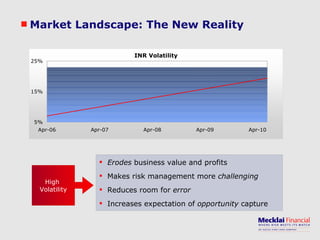
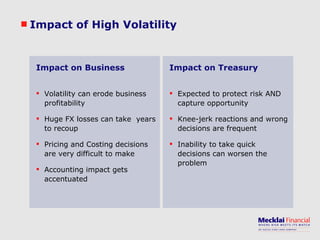
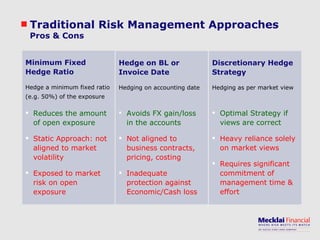
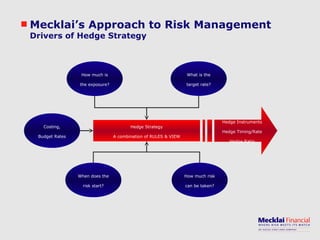
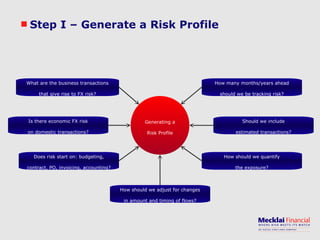
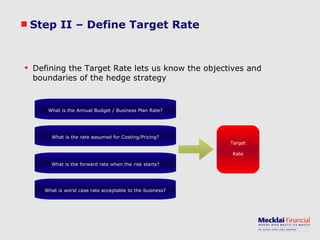
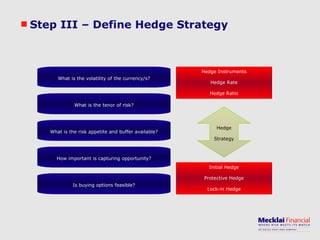
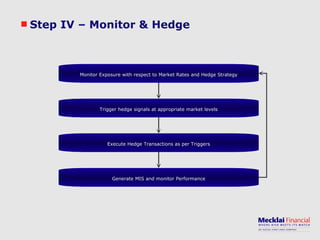
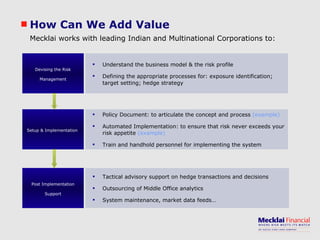
The document discusses managing foreign exchange risk and Mecklai's approach. It outlines the challenges of high volatility in markets and impacts on businesses. Traditional risk management approaches are discussed along with their pros and cons. Mecklai's approach focuses first on understanding the business risks and exposures before developing hedge strategies aligned to the business. The approach involves quantifying exposures, defining risk appetite and target rates, and monitoring hedge strategies. Mecklai works with clients to devise risk management policies, implement automated systems, and provide ongoing support.