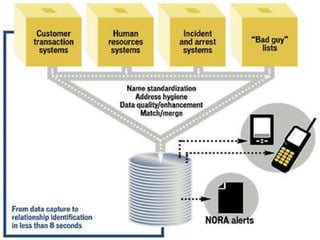
Non-Obvious Relationship Awareness (NORA) is a data mining system developed by Jeff Jonas in 1989, initially for casino fraud detection, which identifies relationships between individuals and organizations using multiple datasets. It features real-time analytics and is employed across various sectors, including law enforcement and retail, although it raises privacy concerns and relies heavily on data quality. Today, NORA is recognized for its broad applicability and potential in enhancing security and fraud detection.