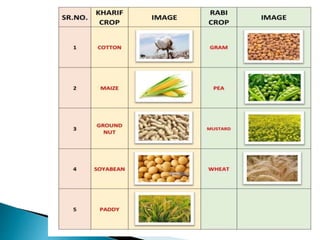
This document provides information about different types of crops and crop cultivation techniques. It discusses kharif and rabi crops, which are sown and harvested in different seasons. The main steps of crop cultivation are described as preparation of soil through ploughing and leveling, selection and sowing of seeds, replenishing soil nutrients, irrigation, crop protection, harvesting, and storage. Traditional and modern methods are outlined for various cultivation activities.