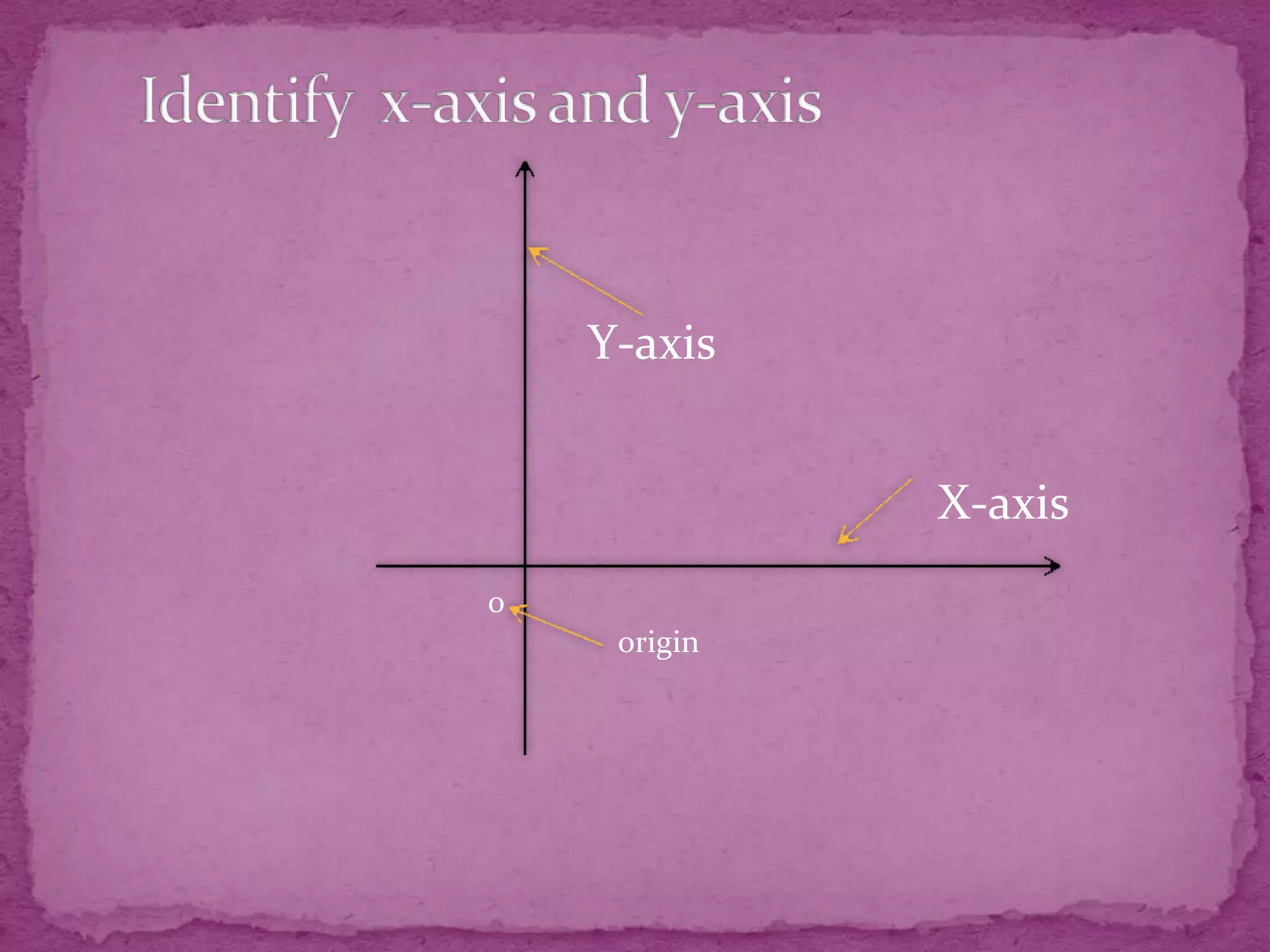
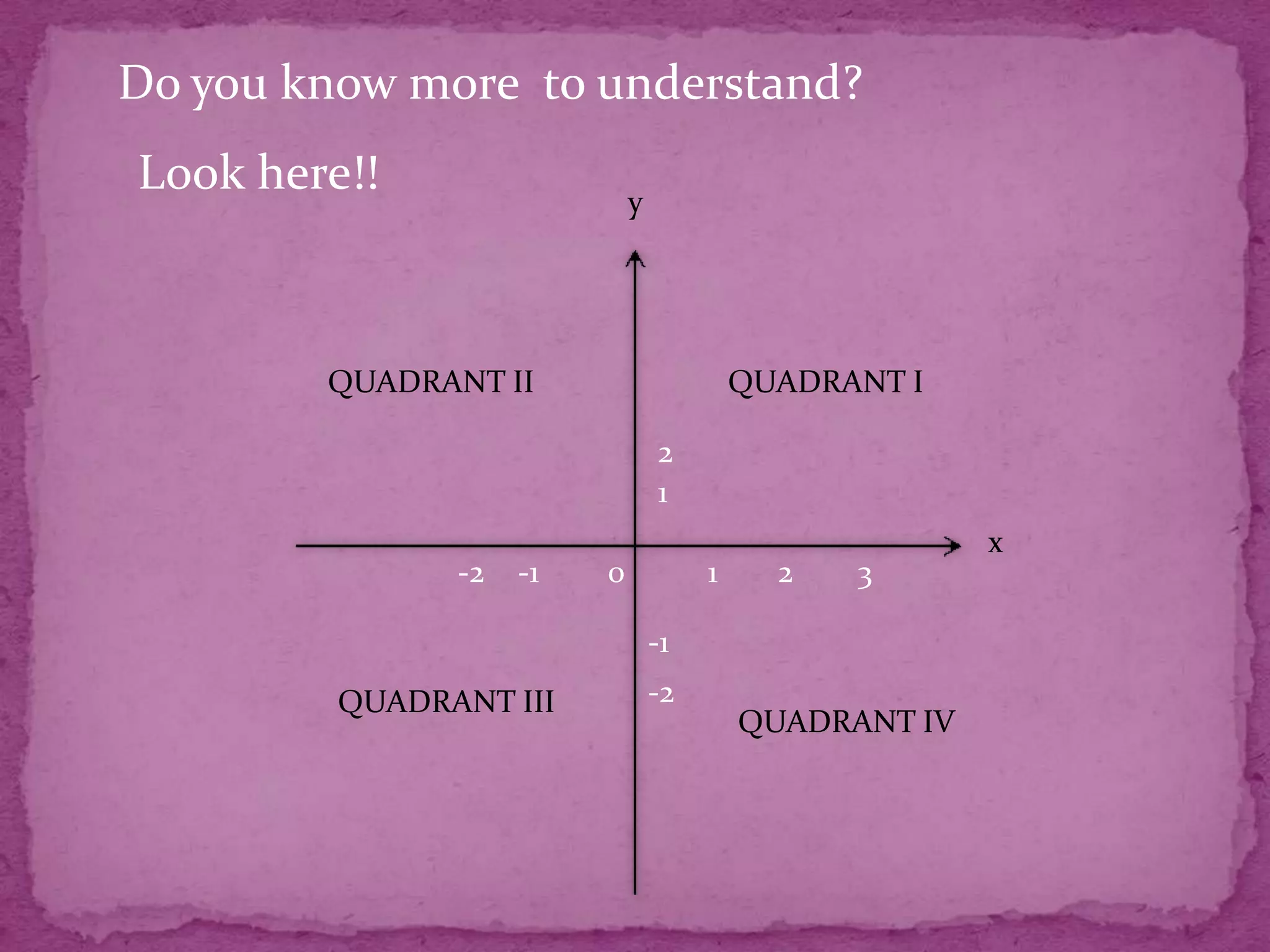
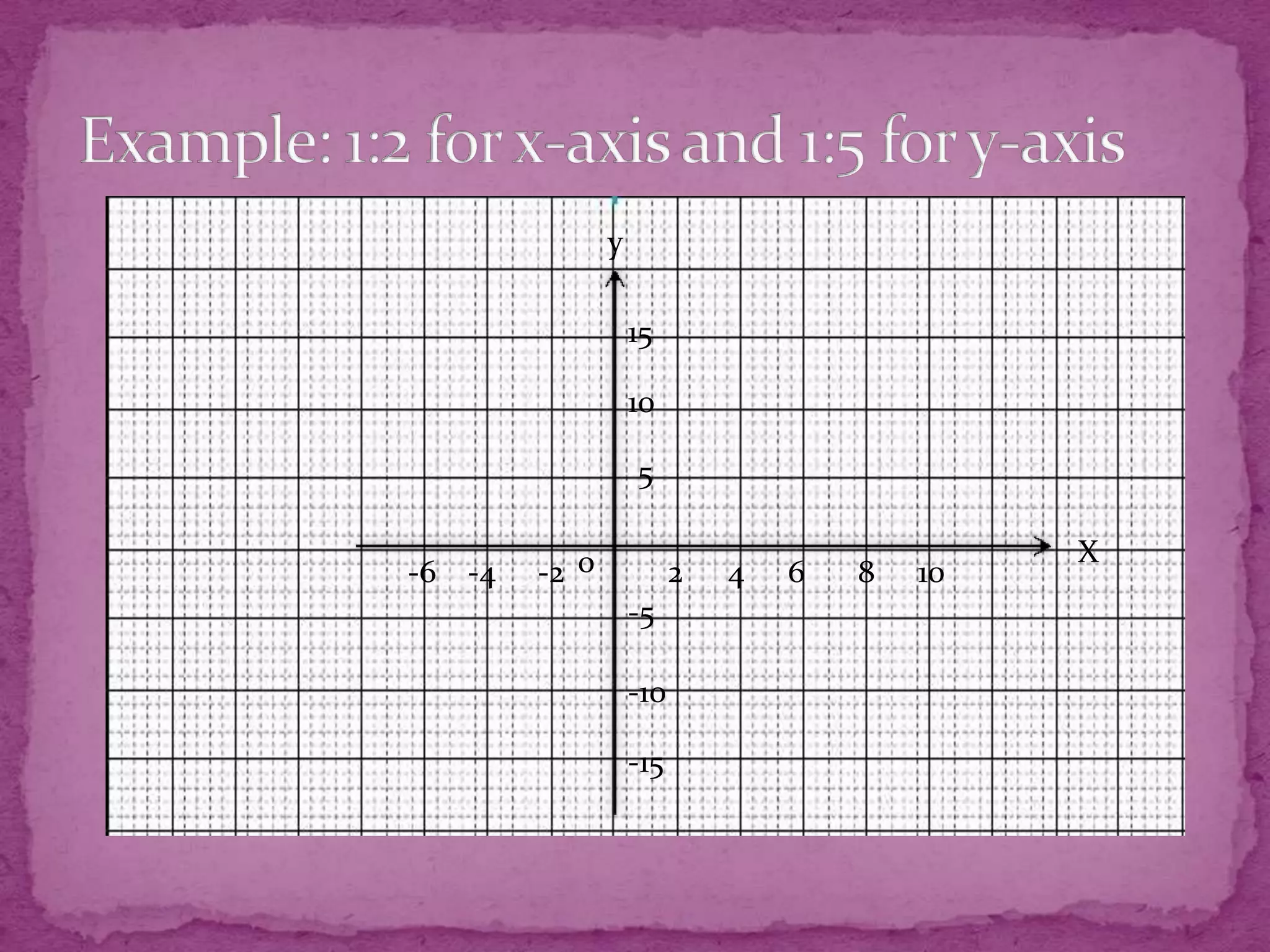
