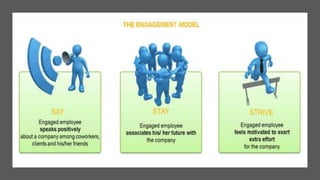
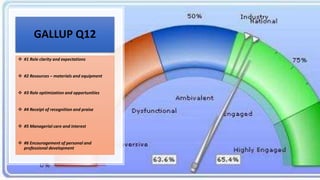
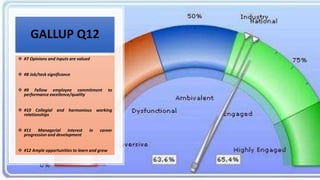
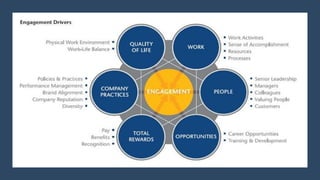
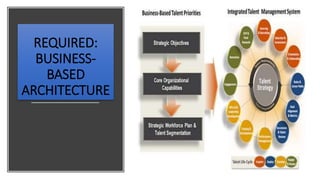
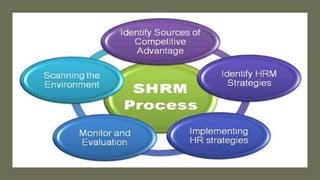
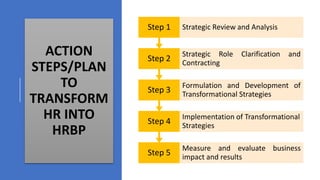
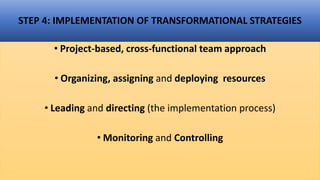
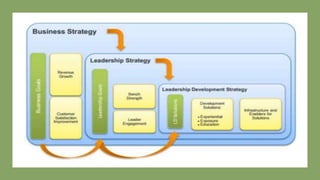
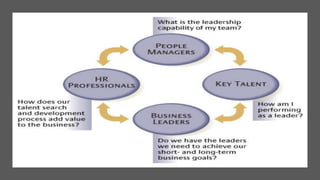
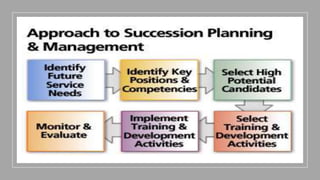
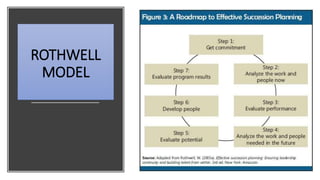
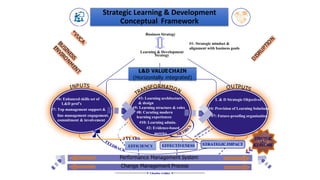
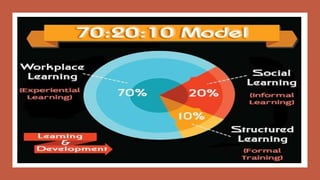
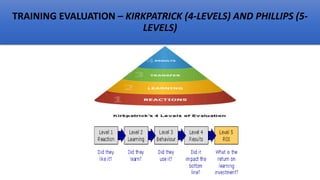
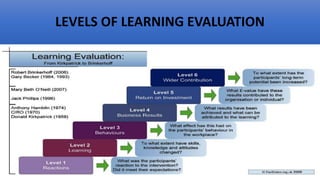
This document provides an overview of a two-day training program on critical human resources management priorities. The program consists of four workshops covering strategic talent management, leadership development, strategic learning and development, and employee engagement. Workshop one focuses on strategic talent management and HR business partnering. Workshop two covers leadership development components, models, and strategies like succession planning and mentoring. Workshop three defines strategic training and development and identifies factors and a maturity model.























































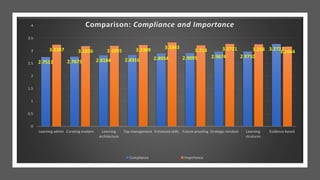
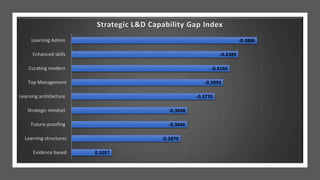

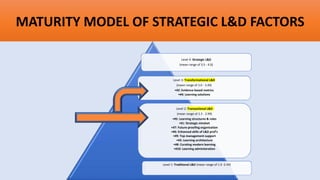
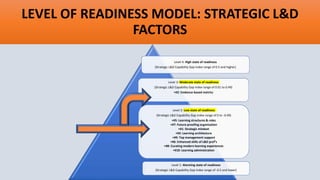

















![DEFINING TRAINING ROI FORMULA
ROI is a key financial metric of the value of training investments and costs. It is a ratio of net benefits to costs,
expressed as a percentage.
The formula can be expressed as:
[(monetary benefits – cost of the training) / cost of the training] x 100](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/strategichumanresourcesmanagementprinciplesprocessmlamuli78february-180211130810/85/Critical-Human-Resources-Management-and-Learning-Development-Priorities-106-320.jpg)