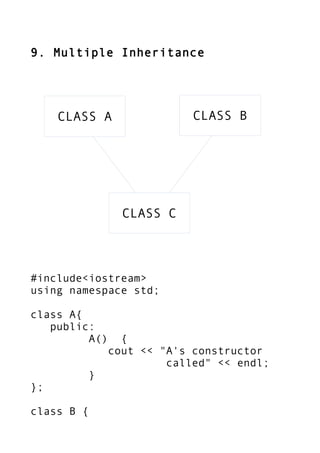
This document contains code snippets for 12 common C++ programs: 1) checking if a number is even or odd, 2) swapping two numbers, 3) checking if a year is a leap year, 4) sorting words in dictionary order, 5) calculating a factorial, 6) generating a Fibonacci series, 7) transposing a matrix, 8) using constructors and destructors, 9) demonstrating multiple inheritance, 10) using static members and functions, 11) exception handling, and 12) file input/output. Each code snippet is followed by sample input/output to demonstrate the program's functionality.





![4. Sort Words in Dictionary Order
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string str[10], temp;
cout << "Enter 10 words: " << endl;
for(int i = 0; i < 10; ++i){
getline(cin, str[i]);
}
for(int i = 0; i < 9; ++i)
for( int j = i+1; j < 10; ++j){
if(str[i] > str[j]){
temp = str[i];
str[i] = str[j];
str[j] = temp;
}
}
cout << "Sorted order is: " << endl;
for(int i = 0; i < 10; ++i){
cout << str[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cpractical-170728094203/85/C-practical-6-320.jpg)



![7. Transpose of Matrix
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a[10][10], trans[10][10], r, c, i,
j;
cout << "Enter rows and columns of
matrix: ";
cin >> r >> c;
// Storing element of matrix entered by user in
array a[][].
cout << endl << "Enter elements of
matrix: " << endl;
for(i = 0; i < r; ++i)
for(j = 0; j < c; ++j)
{
cout << "Enter elements a" << i + 1
<< j + 1 << ": ";
cin >> a[i][j];
}
// Displaying the matrix a[][]
cout << endl << "Entered Matrix: " <<
endl;
for(i = 0; i < r; ++i)
for(j = 0; j < c; ++j){
cout << " " << a[i][j];
if(j == c - 1)
cout << endl << endl;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cpractical-170728094203/85/C-practical-10-320.jpg)
![}
// Finding transpose of matrix a[][] and storing it
in array trans[][].
for(i = 0; i < r; ++i)
for(j = 0; j < c; ++j){
trans[j][i]=a[i][j];
}
// Displaying the transpose,i.e, Displaying array
trans[][].
cout << endl << "Transpose of Matrix: "
<< endl;
for(i = 0; i < c; ++i)
for(j = 0; j < r; ++j)
{
cout << " " << trans[i][j];
if(j == r - 1)
cout << endl << endl;
}
return 0;
}
OUTPUT:
Enter rows and column of matrix: 2 3
Enter elements of matrix:
Enter elements a11: 1
Enter elements a12: 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cpractical-170728094203/85/C-practical-11-320.jpg)






![12. File Handling
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main () {
char data[100];
// open a file in write mode.
ofstream outfile;
outfile.open("afile.dat");
cout << "Writing to the file" << endl;
cout << "Enter your name: ";
cin.getline(data, 100);
// write inputted data into the file.
outfile << data << endl;
cout << "Enter your age: ";
cin >> data;
cin.ignore();
// again write inputted data into the file.
outfile << data << endl;
// close the opened file.
outfile.close();
// open a file in read mode.
ifstream infile;
infile.open("afile.dat");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cpractical-170728094203/85/C-practical-19-320.jpg)
