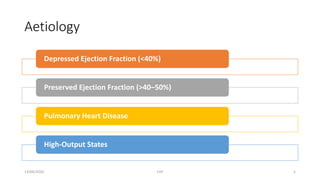
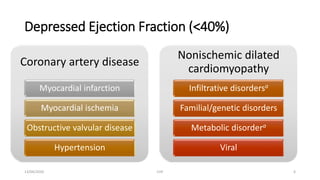
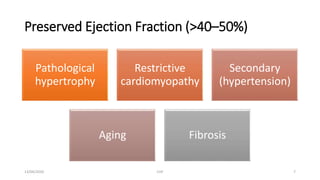
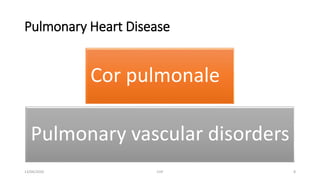
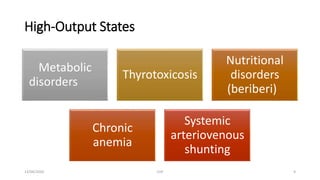
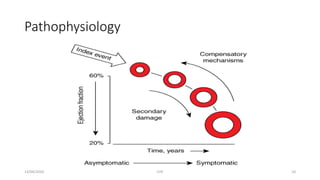
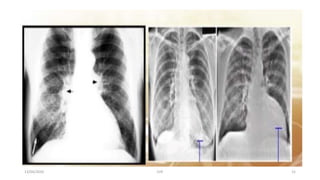
The document discusses congestive heart failure (CHF). It begins with objectives which are to define CHF, discuss its causes, pathophysiology, clinical features, and investigations. It then defines CHF and provides details on its various etiologies including depressed ejection fraction, preserved ejection fraction, pulmonary heart disease, and high-output states. The pathophysiology section explains how heart failure progresses following an initial decline in pumping capacity. It also covers types of CHF and lists common clinical features and investigations used to evaluate patients with CHF.