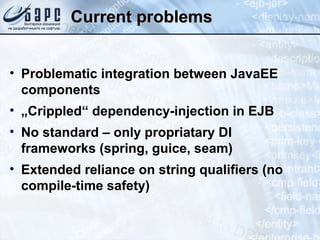
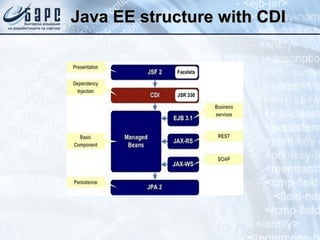
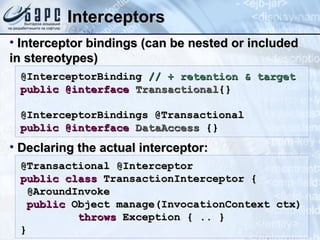
This document provides an overview of Contexts and Dependency Injection (CDI), the Java EE standard for dependency injection and component management defined in JSR-299. It discusses the history and goals of CDI, key concepts like beans and injection, and how CDI integrates with and improves upon other Java EE technologies like EJBs and JSF. The document also demonstrates several CDI features through code examples, such as qualifiers, producers, decorators, and interceptors.