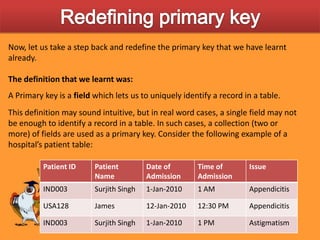
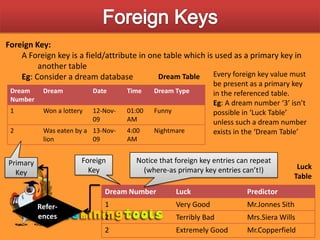
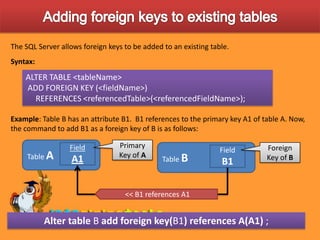
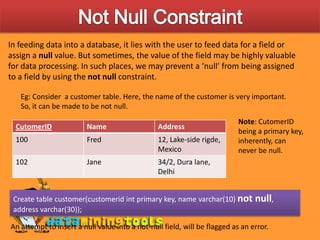
This document discusses various ways to customize databases in SQL Server, including managing data integrity through primary keys, foreign keys, and constraints. Primary keys uniquely identify records, can be a single field or multiple fields, and can be added to tables during or after creation. Foreign keys reference primary keys in other tables and have similar rules for addition. Not null, unique, and check constraints enforce data rules and prevent invalid entries. Customizations like these help optimize efficiency and ensure accuracy of the stored data.