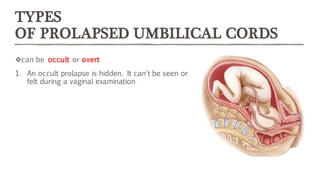
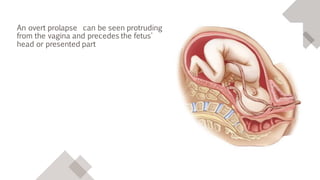
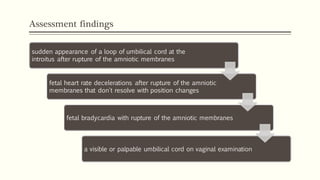
An occult or overt prolapsed umbilical cord occurs when the umbilical cord falls in front of, lies beside, or hangs below the fetal presenting part during delivery. It is an obstetric emergency that requires immediate intervention to prevent fetal hypoxia and associated increased morbidity and mortality. Risk factors include prematurity, multiple pregnancy, polyhydramnios, and malpresentations. Management of prolapsed cord involves preparing for immediate delivery, positioning the patient, administering oxygen, and manually elevating the presenting part and separating the cord until an emergency cesarean delivery or expedited vaginal delivery can be performed.