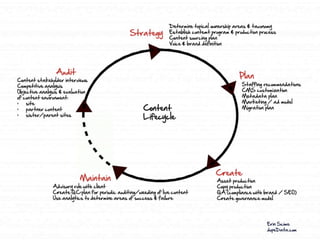
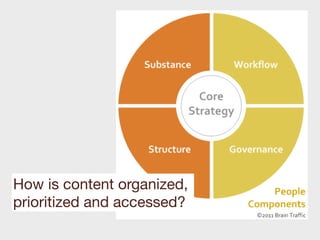
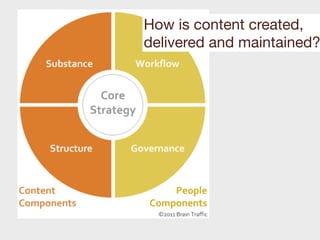
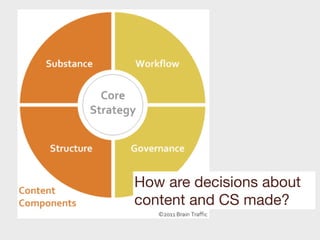
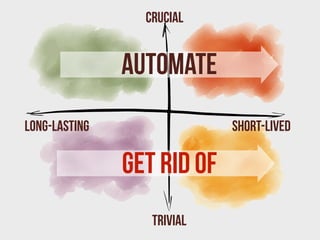
This document provides a summary of content strategy concepts and best practices. It discusses how content strategy guides plans for creating, delivering, and governing content to achieve business goals. It also covers defining the substance and structure of content, establishing workflows and ownership, and using tools like content audits, style guides, and governance policies. The document recommends resources like books, websites, and people in the field to learn more about developing an effective content strategy.