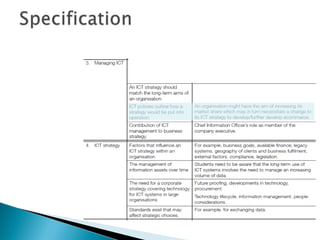
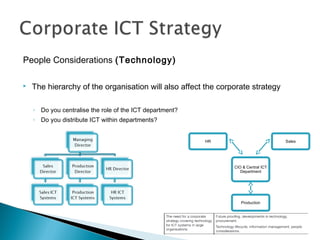
This document discusses ICT strategy development. It provides context on strategic plans and ICT strategies, and the purpose of a Chief Information Officer. Organisations must consider both internal and external factors when developing an ICT strategy. Internally, they should consider business goals, finances, legacy systems and information assets. Externally, key factors include technology changes, competitors, and compliance with various laws and regulations. The document provides examples of how these factors influence ICT strategy decisions.