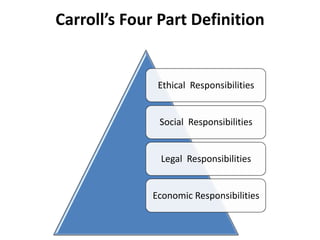
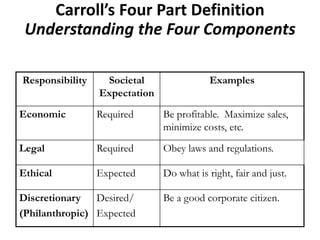
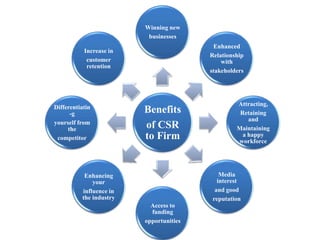
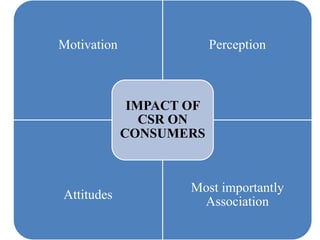
This presentation discusses corporate social responsibility (CSR) and its importance. It defines CSR using Carroll's four part model of economic, legal, ethical, and philanthropic responsibilities. It outlines the CSR requirements for large Indian companies under new rules. It addresses myths about CSR and highlights benefits like improved reputation, customer loyalty, and attracting employees. Examples of CSR initiatives from various Indian companies are provided relating to health, education, environment and community. Challenges of implementing CSR are also discussed.
![A presentation on
Corporate Social Responsibility
School of Management Studies
Presented By:
Amit Kumar
Durgesh Kumar
Anil Kumar
Ujjwal Mishra
[2012MB72]
[2012MB88]
[2012MB06]
[2012MB01]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corporatesocialresponsibility-131208105327-phpapp02/75/Corporate-social-responsibility-1-2048.jpg)