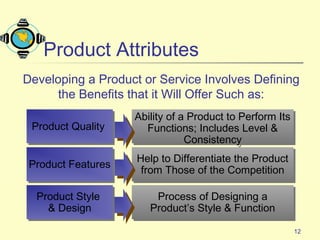
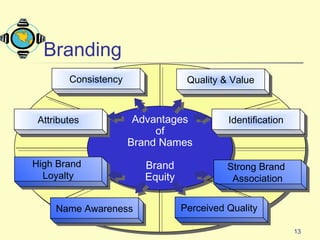
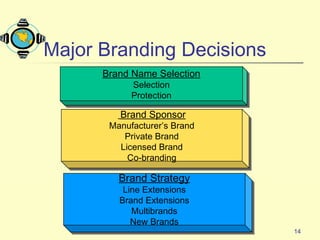
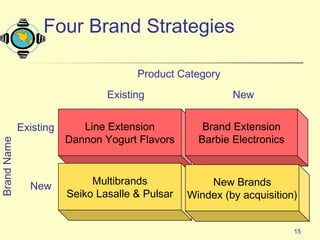
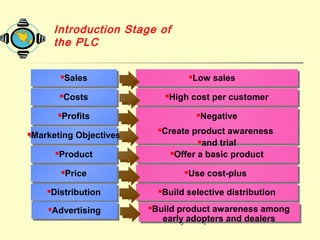
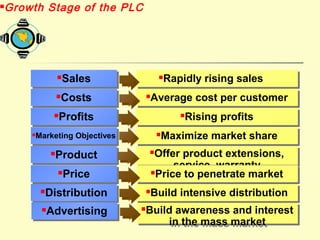
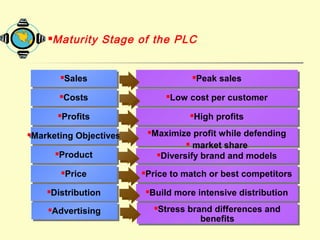
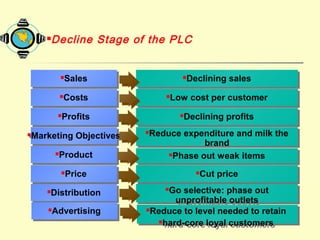
The document discusses various topics related to product strategy and new product development including:
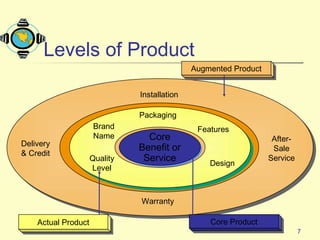
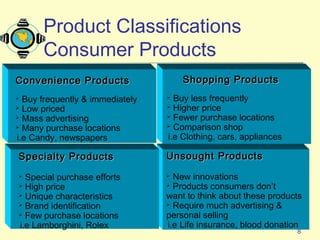
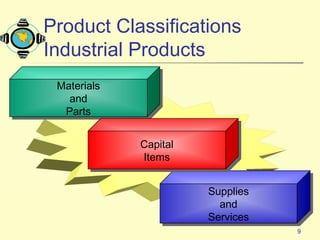
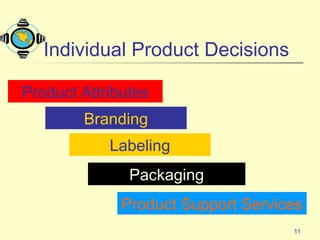
1. It defines what a product is and classifies products into different types such as consumer products, industrial products, and other marketable entities.
2. It covers branding strategies such as line extensions, brand extensions, multibrands, and new brands.
3. It outlines the new product development process from idea generation through commercialization.