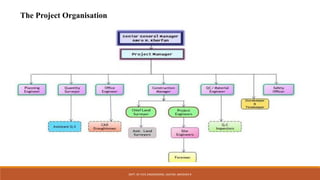
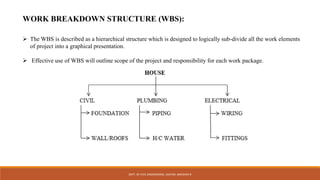
The document discusses construction management and entrepreneurship. It defines management as the process of planning, organizing, directing, and controlling organizational resources to achieve goals. Some key characteristics of management are that it is a continuous process, both an art and a science, involves decision making, and aims to achieve predetermined objectives. The main functions of management are planning, organizing, staffing, directing, controlling, innovation, and representation. Construction project management involves planning, coordinating, and controlling all aspects of a construction project from start to finish. Common project planning tools include Gantt charts, work breakdown structures, and critical path methods.