Embed presentation
Download to read offline


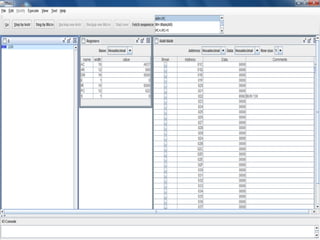
![• BUN
• Opcode =8
PC <- AR
• BUN_I
• Opcode =9
AR <- Main[AR]
PC <- AR](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1838drishti-160621084309/85/Computer-System-Architecture-BUN-instruction-3-320.jpg)
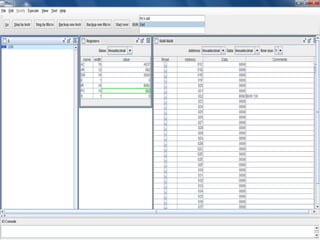
![BEFORE
EXECUTION…
DIRECT :
AC=A937
PC=022
Main[AR]=082](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1838drishti-160621084309/85/Computer-System-Architecture-BUN-instruction-4-320.jpg)

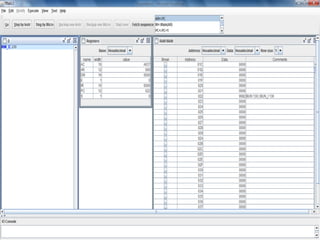
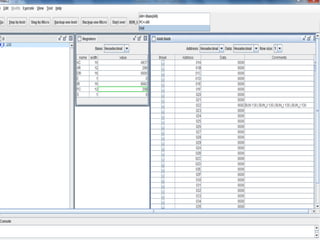
![BEFORE EXECUTION…
INDIRECT :
AC=A937
PC=022
Main[AR]=298
Main[298]=B8F2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1838drishti-160621084309/85/Computer-System-Architecture-BUN-instruction-8-320.jpg)



This document discusses direct and indirect branch instructions in computer system architecture. Direct branch instructions change the program counter (PC) directly to a new address, while indirect branch instructions first load the address from memory into the address register (AR) and then change the PC to that address. Examples are provided of before and after memory contents and register values for both direct and indirect branch instructions.


![• BUN
• Opcode =8
PC <- AR
• BUN_I
• Opcode =9
AR <- Main[AR]
PC <- AR](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1838drishti-160621084309/85/Computer-System-Architecture-BUN-instruction-3-320.jpg)
![BEFORE
EXECUTION…
DIRECT :
AC=A937
PC=022
Main[AR]=082](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1838drishti-160621084309/85/Computer-System-Architecture-BUN-instruction-4-320.jpg)



![BEFORE EXECUTION…
INDIRECT :
AC=A937
PC=022
Main[AR]=298
Main[298]=B8F2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1838drishti-160621084309/85/Computer-System-Architecture-BUN-instruction-8-320.jpg)



