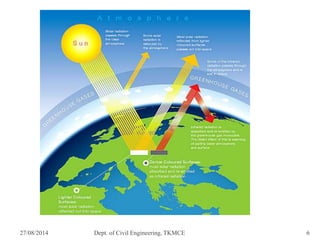
The document discusses cool pavements, which are pavement surfaces designed to reduce the urban heat island effect. It first introduces the topic and defines urban heat islands as metropolitan areas that are often warmer than surrounding rural areas due to human activity and dark pavements. It then describes different types of cool pavements, including reflective and permeable pavements, and provides examples like Portland cement concrete, white-topping, asphalt sealcoats and coatings. Benefits of cool pavements are also listed, such as improved water quality, safety and reduced nighttime temperatures. The document concludes by noting that cool pavements provide a cost-effective way to lower urban temperatures compared to conventional dark surfaces.