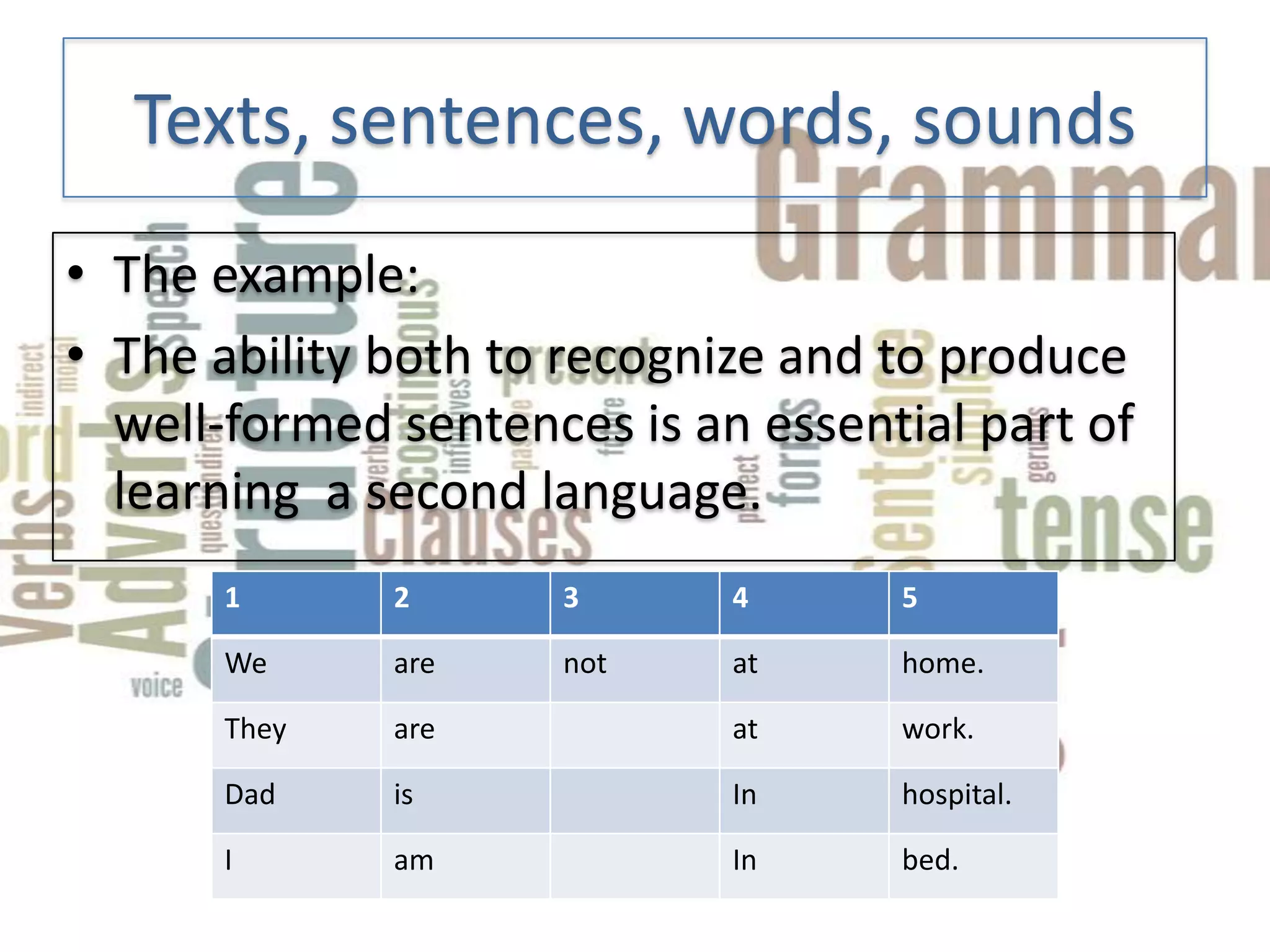
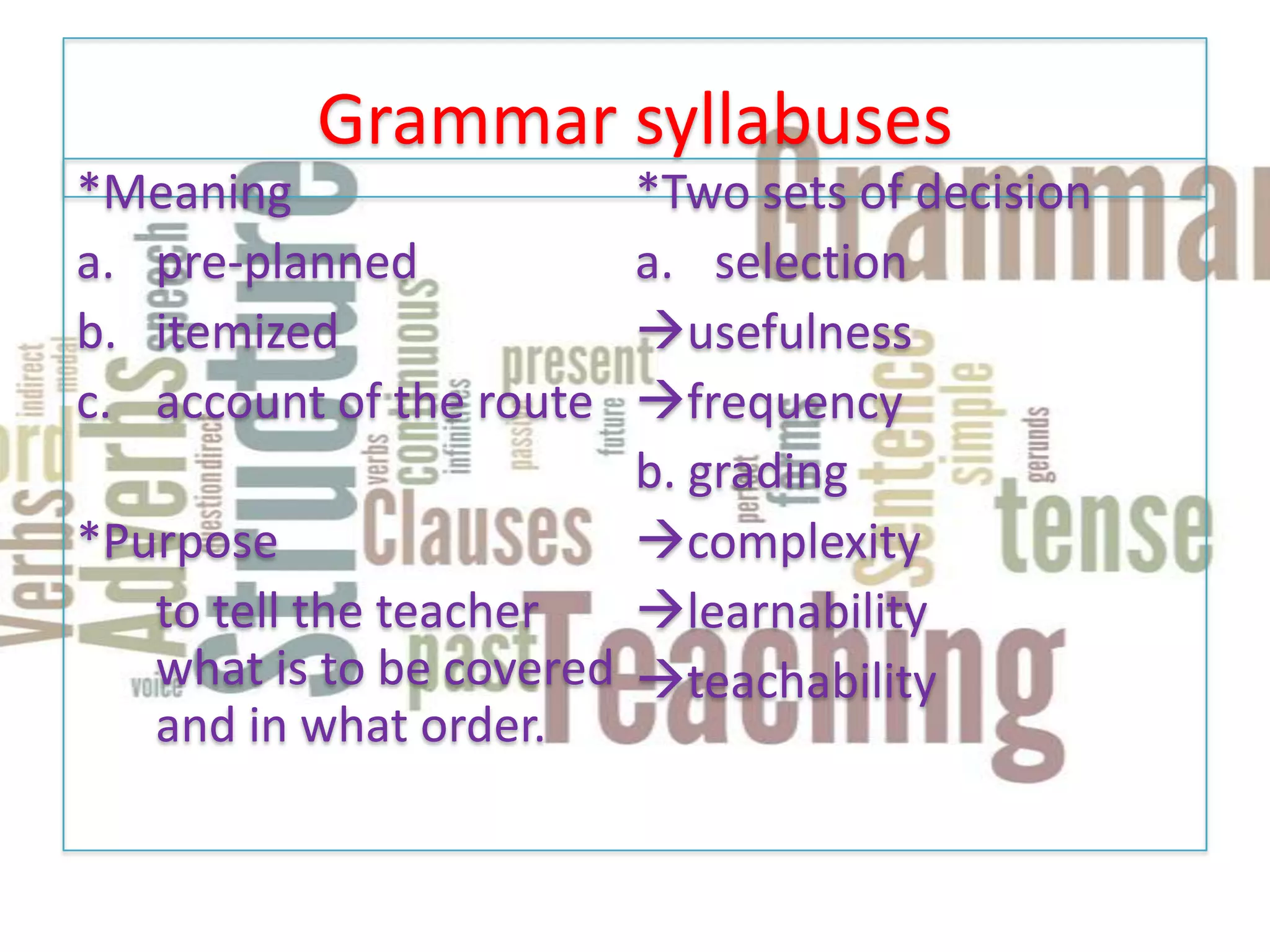
This document discusses how to teach grammar. It covers defining grammar and its components like texts, sentences, words and sounds. It discusses two approaches to teaching grammar - deductive and inductive learning. Inductive learning involves students deriving grammar rules from examples without being directly taught the rules. The document also discusses using different types of texts and contexts as a way to teach grammar in a more meaningful way for students. Sources of texts that can be used include course books, authentic materials, and materials generated by teachers or students.