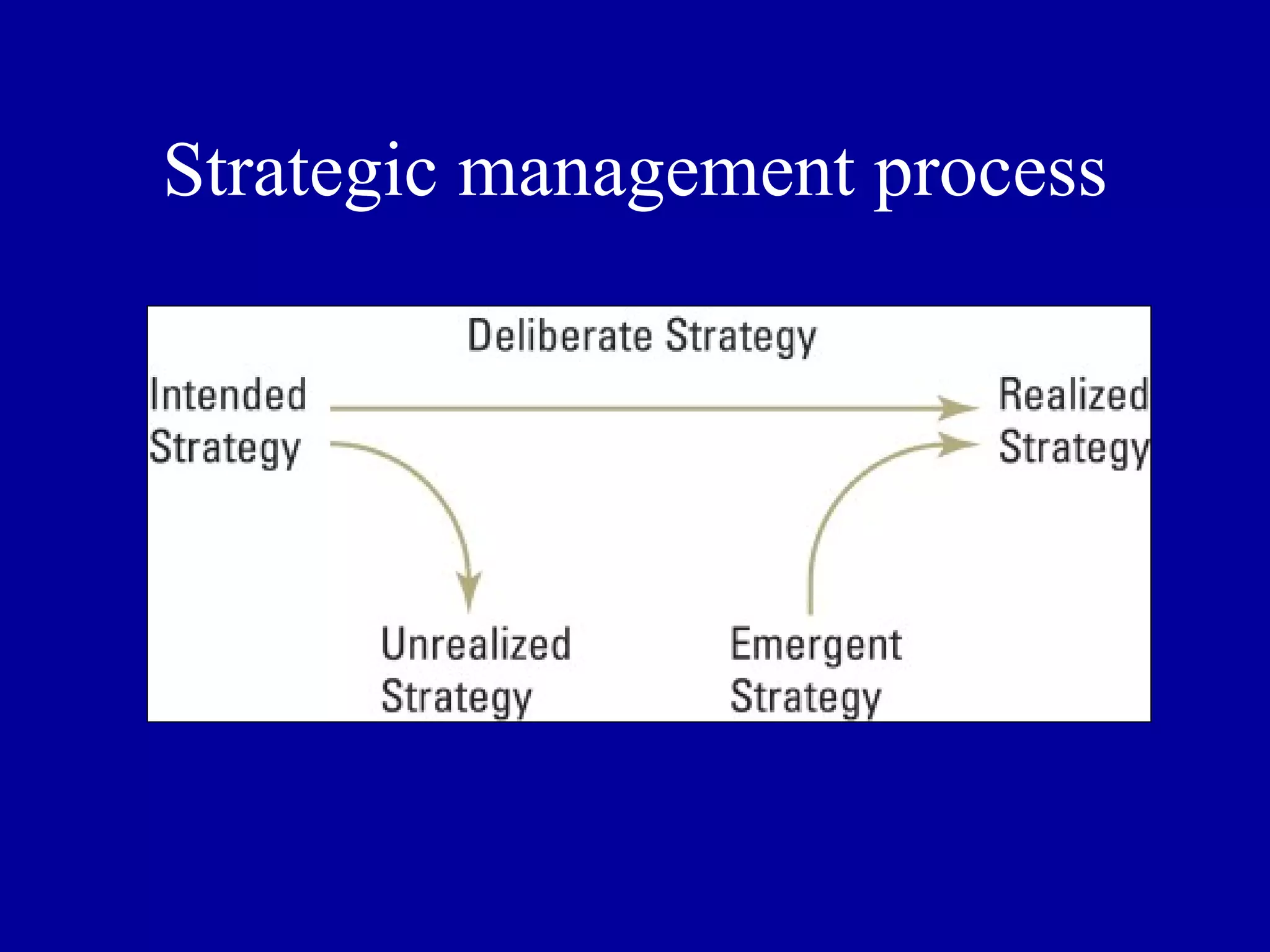
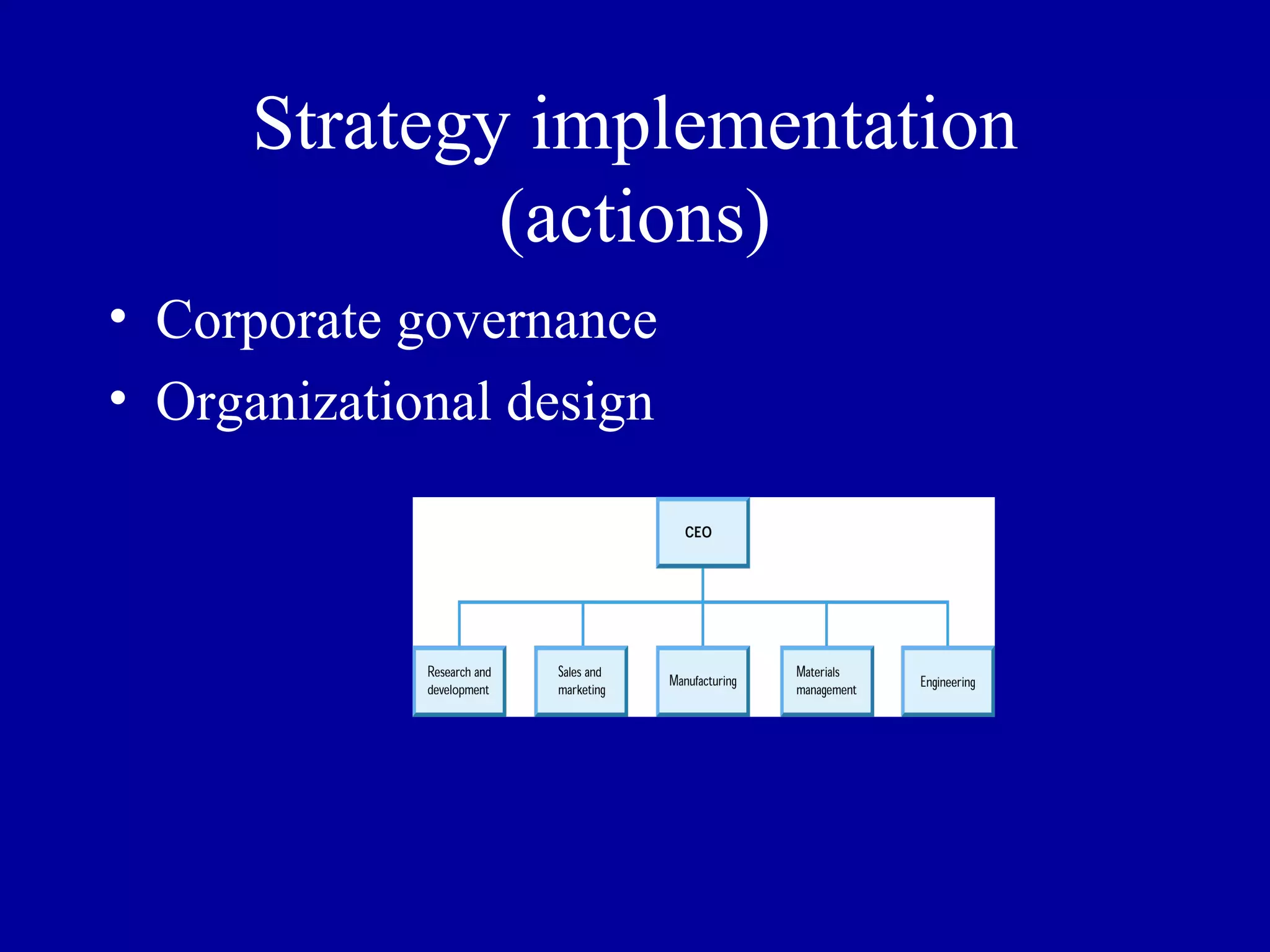
Strategic management involves analyzing a firm's internal and external environment to make decisions and take actions to create and sustain competitive advantage over the long term. It encompasses the entire organization and its stakeholders. The three major steps are strategy analysis, formulation of decisions, and implementation of actions. Strategic management ensures consistency among a firm's goal hierarchy including its vision, mission, and objectives.