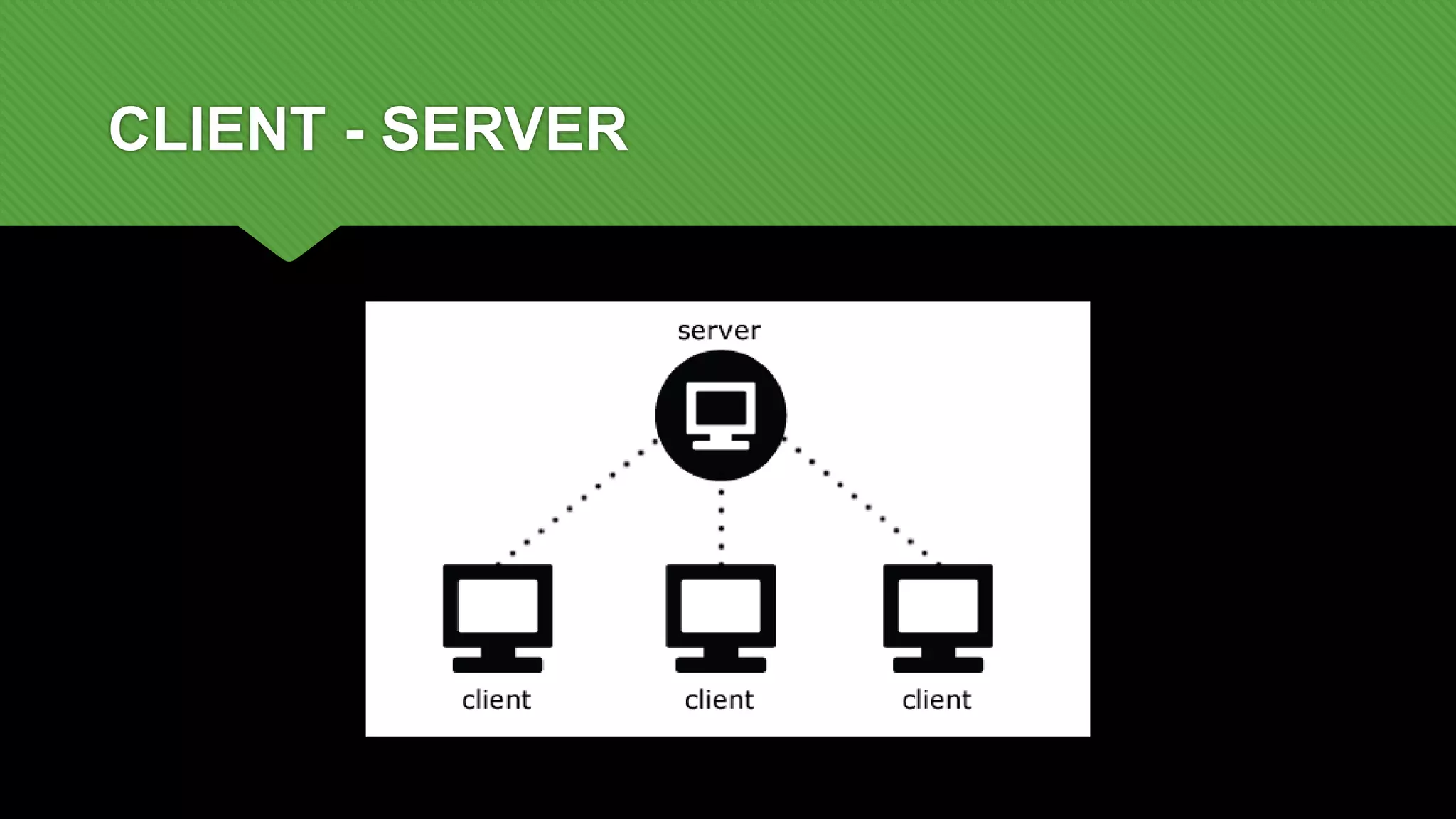
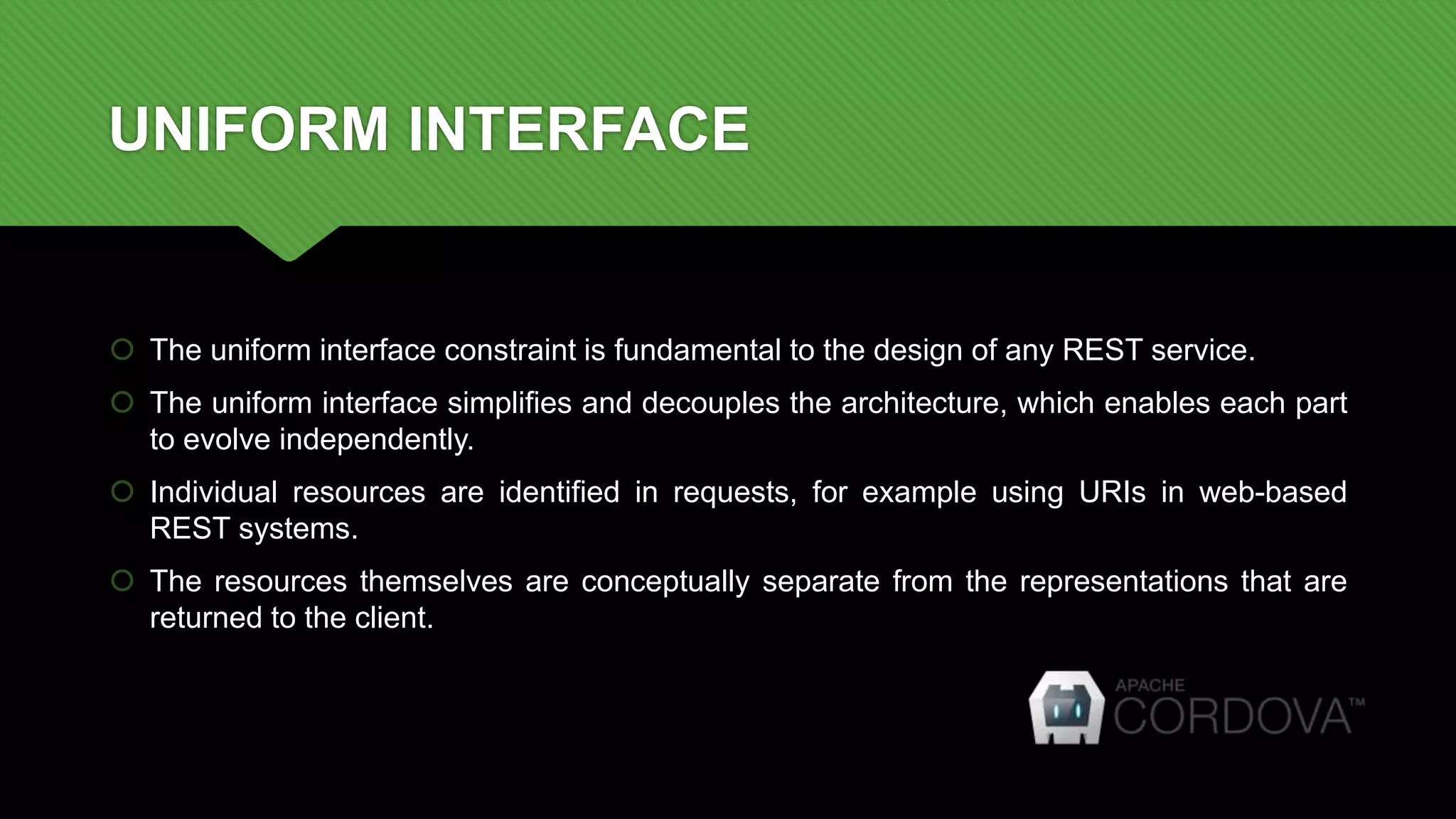
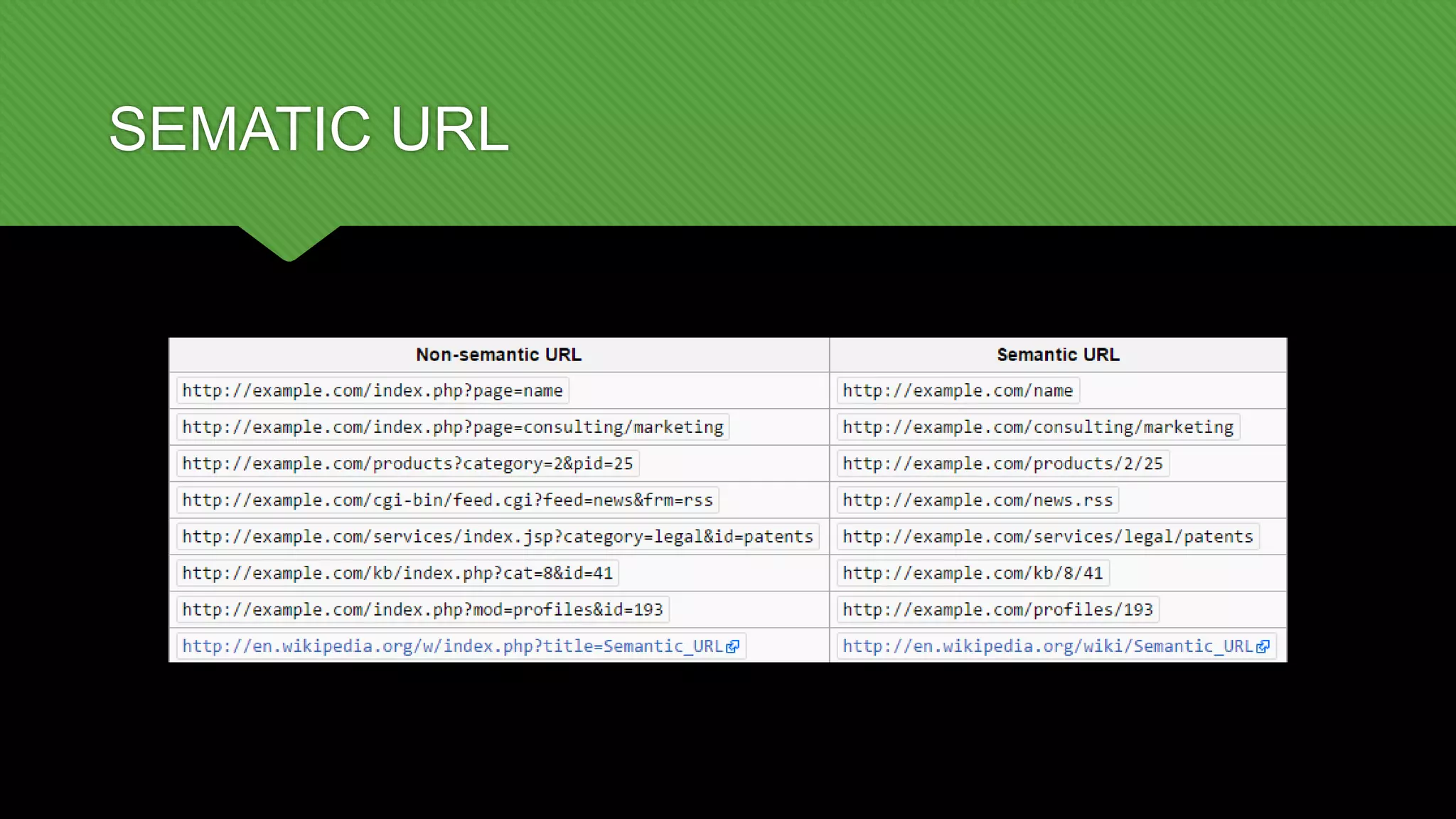
REST is an architectural style for building scalable web services that are simple, lightweight and focused on standards. The key aspects of REST include using a stateless, client-server protocol like HTTP with standard operations like GET, PUT, POST and DELETE. Resources are uniquely identified and encapsulated, and the interface is designed to be self-descriptive with hypermedia. This allows RESTful services to evolve independently of clients.