The document provides information about the Business Mathematics course offered at Punjab College of Technical Education in Ludhiana. [1] It outlines the course topics which include matrix algebra, binomial theorem, functions, limits, and calculus among others. [2] The learning outcomes, textbooks, assignments, tests, and lecture schedule with topics are also detailed. [3] The document comprehensively outlines the structure and components of the Business Mathematics course.

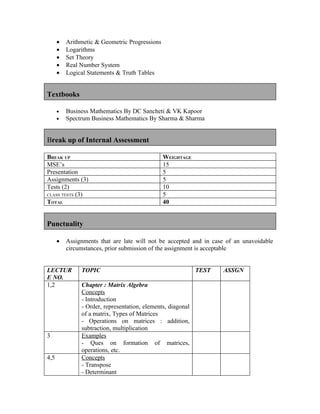
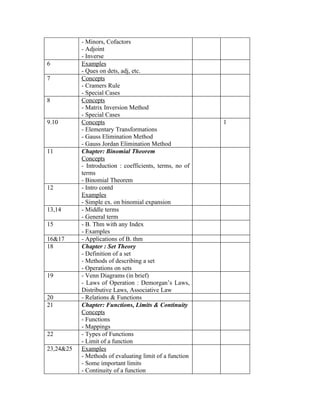
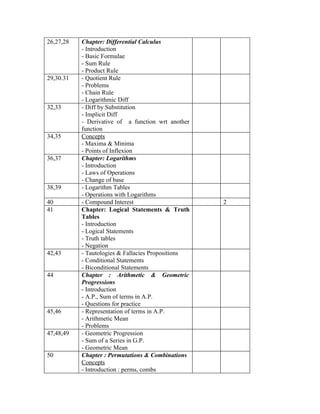
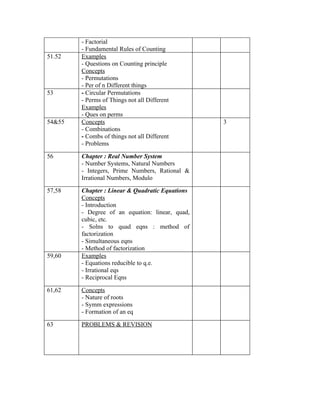



![Assignment no.3
Logical Statements&Truth Tables, A.P. & G.P and Permutations & Combinations
1. Simplify : ( p ∨ q) .
2. Prove that p → (q ∧ r ) = ( p → q) ∧ ( p → r ) .
3. How many numbers are there between 100 and 1000 such that every digit is either
2 or 3?
4. Construct the truth table for the statement ( p ∧ q ) ∨ (: r ) .
5. In how many ways, the letters of the word ‘RAM’ can be arranged?
6. Show that [( p ⇒ q ) ∧ ( q ⇒ r ) ⇒ ( p ⇒ r )] is a tautology.
7. How many different committees can be formed consisting of 4 men & 3 women out
of 7 men & 5 women?
8. Show that p ∧ ( p ∨ q ) = p , where p, q are logical statements.
9. What do you mean by permutations?
n
10. Find the value of Cn −3 .
11. Find the sum of the series 72 + 70 + 60 + …… + 40
th th
12. If a, b, c are the p , q and r terms of a G.P., then prove that
th
a q −r br − p c p −q = 1
13. Find the sum of 50 terms of the seqn. 7, 7.7, 7.77, 7.777,……..
14. If the m term of an A.P. is 1/n and n term is 1/m, then show that the mnth term
th th
is 1.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cdocumentsandsettingspendrivedesktopmathsmodule-100825052927-phpapp02/85/C-Documents-And-Settings-Pen-Drive-Desktop-Maths-Module-9-320.jpg)

