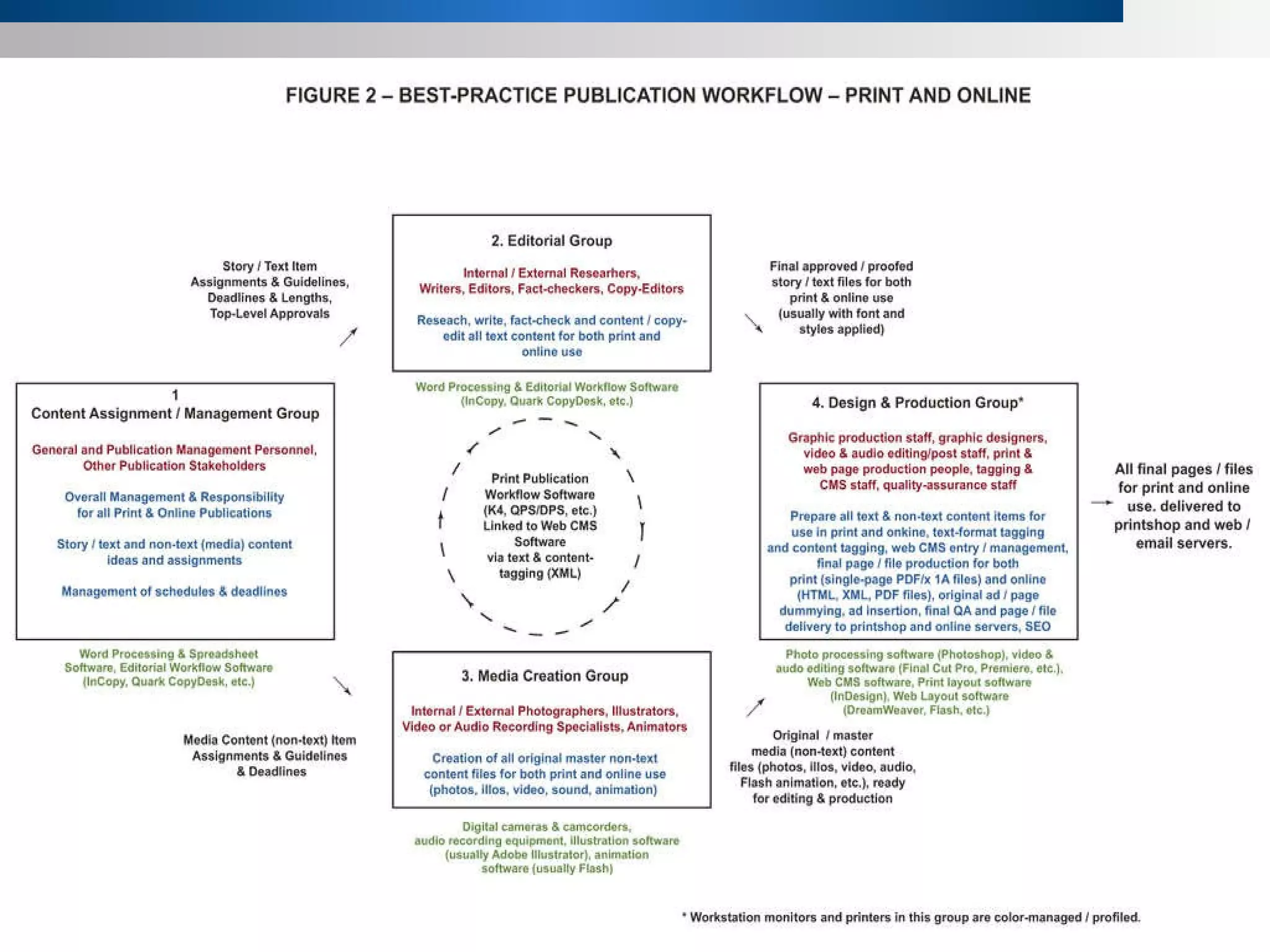
1) Content is the cornerstone of publications and includes text, graphics, audio, video and data. Publishers add value through packaging and connecting different media.
2) Content trends include expansion of multimedia, user-generated content, and constantly updated content. This requires new skills and less control by editors.
