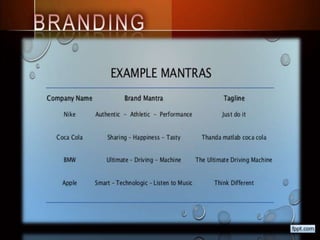
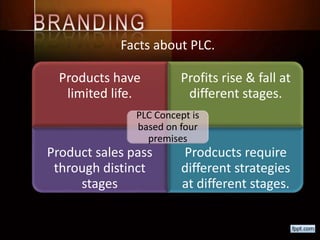
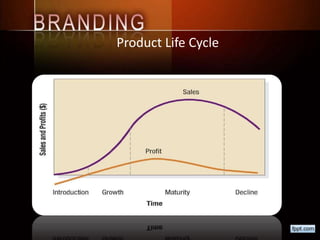
This document discusses concepts related to crafting an effective brand positioning strategy. It defines key terms like positioning, competitive frame of reference, points of difference/parity, and differentiation strategies. It also outlines the typical stages in a product life cycle, from development and introduction to growth, maturity, and decline. Finally, it distinguishes between style, fashion, and fad life cycles in consumer products.