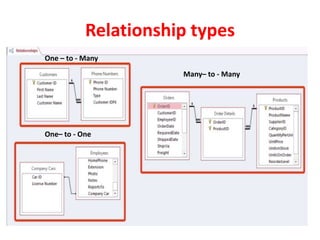
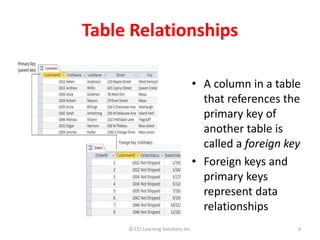
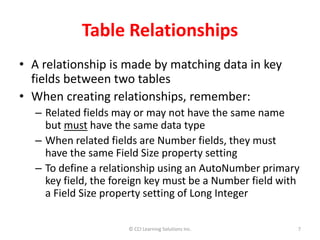
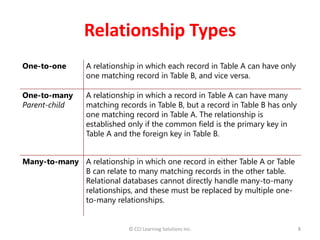
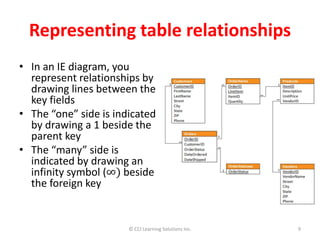
Relationships between tables are critical in a relational database because they link data separated across tables and impact how queries retrieve answers. There are three main relationship types: one-to-many, which is most common; many-to-many, used in transaction and student databases; and one-to-one, which is rare. A primary key uniquely identifies records in a table and cannot be duplicated or contain null values. Foreign keys in one table reference the primary key of another table to represent relationships. Relationships are defined by matching keys between tables which must have the same data type and field size.