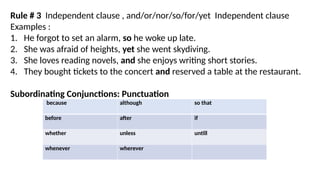
The document outlines the use of coordinating and subordinating conjunctions, including examples and punctuation rules. It explains how conjunctions connect words, phrases, or clauses and provides guidelines for their punctuation based on specific scenarios. Additionally, it discusses conjunctive adverbs and their role in linking independent clauses with examples.