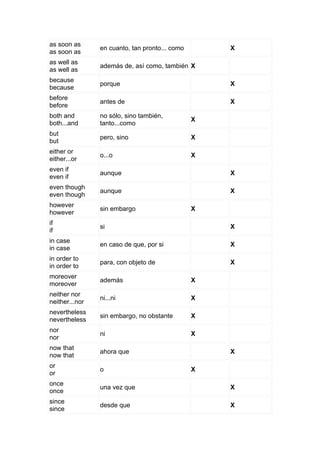
This document discusses conjunctions in Spanish and English. It defines conjunctions as words used to link words and sentences together. There are two types of conjunctions - coordinating and subordinating. Coordinating conjunctions link elements that have equal importance, such as "and, but, or." Subordinating conjunctions introduce dependent clauses, such as "although, because, since, until." Examples are provided of conjunctions in English and their Spanish translations.