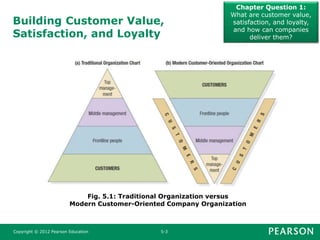
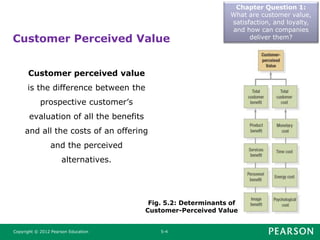
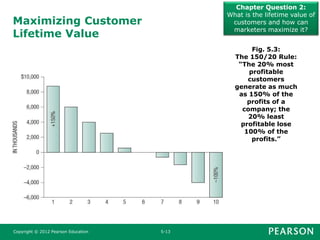
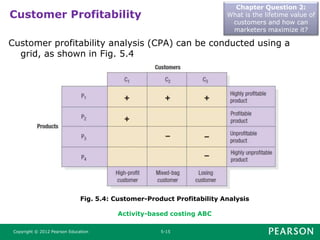
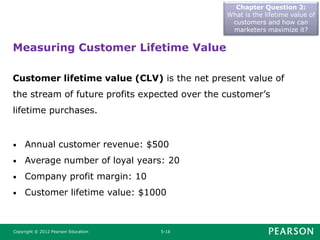
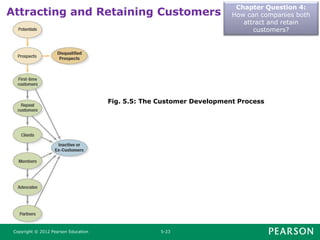
This document summarizes key concepts from Chapter 5 of the marketing textbook. It discusses customer value, satisfaction, and loyalty. Companies can deliver these through understanding customer perceived value and delivering a strong value proposition. Monitoring customer satisfaction through surveys and complaints handling is also discussed. The chapter covers maximizing customer lifetime value through customer relationship management and database marketing techniques.