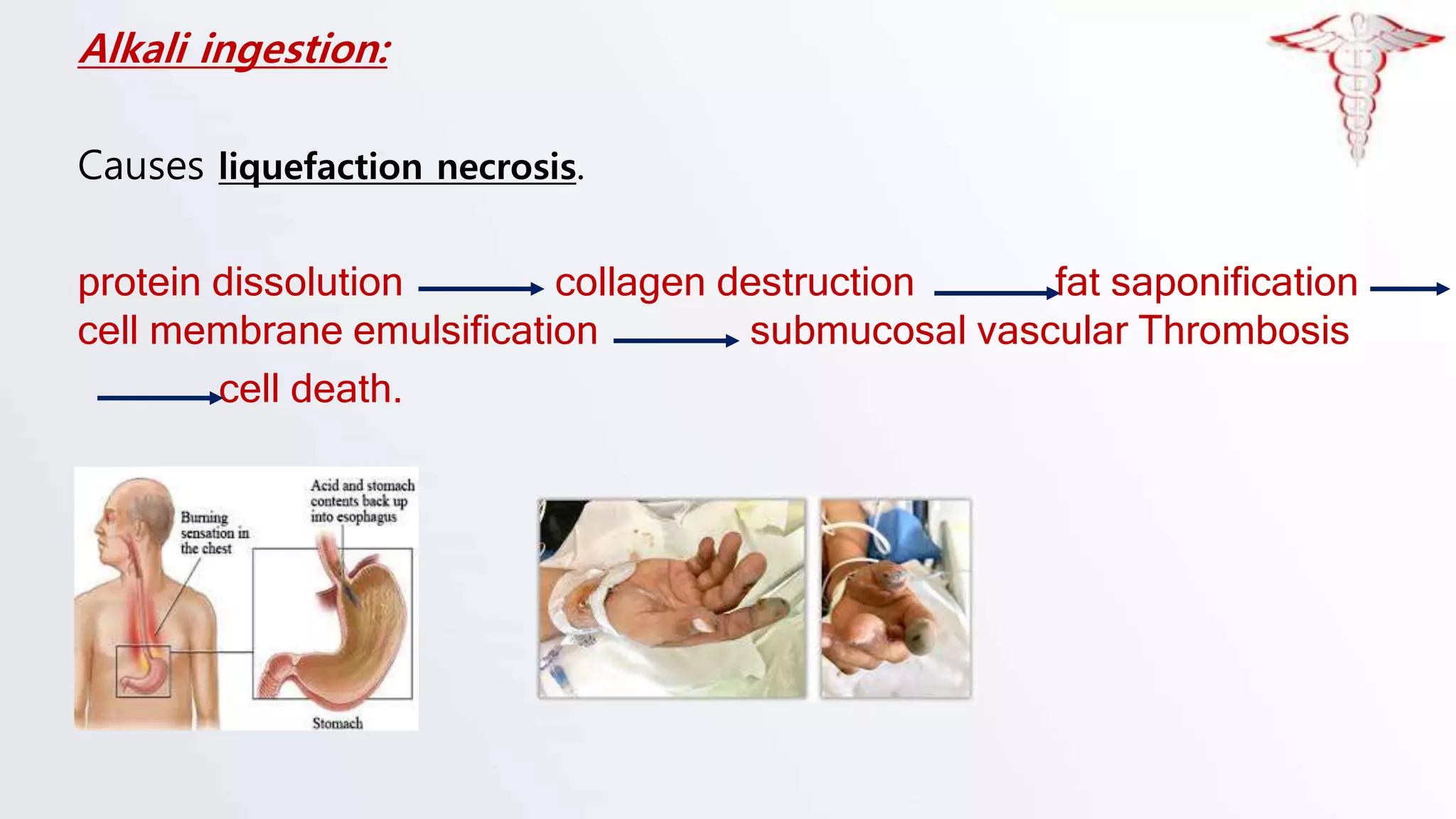
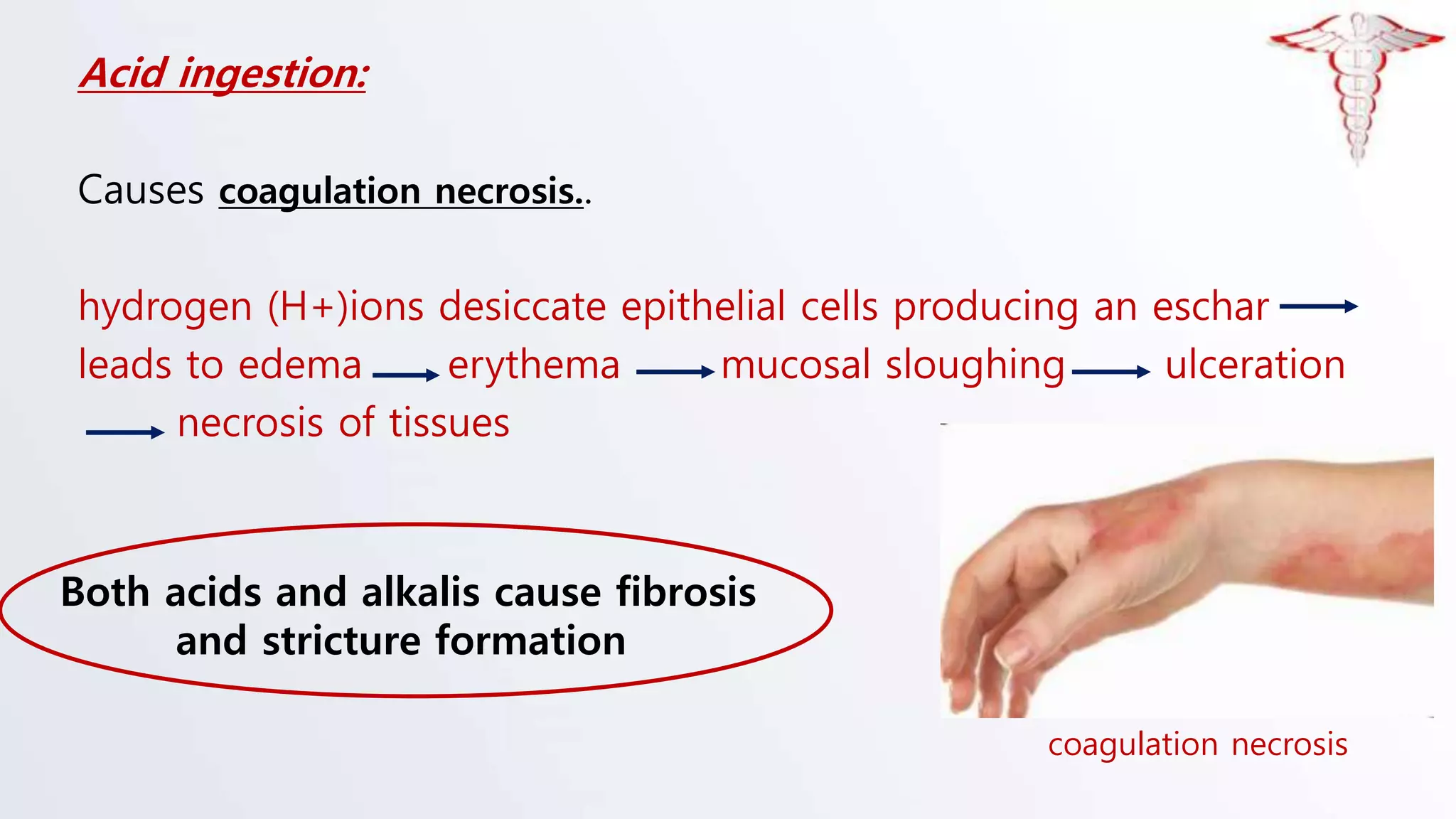
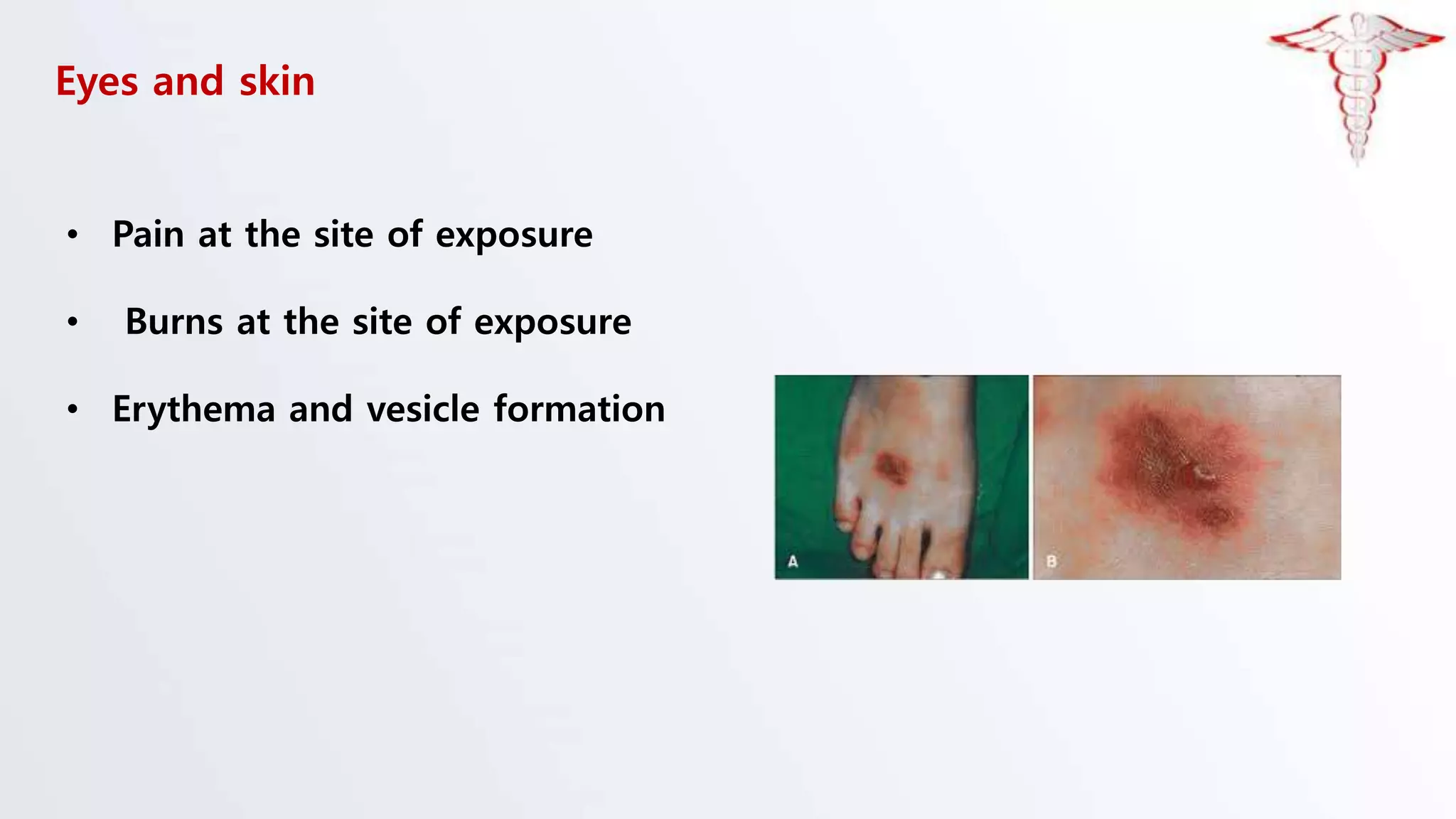
The document discusses corrosive poisons, their definitions, types, mechanisms of action, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and management strategies. Corrosive substances can cause severe tissue damage upon contact, especially affecting the gastrointestinal tract and respiratory systems, with a high prevalence in children. Management involves early admission and careful monitoring, with interventions like endoscopy depending on the severity of injury.