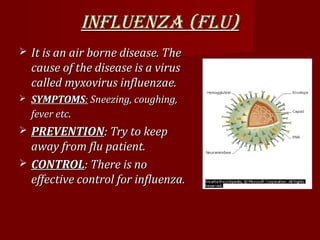
Communicable diseases like malaria, influenza, hepatitis, rabies, AIDS, tuberculosis, cholera, typhoid, and diarrhea can be spread from person to person through various means such as insects, air, food, water, sexual contact, and contaminated objects. Their symptoms and methods of prevention are described. Malaria symptoms include fever, chills, and sweats. Prevention methods include insecticide use and mosquito netting. Influenza spreads through air and its prevention focuses on avoiding infected individuals. [/SUMMARY]