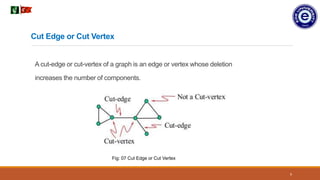
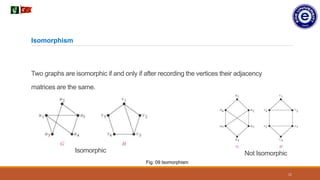
1. Graph theory can be used to model connectivity problems in computer networks. Connectivity refers to whether messages can be sent between any two computers using intermediate links.
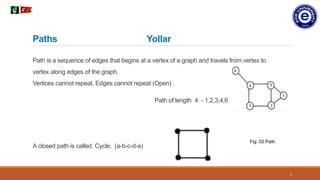
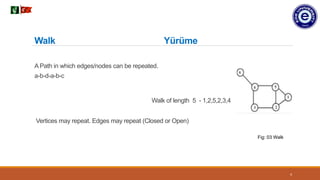
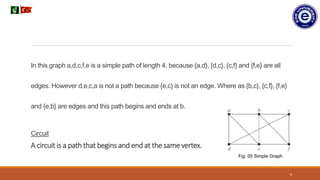
2. There are different path types in graphs including simple paths where vertices and edges cannot be repeated, and walks where vertices and edges may be repeated.
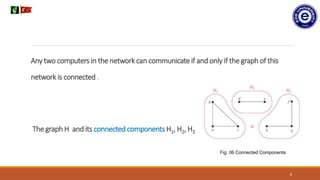
3. A computer network is represented by a graph where computers are vertices and communication links are edges. For any two computers to communicate, the graph must be connected - meaning there is a path between any two vertices.