The document discusses various concepts related to constructors in Java including:
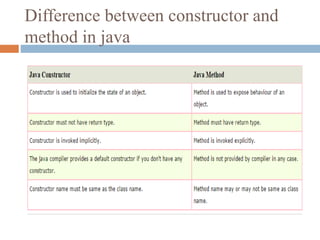
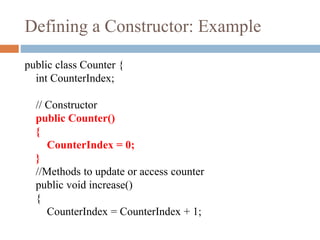
- Constructors are special methods that are invoked automatically when an object is created to initialize the object. They have the same name as the class.
- A class can have multiple constructors as long as they have different parameters. This is known as constructor overloading.
- Constructors without parameters are used to set default values. Parameterized constructors allow passing different values when creating distinct objects.
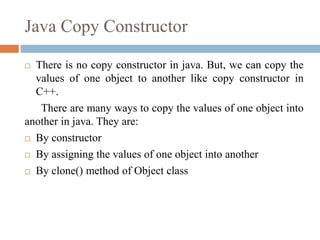
- Examples are provided to demonstrate default, parameterized, and multiple constructors. Copy constructors and differences between constructors and methods are also briefly covered.

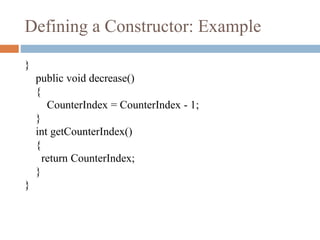
![Trace counter value at each statement
and What is the output ?
class MyClass {
public static void main(String args[])
{
Counter counter1 = new Counter();
counter1.increase();
int a = counter1.getCounterIndex();
counter1.increase();
int b = counter1.getCounterIndex();
if ( a > b )
counter1.increase();
else](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/conceptofconstructors-161009130926/85/Concept-of-constructors-5-320.jpg)
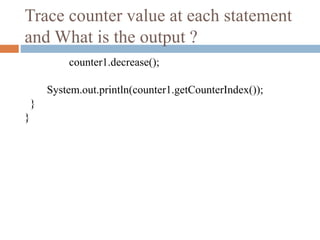

![Java parameterized constructor
name = n;
}
void display(){System.out.println(id+” ”+name);}
public static void main(String args[]){
Student4 s1 = new Student4(01,”Raj”);
Student4 s2 = new Student4(02,”Kamal”);
s1.display();
s2.display();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/conceptofconstructors-161009130926/85/Concept-of-constructors-8-320.jpg)

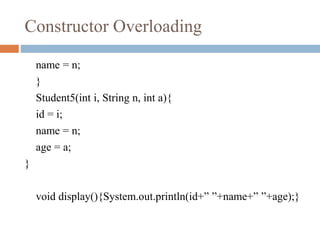
![Constructor Overloading
public static void main(String args[]){
Student5 s1 = new Student4(01,”Raj”);
Student5 s2 = new Student4(02,”Kamal”,21);
s1.display();
s2.display();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/conceptofconstructors-161009130926/85/Concept-of-constructors-11-320.jpg)
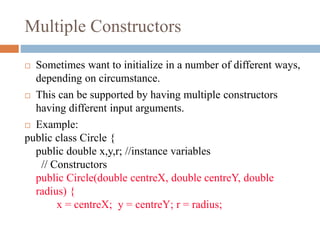
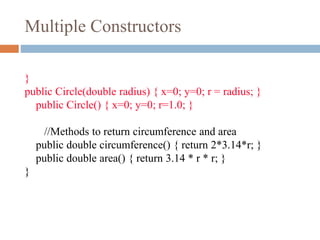
![Initializing with constructors
public class TestCircles {
public static void main(String args[]){
Circle circleA = new Circle( 10.0, 12.0, 20.0);
Circle circleB = new Circle(10.0);
Circle circleC = new Circle();
}
}
circleA = new Circle(10, 12, 20) circleB = new Circle(10)
Centre = (0,0)
Radius=10
circleC = new Circle()
Centre = (0,0)
Radius = 1
Centre = (10,12)
Radius = 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/conceptofconstructors-161009130926/85/Concept-of-constructors-14-320.jpg)