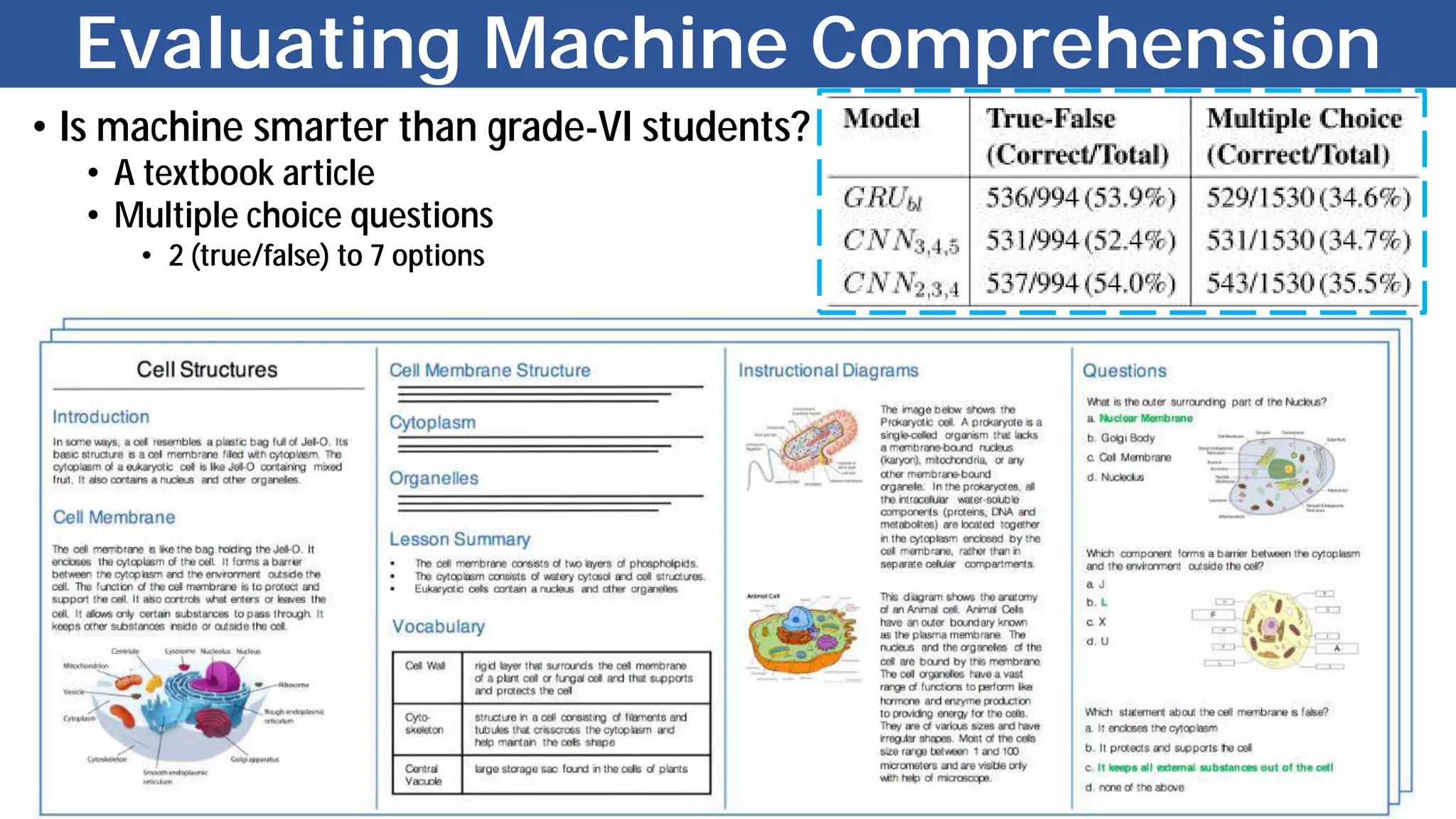
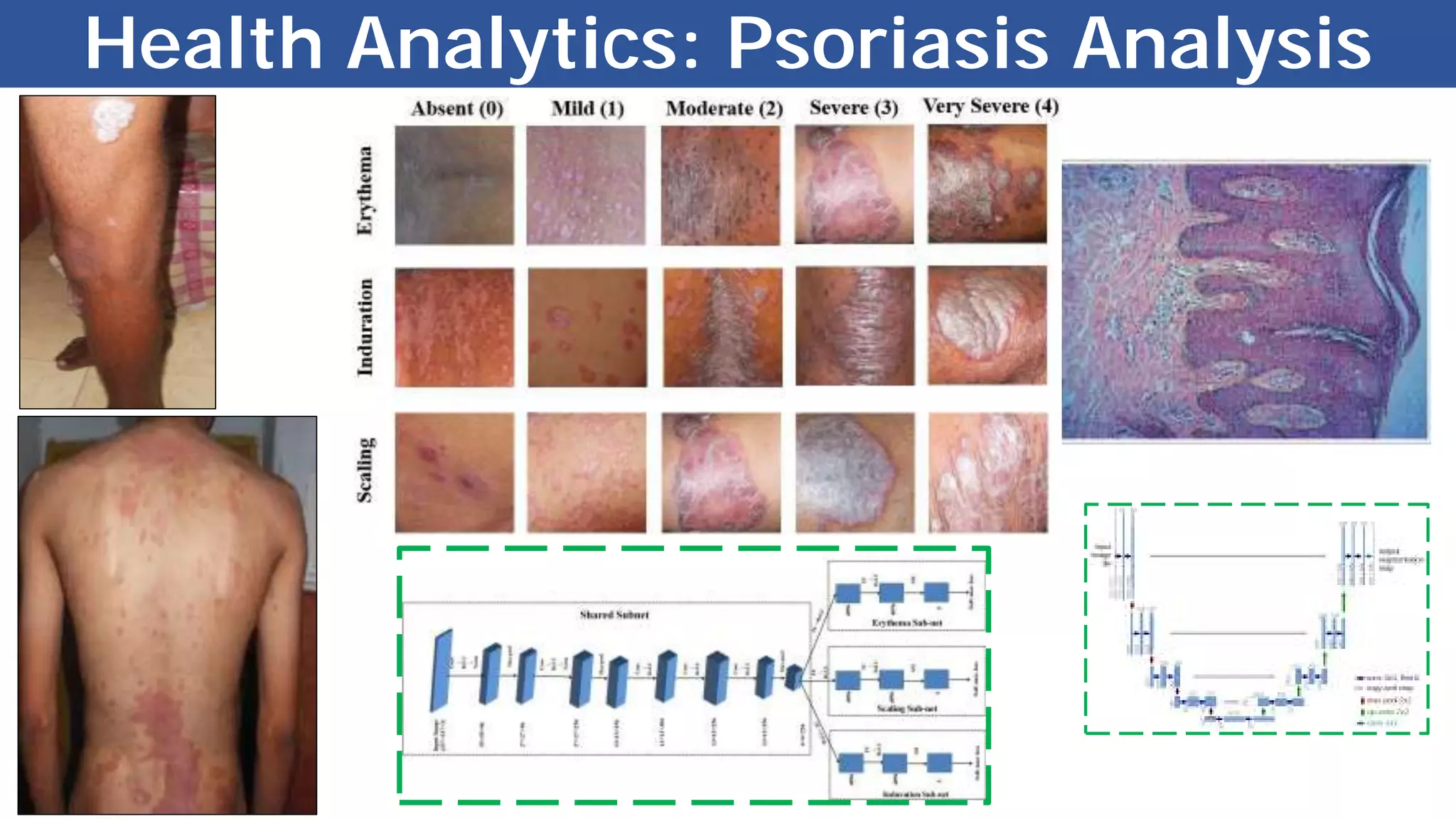
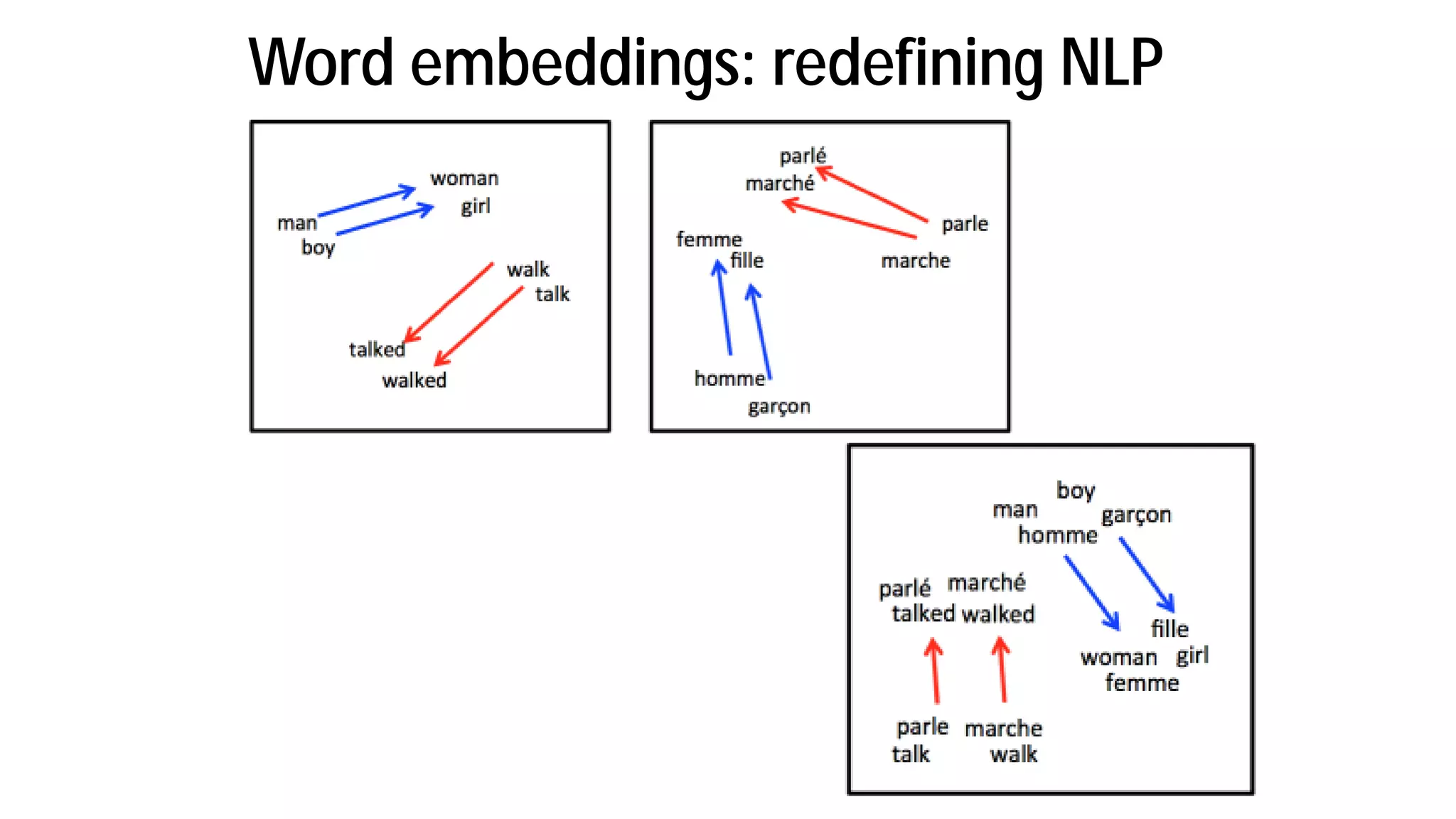
