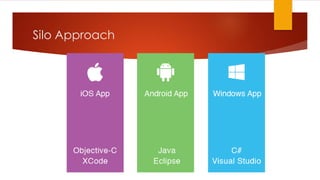
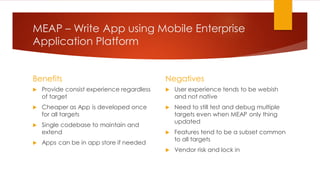
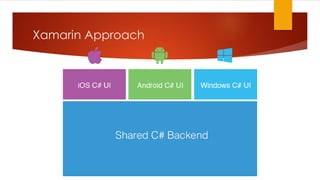
The document discusses various strategies for cross-platform app development, highlighting the emergence of Xamarin as a preferred solution for leveraging .NET technologies. It outlines the pros and cons of different approaches like silo development, web-based apps, and mobile enterprise application platforms. Xamarin, particularly through its Forms toolkit, allows for high code reuse and rapid application development while providing native app experiences across multiple platforms.