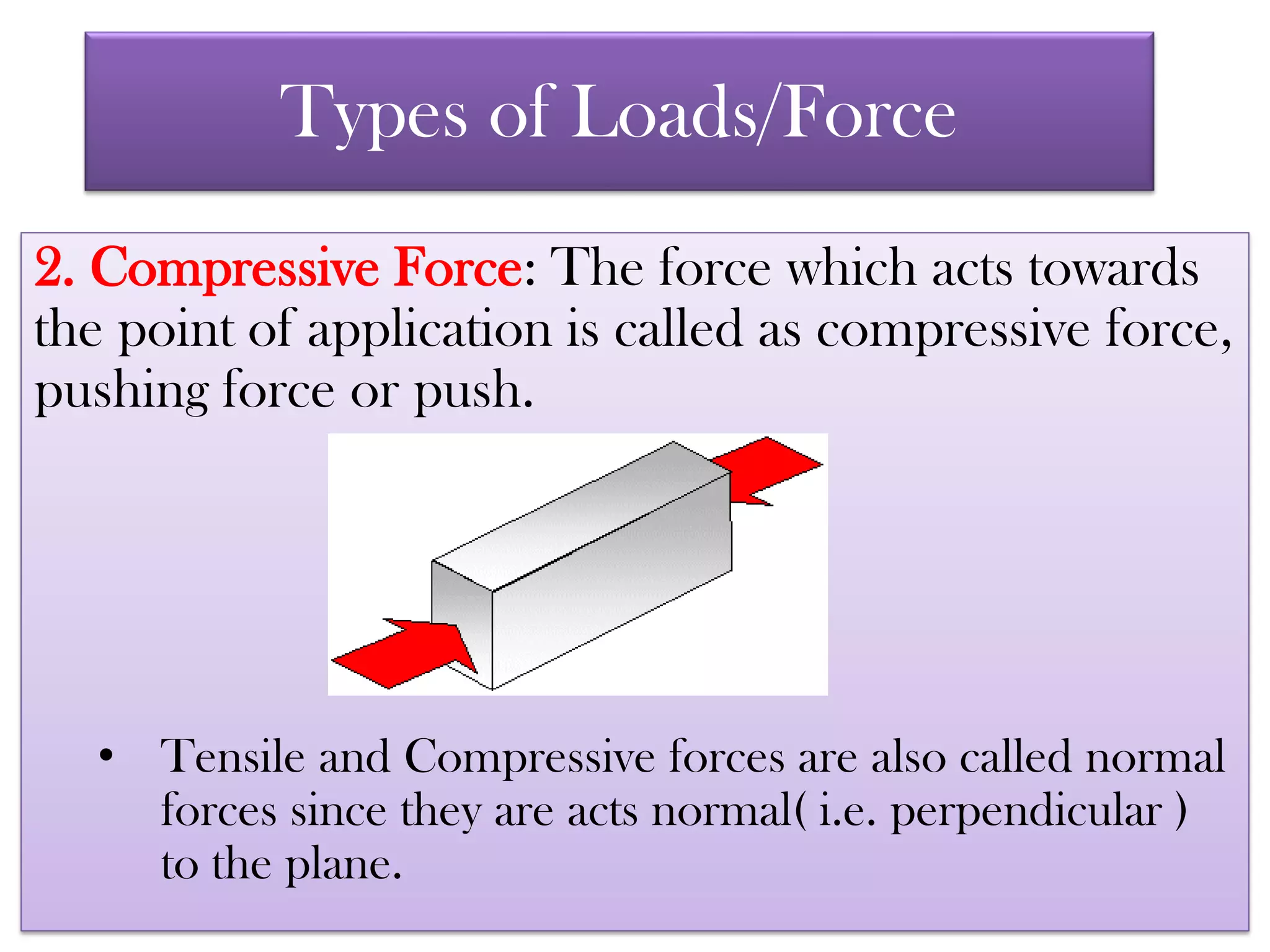
The document explains the concepts of stress and strain, defining elastic, plastic, and rigid bodies. It elaborates on various types of forces, stresses, and strains, including tensile, compressive, and shear forces, and introduces the key formulas for calculating stress, strain, and Young's modulus. It also presents practical problems and solutions related to the application of these concepts in engineering contexts.