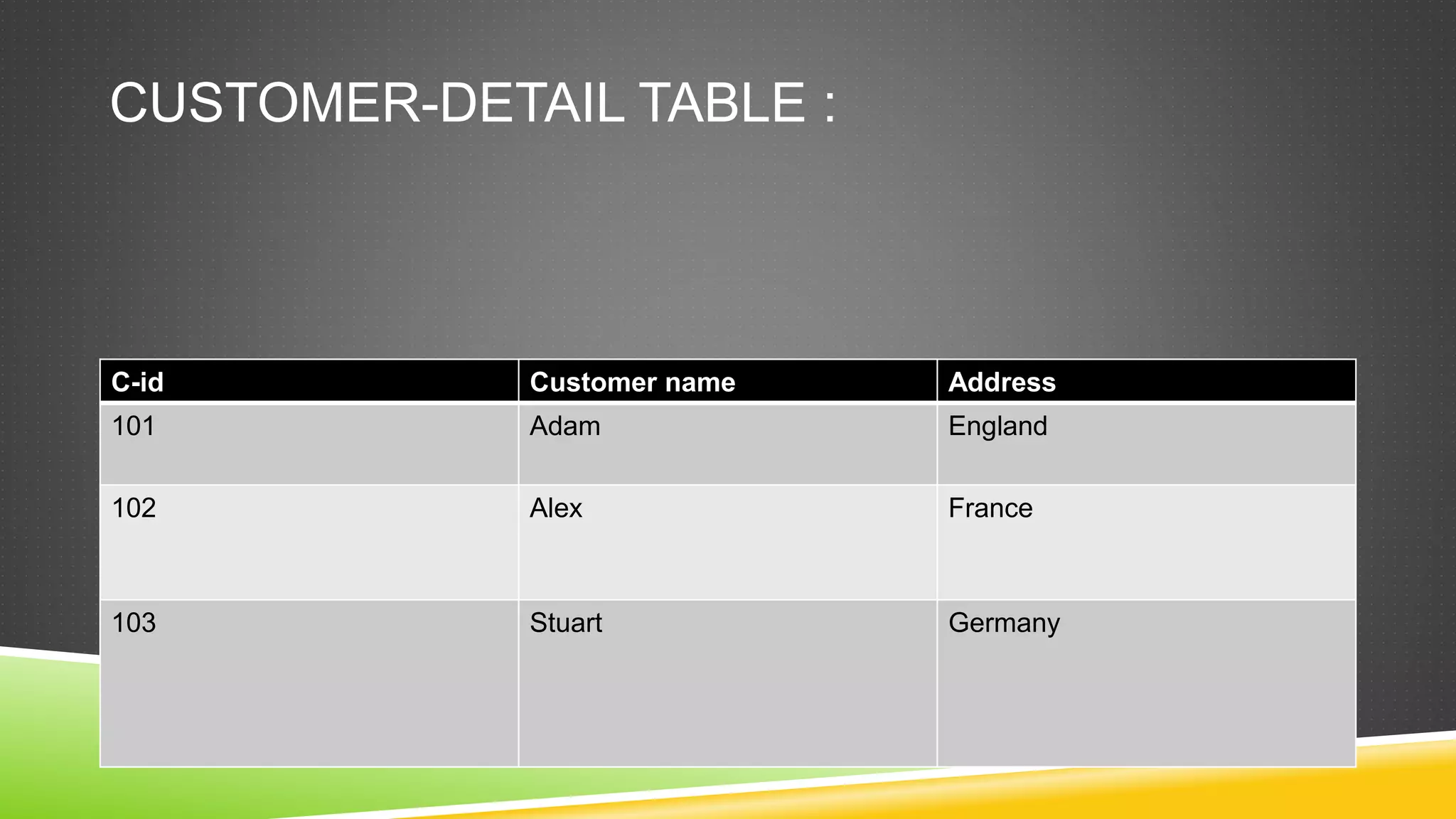
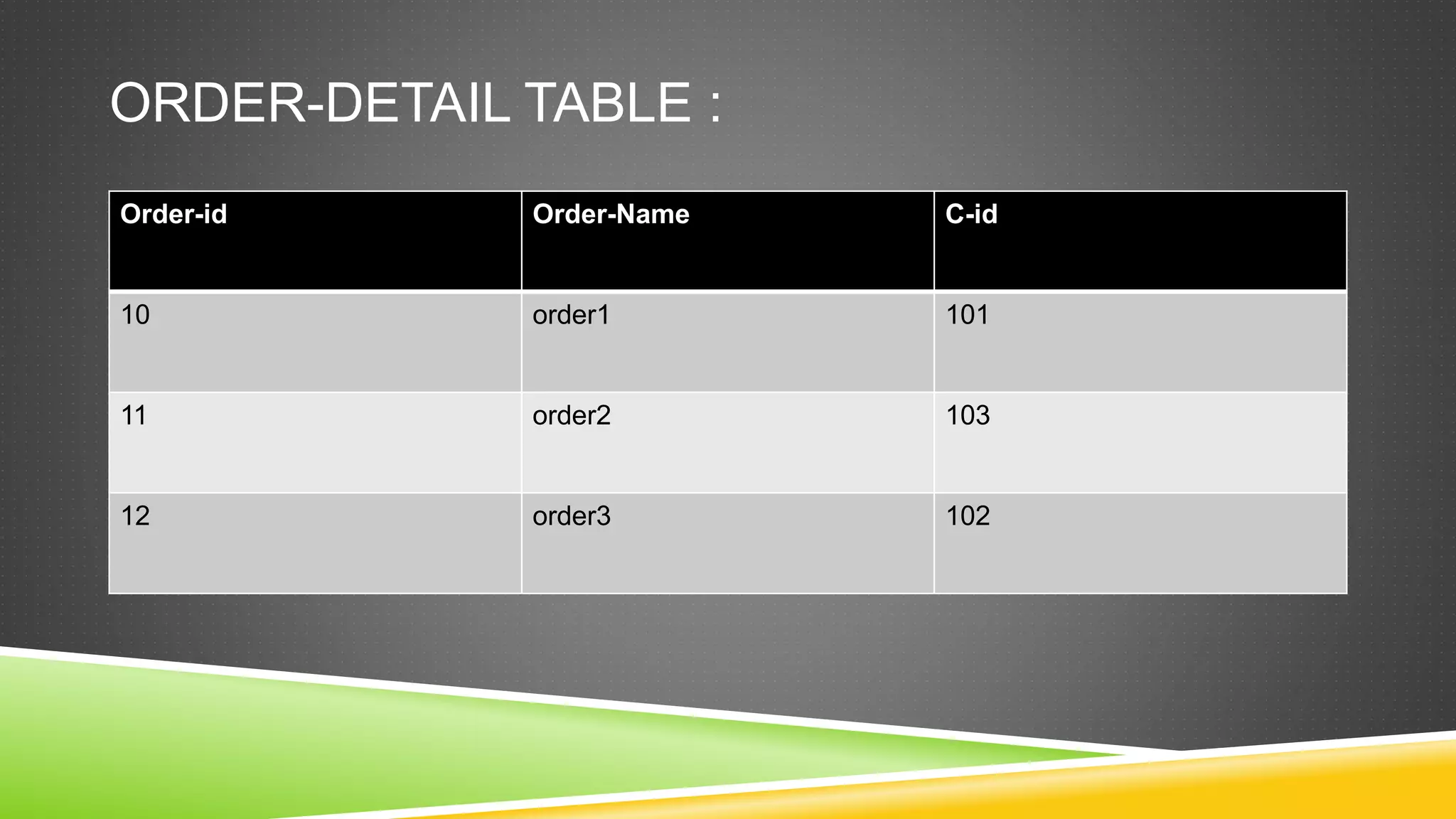
This document defines and describes different types of database constraints. It discusses table-level and column-level constraints. The most common constraints are listed as not null, primary key, unique key, and foreign key. Examples are provided for each constraint type to illustrate how they can be applied when creating or altering tables to maintain data integrity. A foreign key specifically relates data between two tables by referencing the primary key of another table.