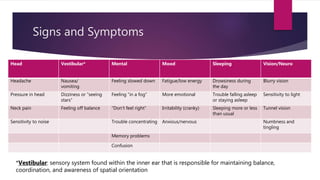
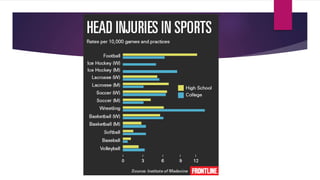
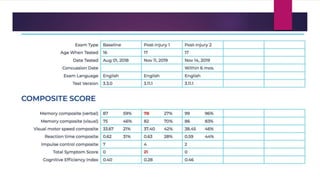
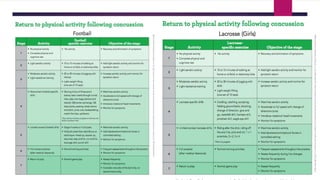
A concussion is a type of traumatic brain injury caused by a blow or hit to the head that causes the brain to move rapidly within the skull. This results in chemical changes in the brain, and symptoms may include headache, dizziness, fatigue, and difficulty concentrating. While often called "mild" injuries, concussions are serious and cannot be seen on x-rays or CT scans. Athletes who have previously sustained a concussion are at greater risk for future concussions. Proper diagnosis and a gradual return to activity under medical supervision are important for recovery.