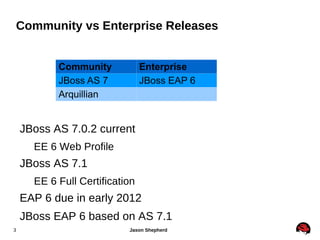
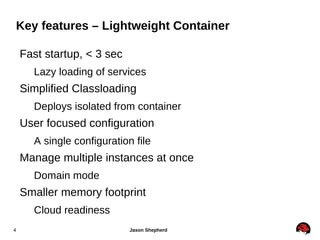
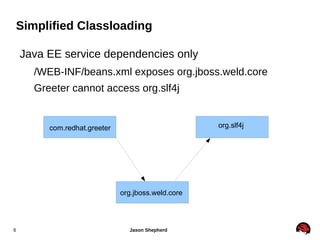
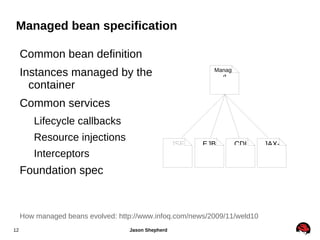
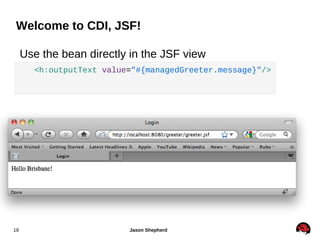
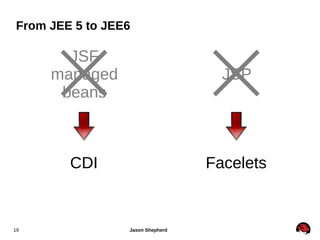
JBoss Application Server 7 includes several key features:
1. It is a lightweight Java EE 6 compliant container that provides fast startup times of less than 3 seconds.
2. It simplifies classloading and configuration for easier management and deployment.
3. It supports the use of managed beans, dependency injection and common services as specified by the CDI specification.