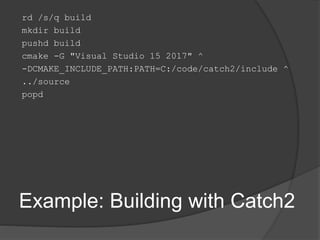
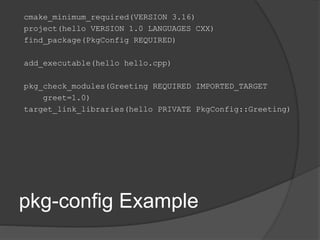
The document provides an extensive overview of CMake and its functionalities related to handling libraries in C++. It covers key topics like library types, find_package, pkg-config, and custom find modules, detailing how to manage dependencies and link libraries in various contexts. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of understanding target properties and build configurations for effective CMake usage.












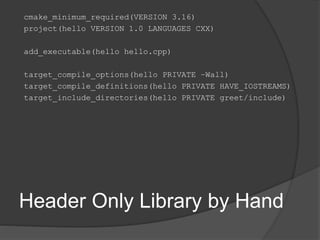





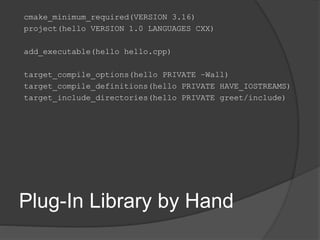

![find_package
find_package(<PackageName> [version]
[EXACT] [QUIET] [MODULE] [REQUIRED]
[[COMPONENTS] [components...]]
[OPTIONAL_COMPONENTS components...]
[NO_POLICY_SCOPE])
Finds and loads settings from an external
project
Sets <PackageName>_FOUND if found
Sucess results in variables and imported
targets describing the found package
Unifies header only, static and dynamic
libraries](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/consuminglibrarieswithcmake-200213201526/85/Consuming-Libraries-with-CMake-21-320.jpg)

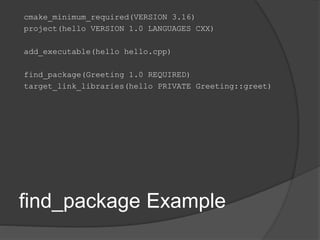




![find_file
find_file(<var>
name | NAMES name1 [name2...]
[HINTS path1 [path2...ENV var]]
[PATHS path1 [path2...ENV var]]
[PATH_SUFFIXES suffix1 [suffix2 ...]]
[DOC "cache documentation string"]
[NO_DEFAULT_PATH])
Locates a file according to name, location, suffix
Stores the result in <var>
Consult documentation for more options and
details on search behavior](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/consuminglibrarieswithcmake-200213201526/85/Consuming-Libraries-with-CMake-29-320.jpg)
![find_program
find_program(<var>
name | NAMES name1 [name2...]
[HINTS path1 [path2...ENV var]]
[PATHS path1 [path2...ENV var]]
[PATH_SUFFIXES suffix1 [suffix2 ...]]
[DOC "cache documentation string"]
[NO_DEFAULT_PATH])
Similar to find_file
Locates an executable program
Handles platform specific conventions, e.g.
foo.exe on Windows](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/consuminglibrarieswithcmake-200213201526/85/Consuming-Libraries-with-CMake-30-320.jpg)
![find_path
find_path(<var>
name | NAMES name1 [name2...]
[HINTS path1 [path2...ENV var]]
[PATHS path1 [path2...ENV var]]
[PATH_SUFFIXES suffix1 [suffix2 ...]]
[DOC "cache documentation string"]
[NO_DEFAULT_PATH])
Similar to find_file
Locates a directory containing a file](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/consuminglibrarieswithcmake-200213201526/85/Consuming-Libraries-with-CMake-31-320.jpg)
![find_library
find_library(<var>
name | NAMES name1 [name2...]
[HINTS path1 [path2...ENV var]]
[PATHS path1 [path2...ENV var]]
[PATH_SUFFIXES suffix1 [suffix2 ...]]
[DOC "cache documentation string"]
[NO_DEFAULT_PATH])
Similar to find_file
Handles platform specific library forms, e.g.
libfoo.a, foo.dll, foo.lib](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/consuminglibrarieswithcmake-200213201526/85/Consuming-Libraries-with-CMake-32-320.jpg)

![find_package_handle_standard_ar
gs
find_package_handle_standard_args(<PackageName>
[FOUND_VAR <result-var>]
[REQUIRED_VARS <required-var>...]
[VERSION_VAR <version-var>]
[HANDLE_COMPONENTS]
[CONFIG_MODE]
[REASON_FAILURE_MESSAGE <message>]
[FAIL_MESSAGE <message>]
)
find_package(PackageHandleStandardArgs)
Use REQUIRED_VARS to list requirements:
found files, directories, libraries, etc.
Combined result is in <result-var>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/consuminglibrarieswithcmake-200213201526/85/Consuming-Libraries-with-CMake-34-320.jpg)
![Creating Imported Targets
add_library(<name>
<SHARED|STATIC|MODULE|OBJECT|INTERFACE|UNKNOWN>
IMPORTED [GLOBAL])
Typically specify the library type as
UNKNOWN
Set target properties to specify usage
requirements](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/consuminglibrarieswithcmake-200213201526/85/Consuming-Libraries-with-CMake-35-320.jpg)