1. The document discusses modal verbs and their appropriate use. It provides examples of modal verbs like can, may, should and must.
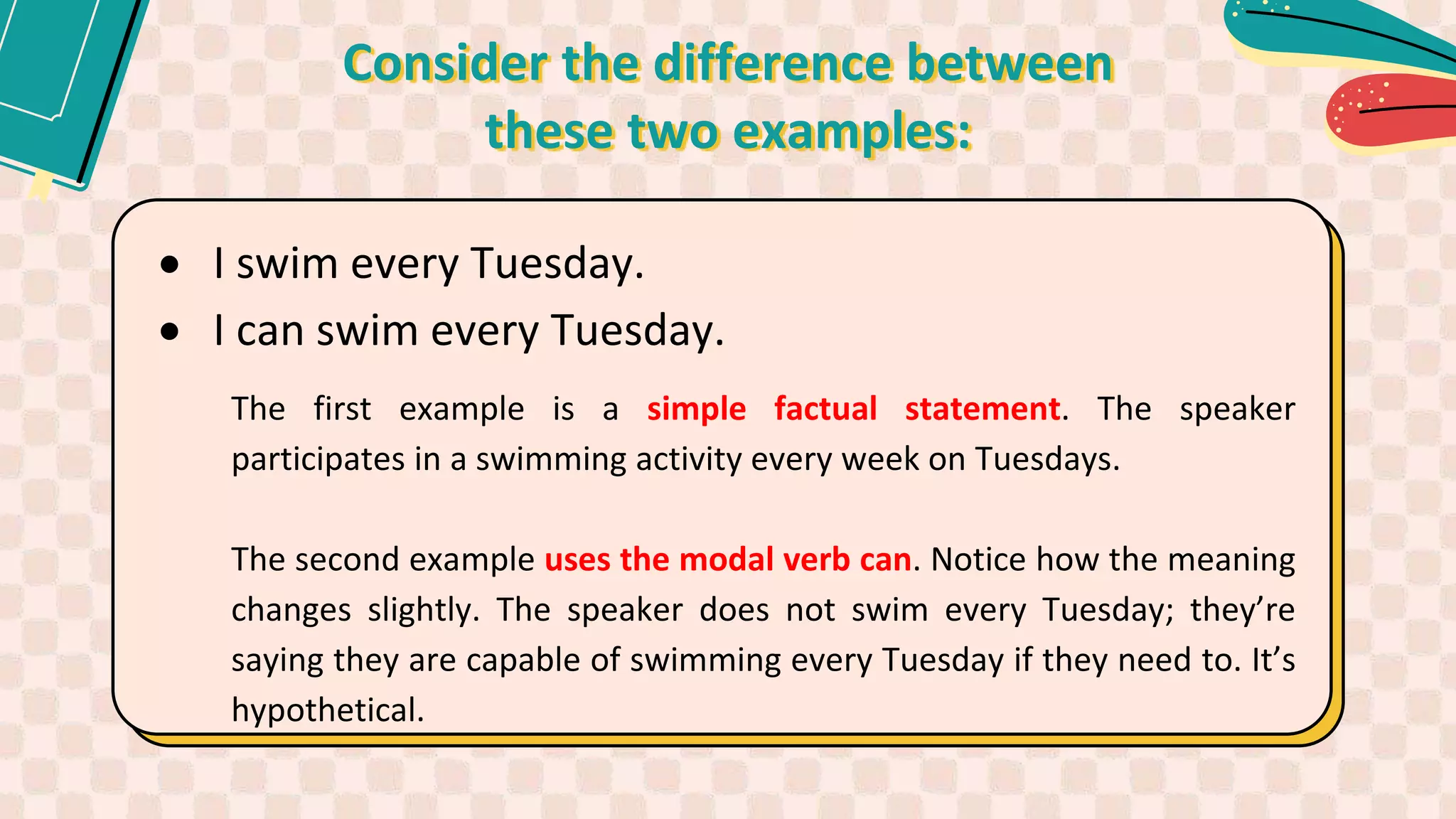
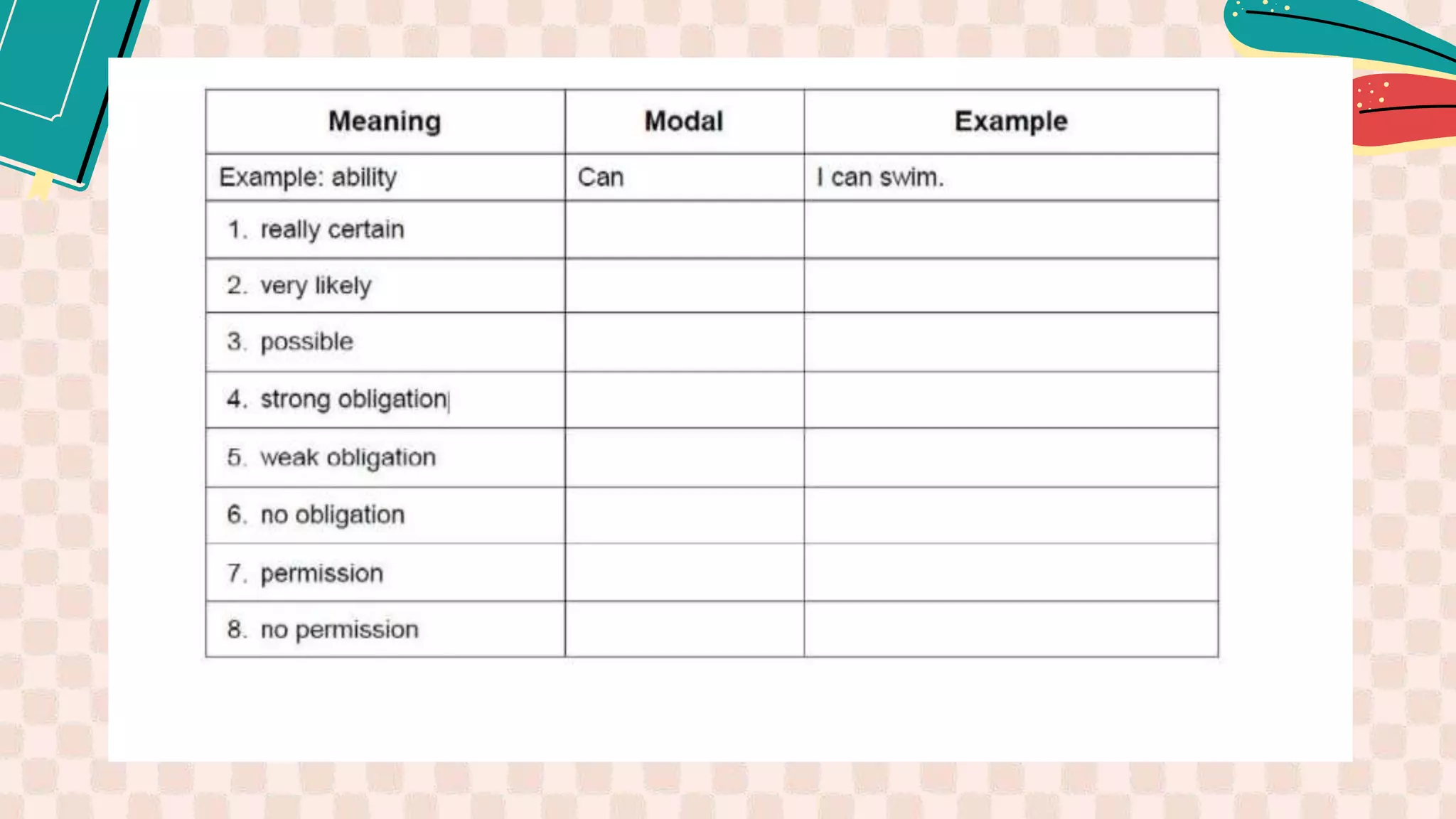
2. It explains how modal verbs are used to show possibility, permission, requests, suggestions, commands, obligations and habits.
3. The class activities include students constructing dialogues and writing essays using modal verbs correctly based on provided criteria.