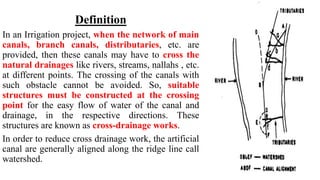
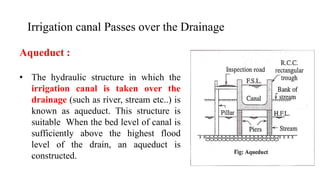
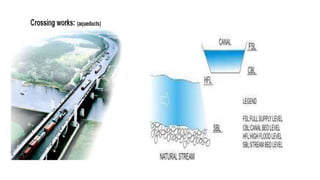
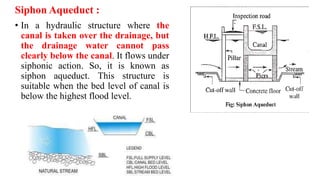
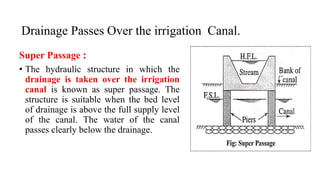
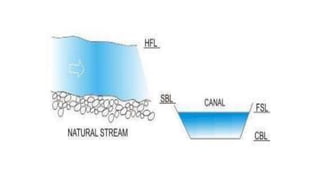
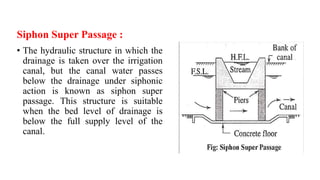
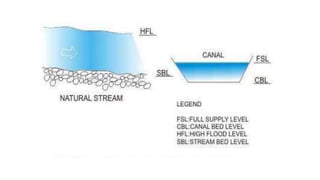
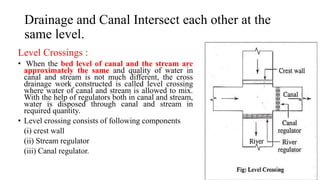
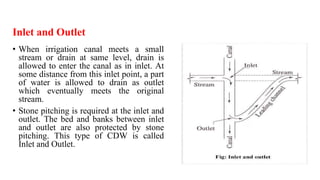
Cross-drainage works refer to structures built where canals intersect natural drainages like rivers or streams. There are three main types: 1) where the irrigation canal passes over the drainage (e.g. aqueduct or siphon aqueduct), 2) where the drainage passes over the irrigation canal (e.g. super passage or siphon super passage), and 3) where the drainage and canal intersect at the same level (e.g. level crossing or inlet and outlet). The type of cross-drainage work constructed depends on factors like the relative bed levels of the canal and drainage, suitable foundation availability, economic considerations, drainage discharge, and construction problems.