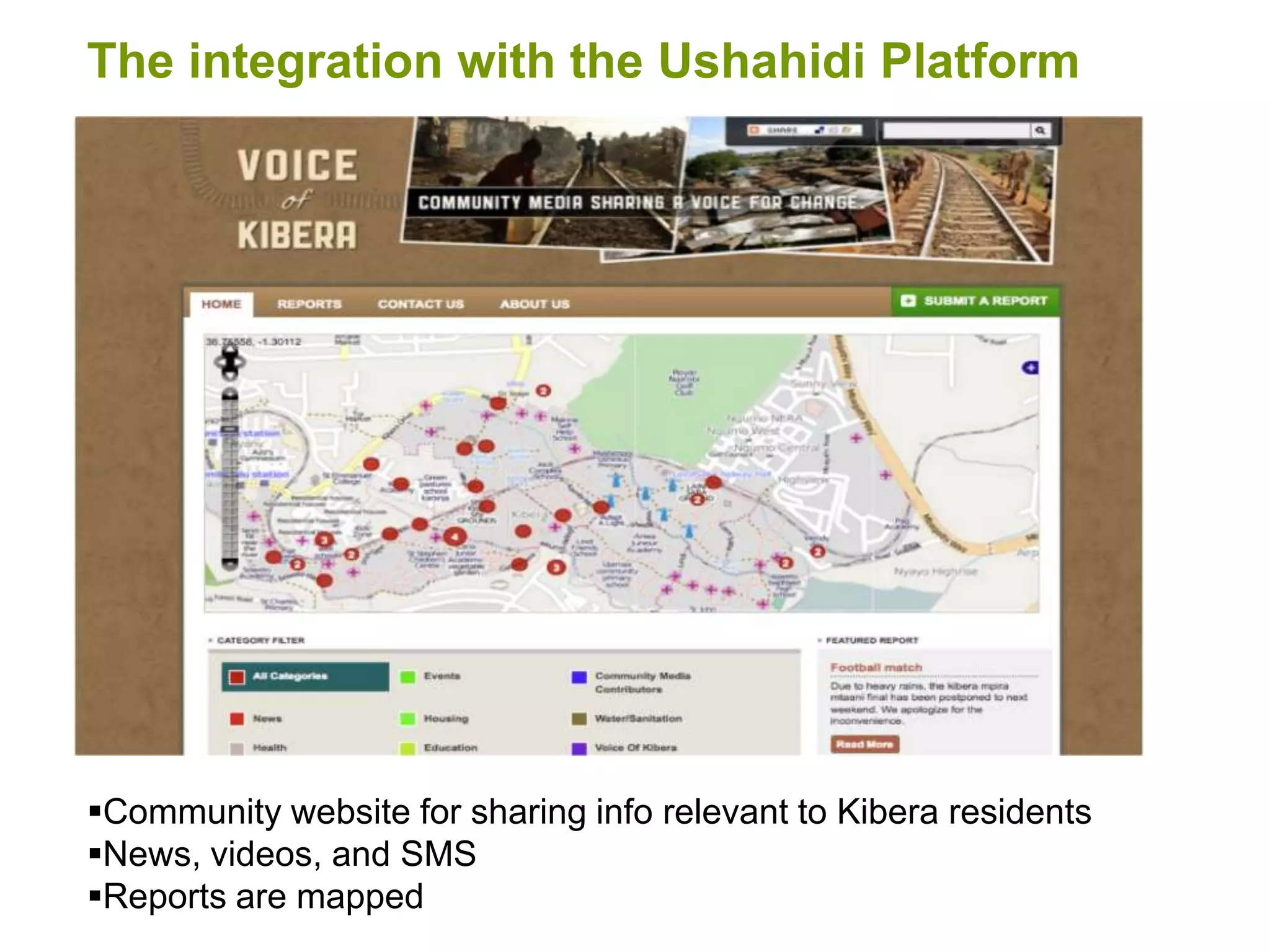
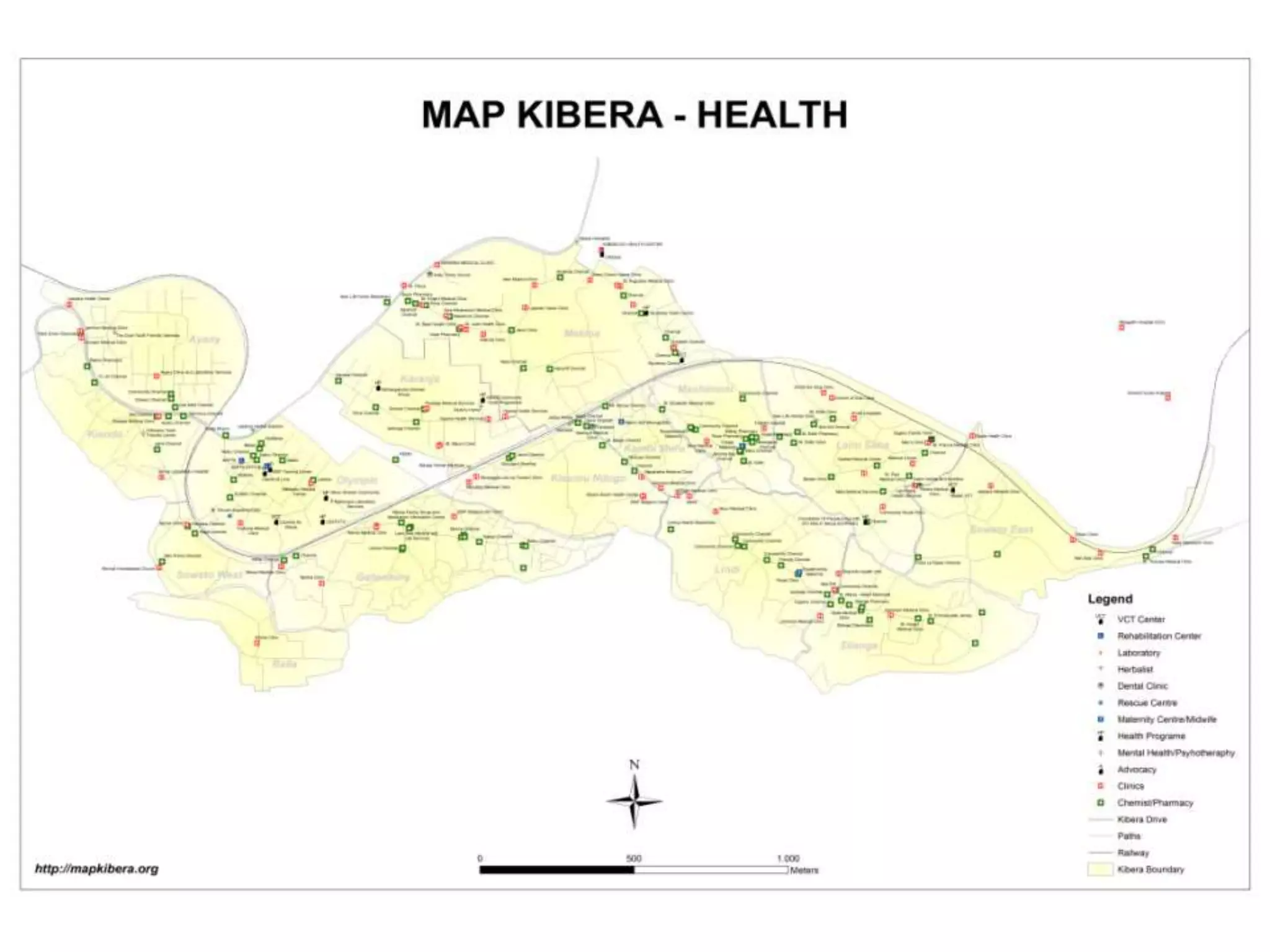
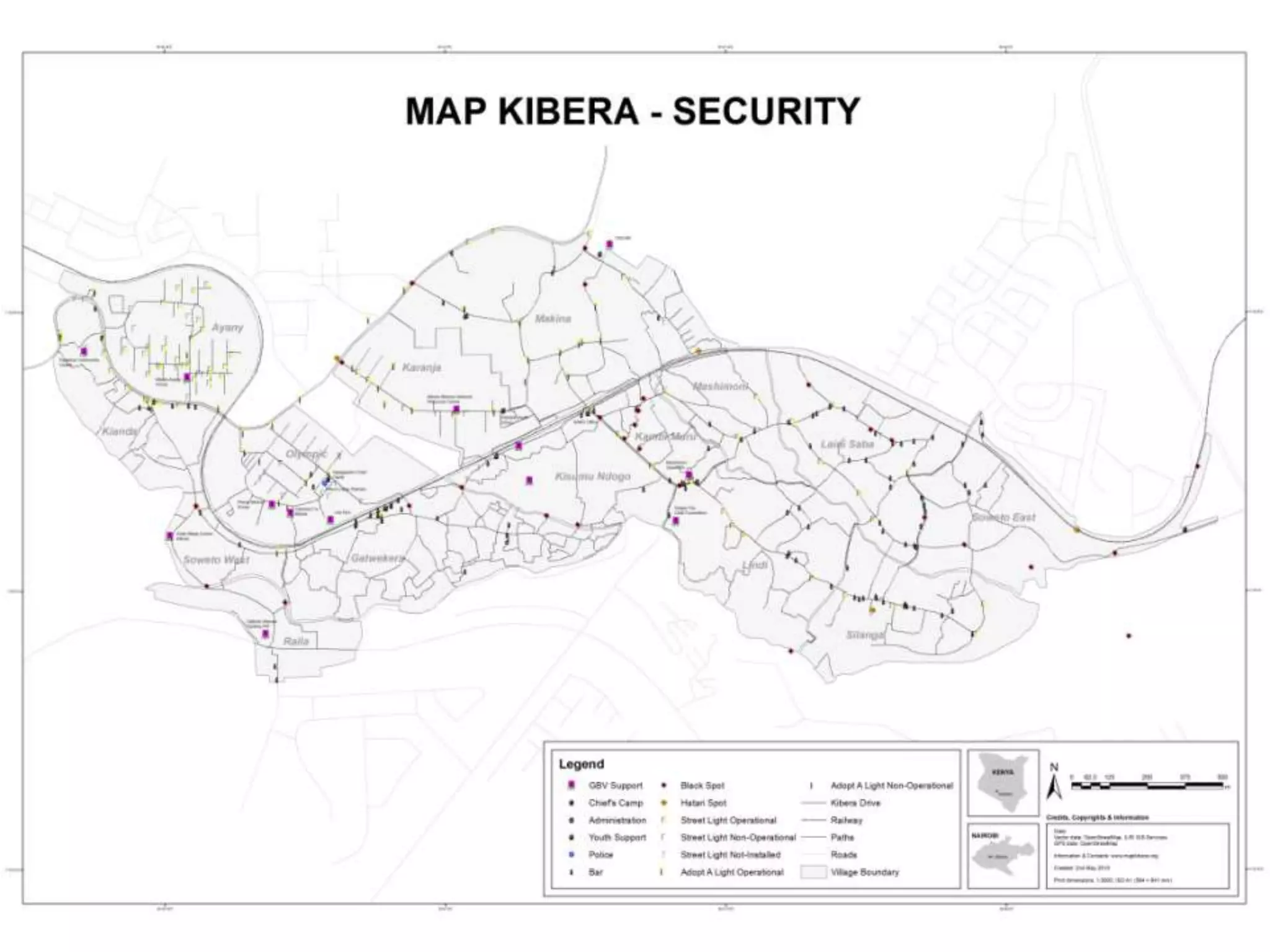
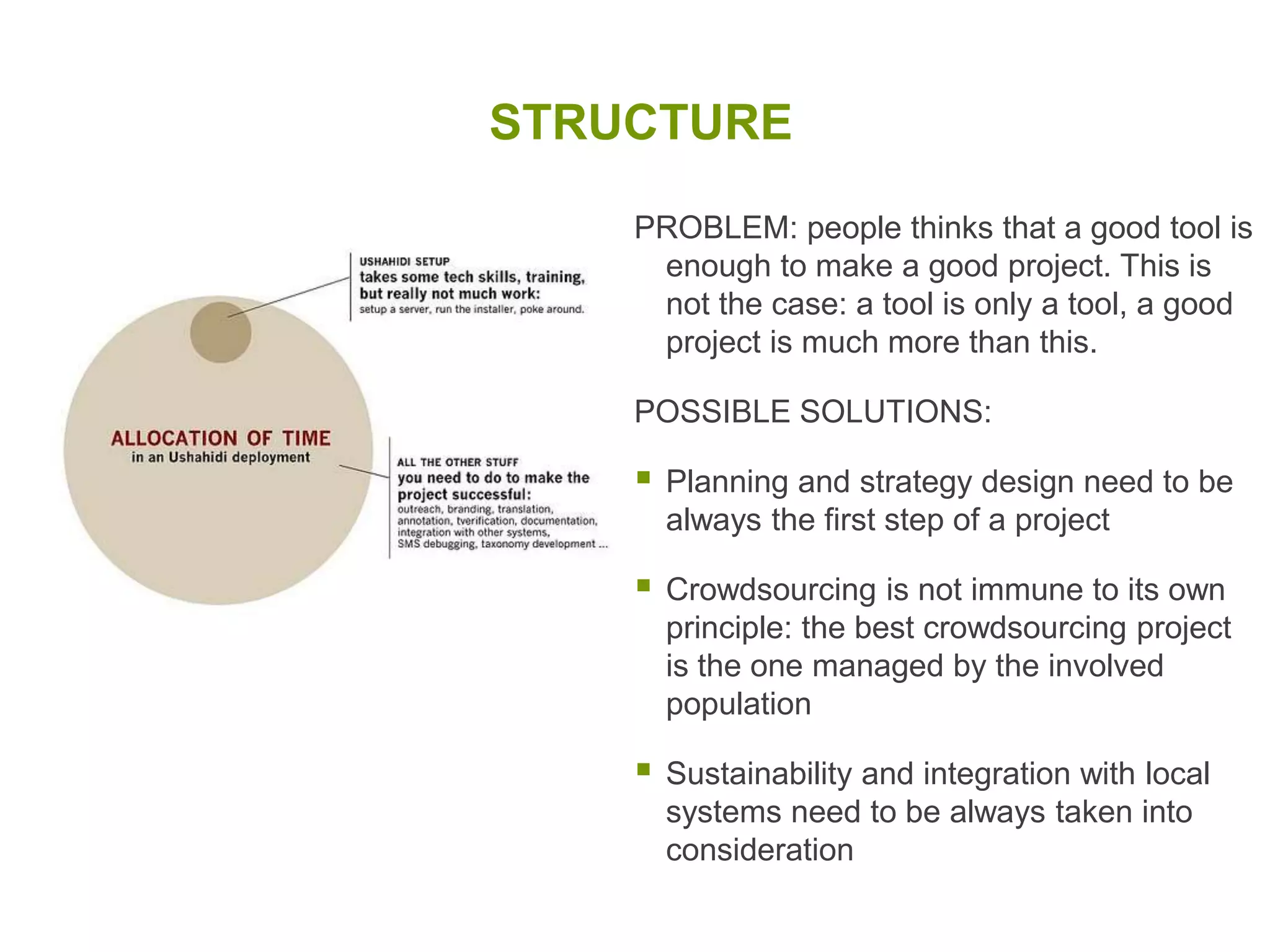
The document discusses the concepts of crowdsourcing and crowdfeeding in participatory information management systems, highlighting their significance during crises and the advantages they provide for real-time information collection. It introduces various methods of crowdsourcing, including unbounded and bounded systems, and tools like Ushahidi and OpenStreetMap that facilitate community engagement in mapping and data sharing. The document also outlines challenges associated with crowdsourcing, including the reliability of information and the need for effective verification and planning in project implementation.