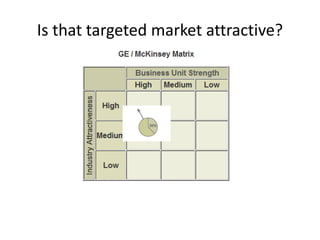
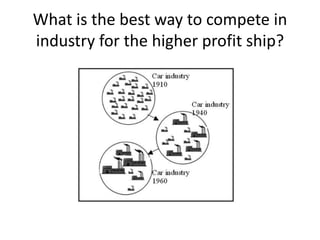
The document discusses concepts related to perfect competition and competitive strategy. It defines characteristics of perfect competition, including homogeneous goods and free entry/exit from the market. It then poses questions about assessing market attractiveness, competing for higher profits, and resources needed for competition. The document goes on to discuss barriers to entry like economies of scale, excess capacity, and switching costs. It also covers retaliatory barriers, forms of rivalry between firms, and how to analyze competitors by identifying and ranking them.