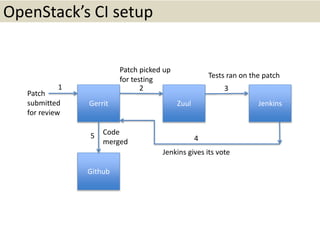
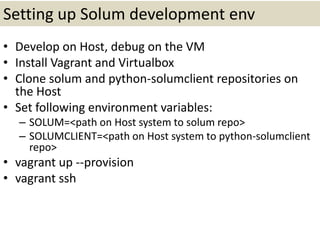
This document provides an overview of contributing to OpenStack. It begins with introducing OpenStack and its various projects. It then focuses on the Solum project, describing its goals, architecture and abstractions. The remainder discusses the tools and processes for contributing code to OpenStack, including setting up a development environment, submitting patches for review, ensuring tests pass, and following best practices. The presentation aims to educate contributors on how to effectively participate in OpenStack development.














![Solum abstractions - Languagepack Example: Python
FROM ubuntu:precise
MAINTAINER Murali Allada
<murali.allada@rackspace.com>
RUN apt-get -yqq update
RUN apt-get -yqq install python-pip
RUN apt-get -yqq install python-dev
COPY build.sh /solum/bin/
https://github.com/rackspace-solum-samples/solum-languagepack-python
#!/bin/bash
# Check if pip is installed
pip help
[[ $? != 0 ]] && echo python-pip is
not installed. && exit 1
# Install app dependencies
cd /app
pip install -r requirements.txt
build.shDockerfile](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/contributing-to-openstack-1-160104112238/85/Contributing-to-OpenStack-16-320.jpg)























![Screen
• Program that allows sharing physical terminal between
different processes
• Entering Solum’s screen session in Devstack
– screen –x stack
• Screen commands
– Move to next window: Ctrl+a n
– Move to previous window: Ctrl+a p
– See all windows: Ctrl+a “
– Enter scrollback/copy mode: Ctrl+a [
– Leave scrollback/copy mode: Ctrl+a ]
– http://www.pixelbeat.org/lkdb/screen.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/contributing-to-openstack-1-160104112238/85/Contributing-to-OpenStack-45-320.jpg)