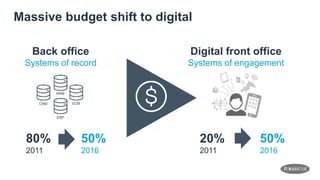
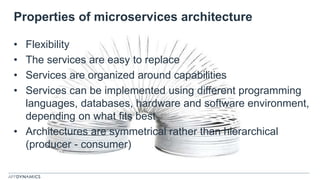
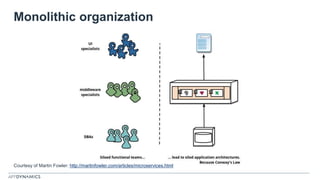
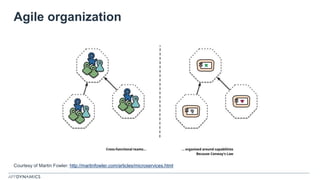
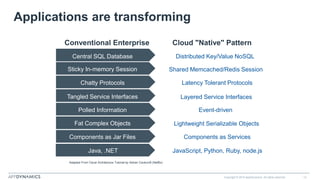
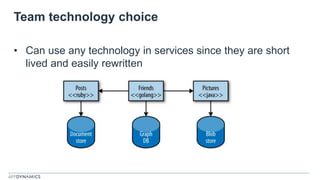
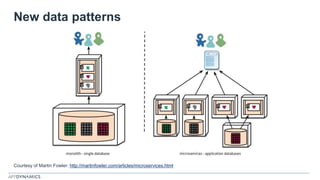
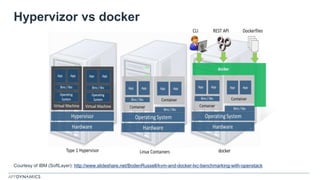
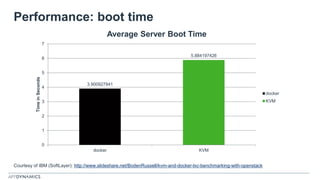
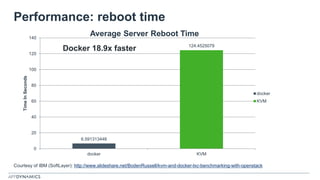
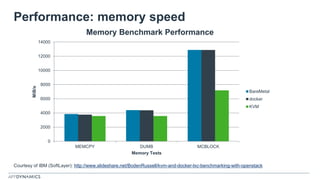
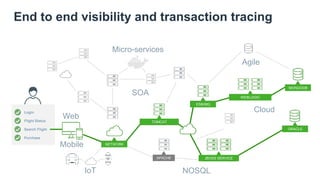
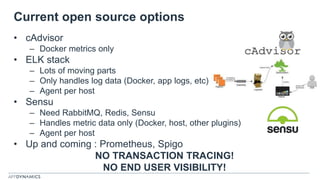
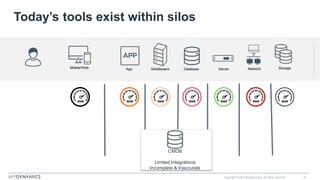
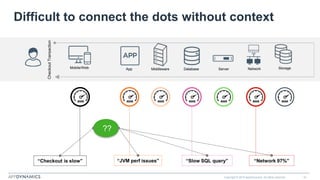
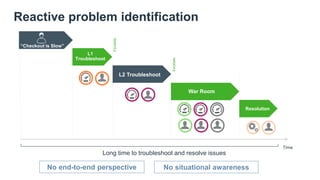
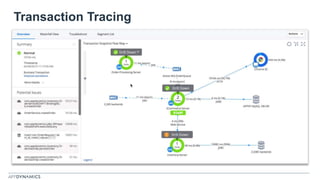
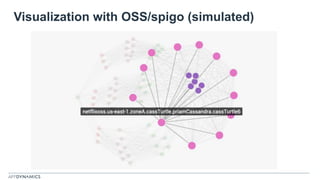
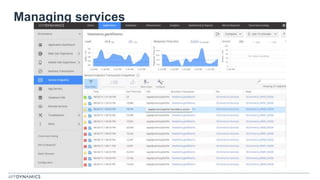
The document discusses the shift from monolithic to microservices architecture, emphasizing its advantages such as flexibility, scalability, and the ability to use various programming languages. It highlights the performance challenges posed by microservices and the growing adoption of containerization technologies like Docker for efficient management. Additionally, it addresses the complexities and monitoring difficulties that arise in microservices environments, alongside current solutions and tools available for management and analytics.