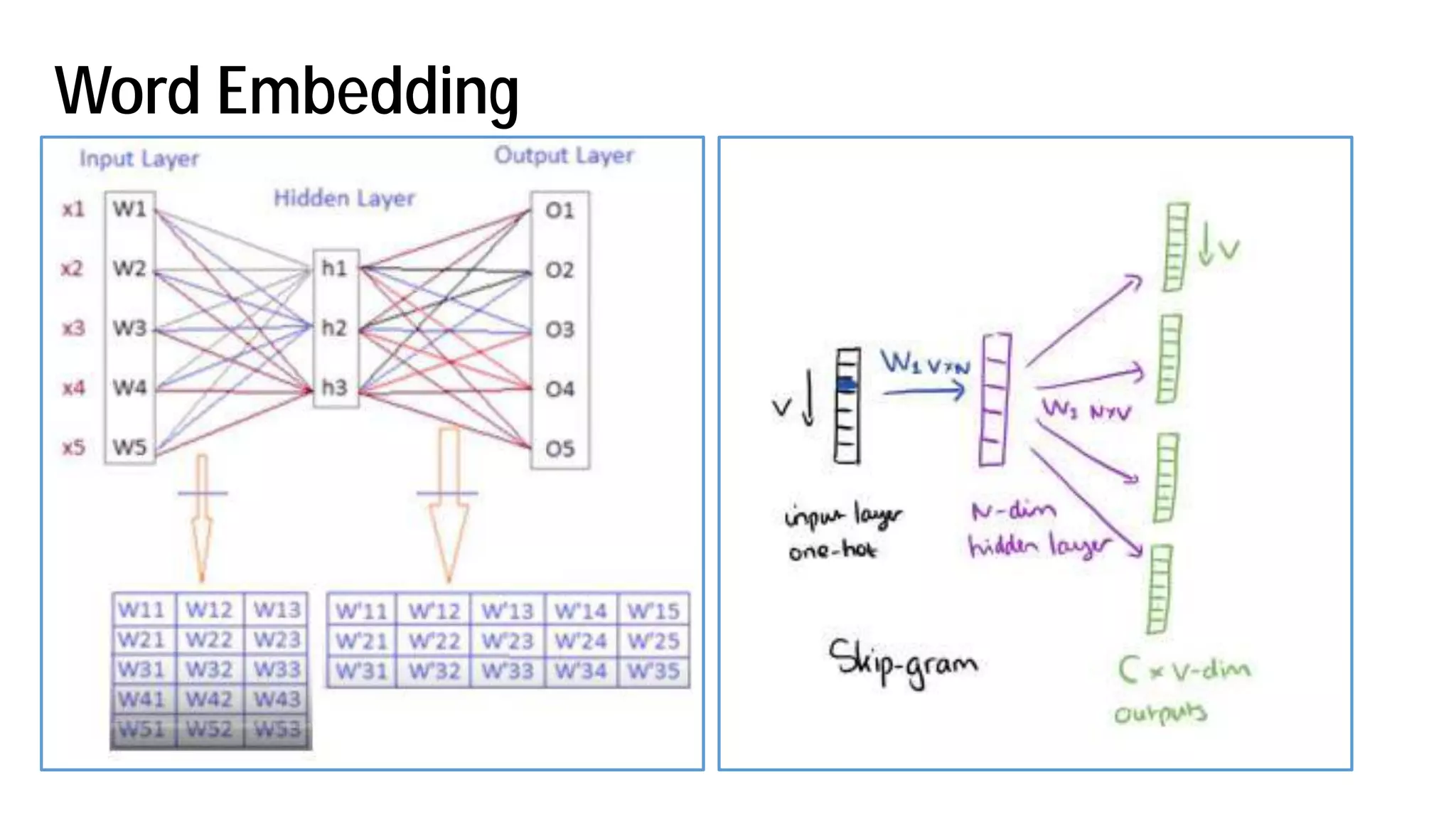
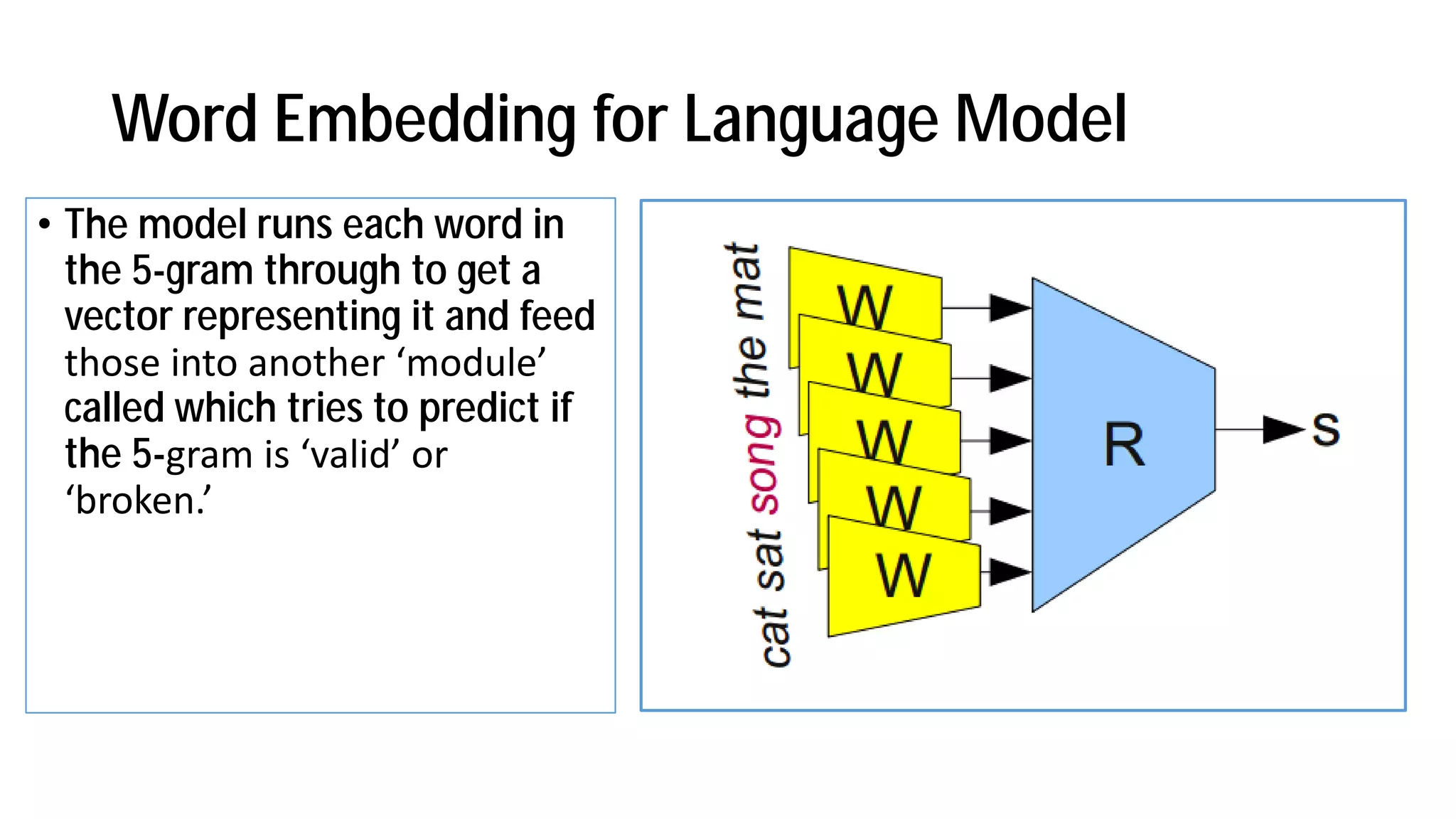