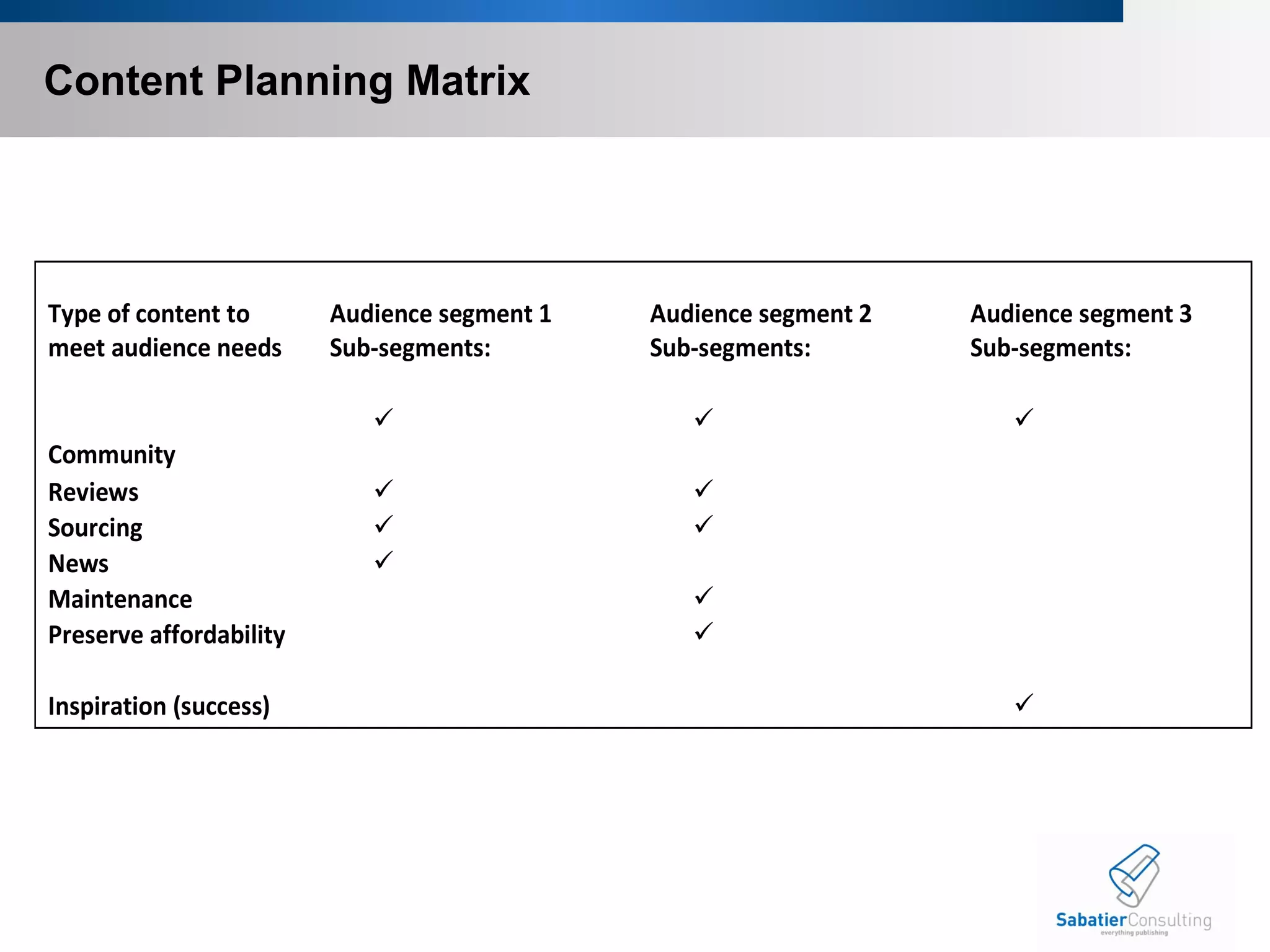
3) Effective content planning determines audience needs, key themes, and gaps to engage and profit audiences across different channels like print, web, and mobile. It is important to define audiences and their distinct needs for each channel.




















![Content Planning Content planning- plans for the creation, publication, and governance of useful, usable content. [It’s deciding what you are going to include and what you are going to leave out.] Key themes and messages Topics Content purpose (bridge audience needs) Content gap analysis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/contentstrategy-final2-090902124758-phpapp01/75/Content-Strategy-Final-2-22-2048.jpg)