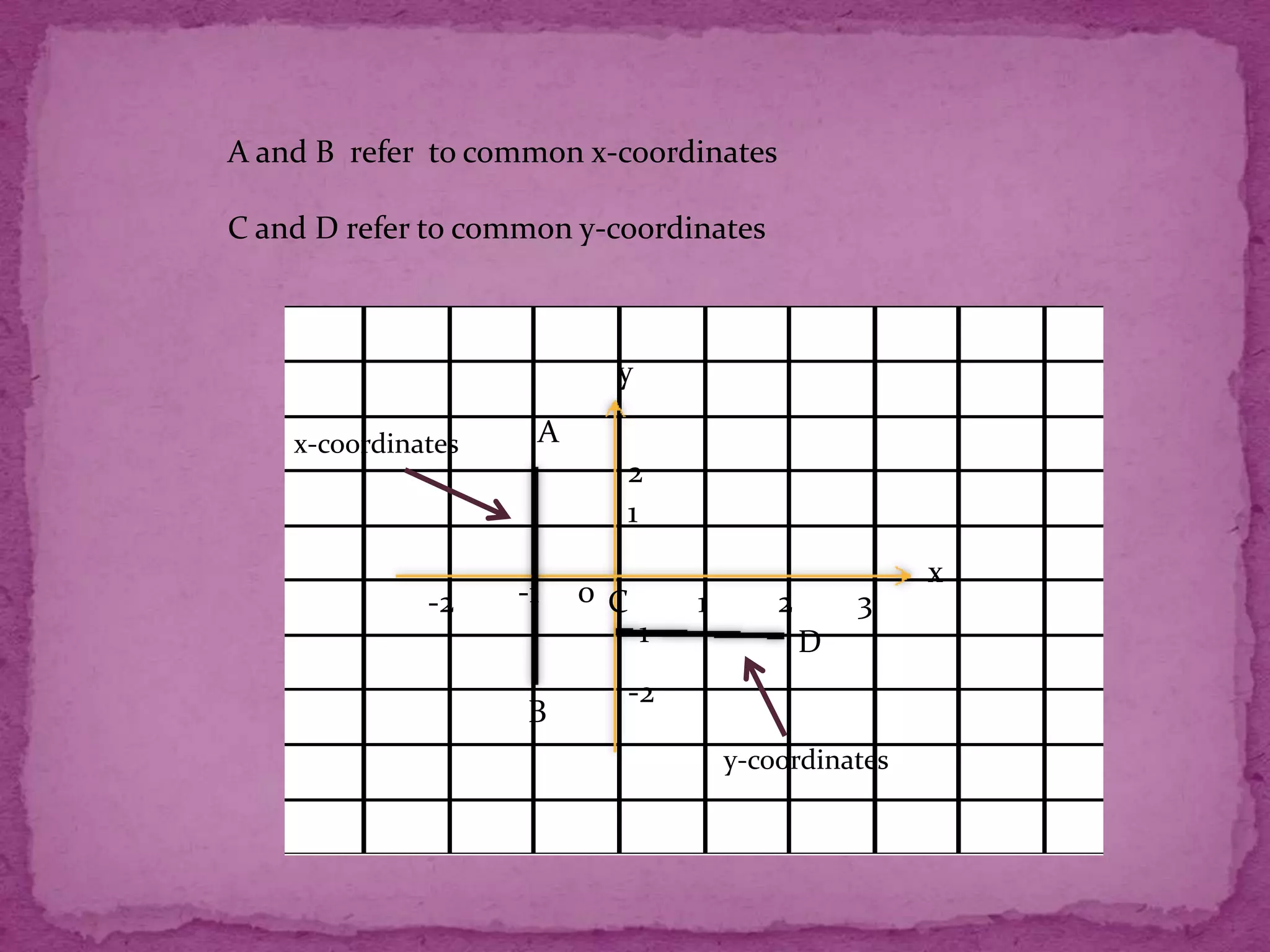
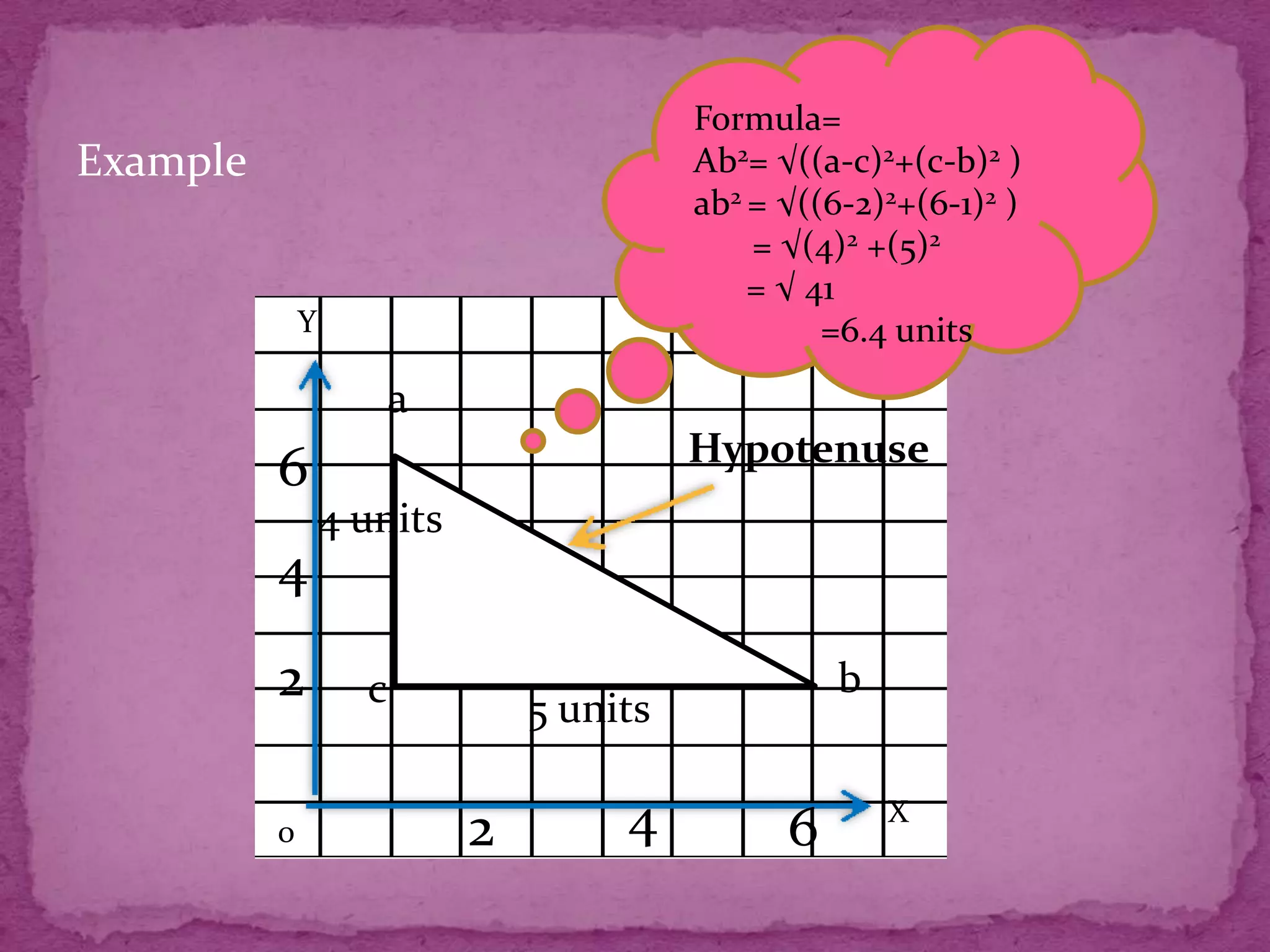
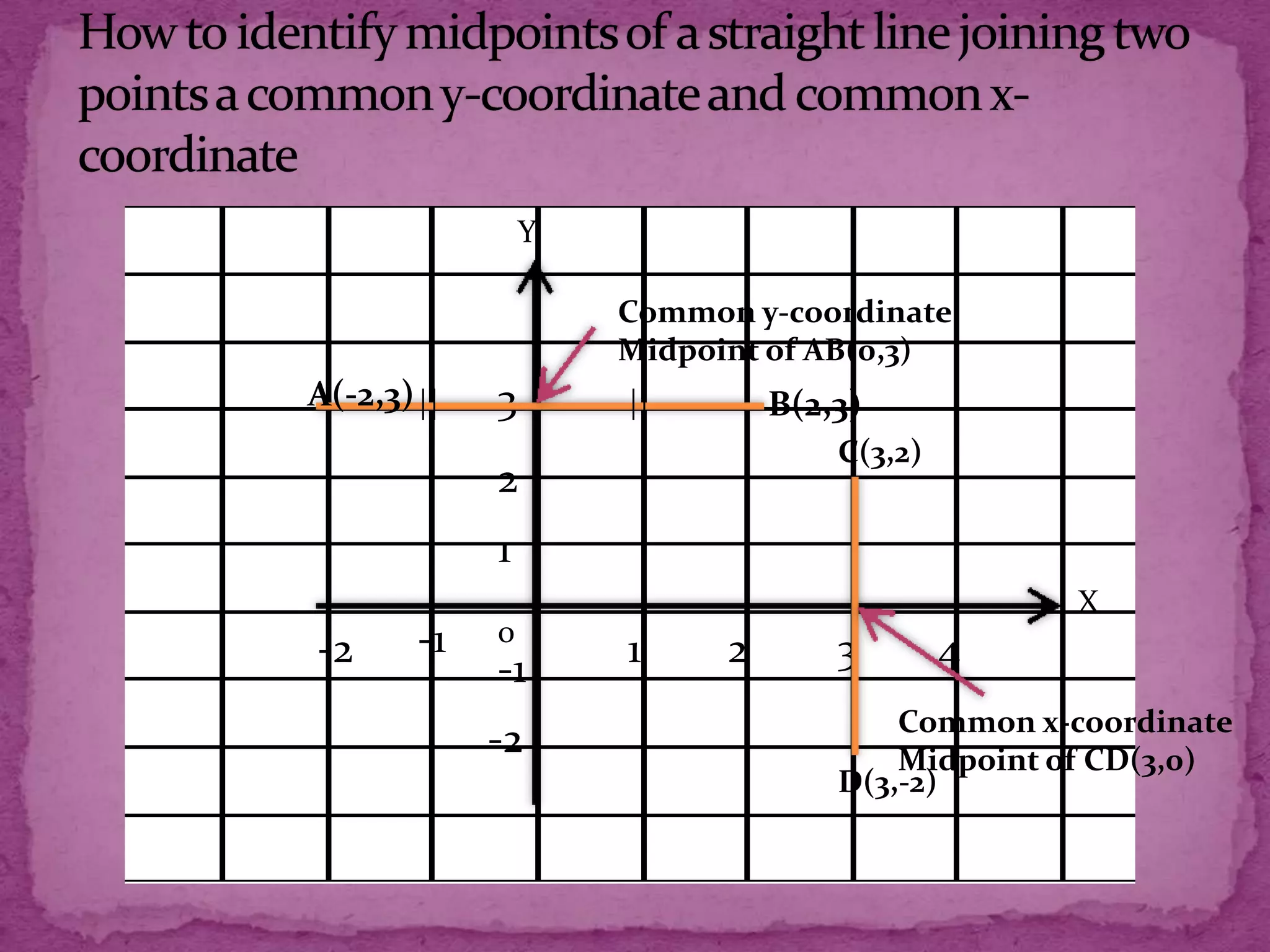
This document provides information about plotting points and calculating distances on a Cartesian plane. It discusses the four quadrants and their definitions. It then explains how to plot points based on their x- and y-coordinates. The document outlines different methods for calculating distances between points, whether they share x- or y-coordinates or not. It also introduces the concept of midpoints and provides examples of finding midpoints between two points.