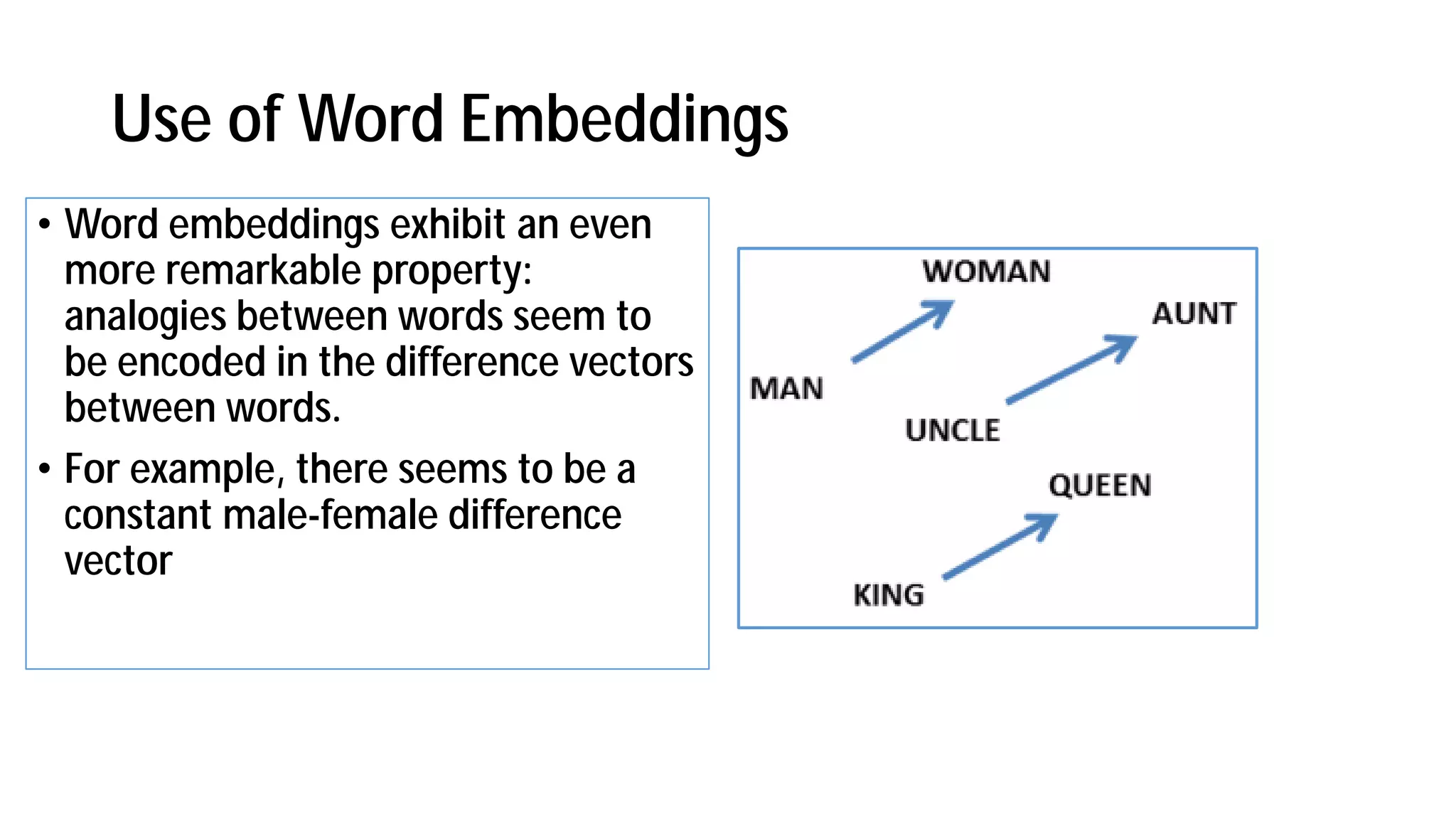
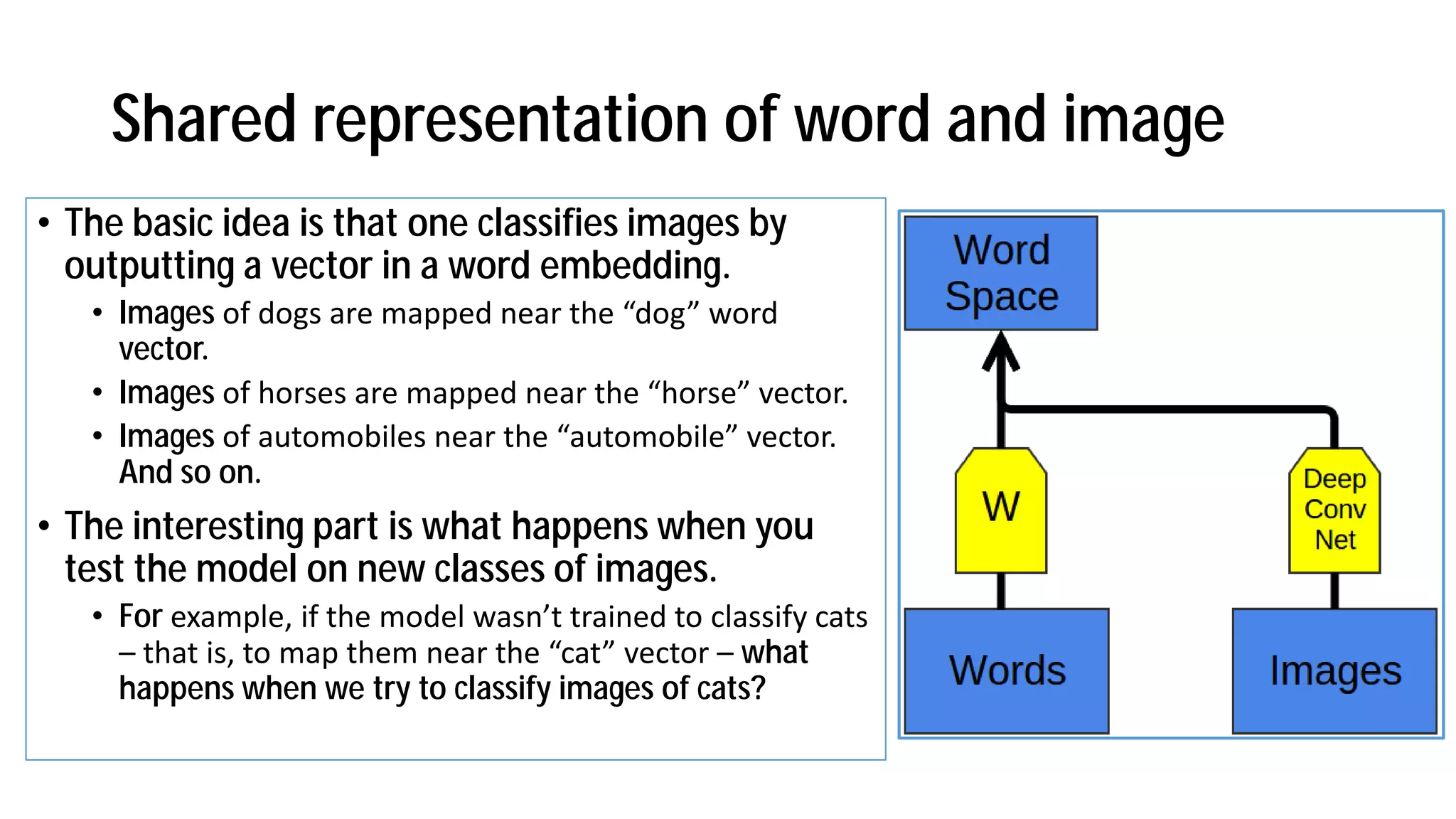
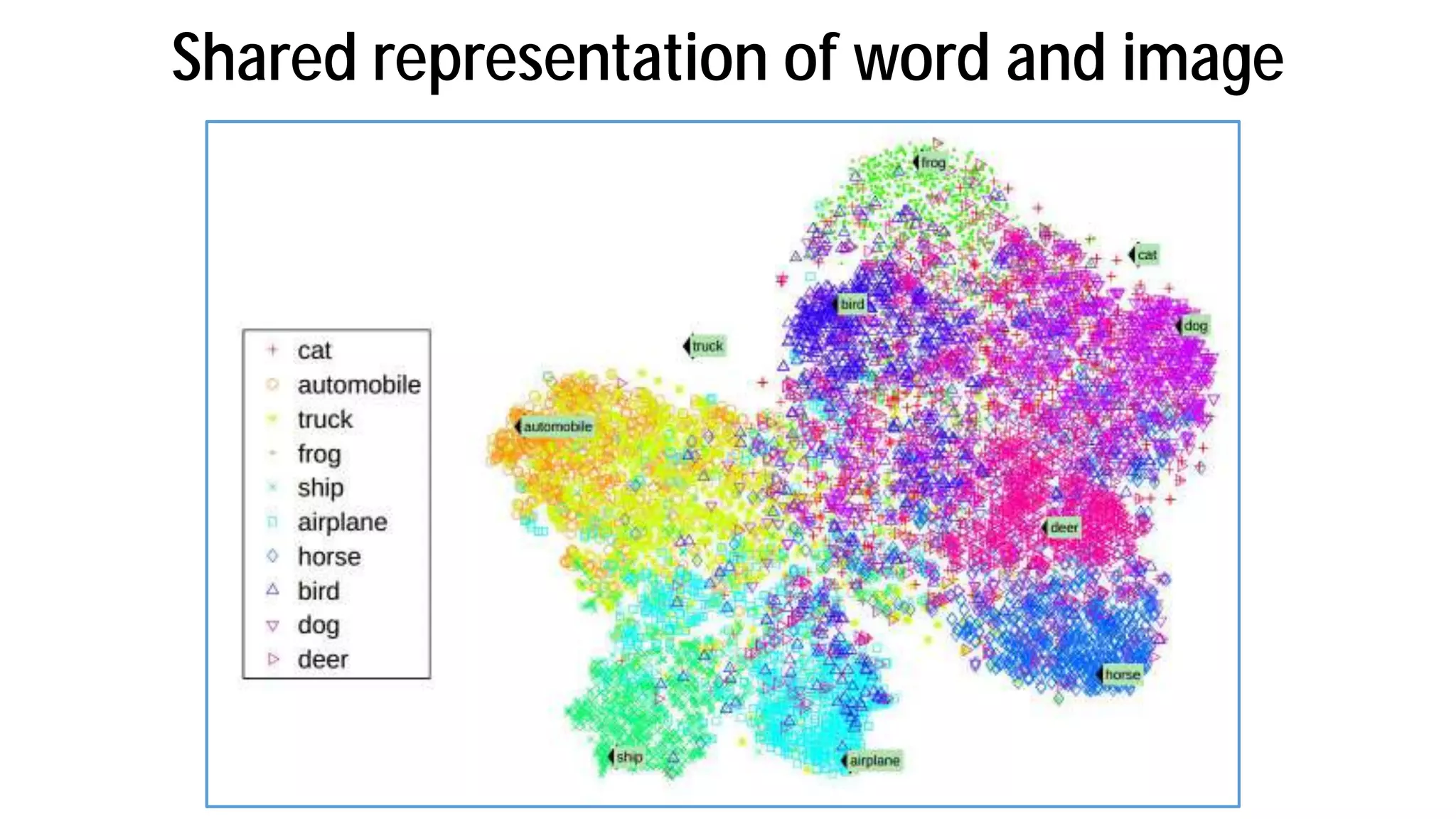
The document discusses the evolution and advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), particularly focusing on the shift towards cognitive computing in the 21st century. It highlights the role of big data, innovative algorithms, and examples like Watson's performance on Jeopardy as key milestones in AI's rebirth. Additionally, it addresses the current challenges in human resources for AI development and the establishment of research centers dedicated to AI and ML applications.