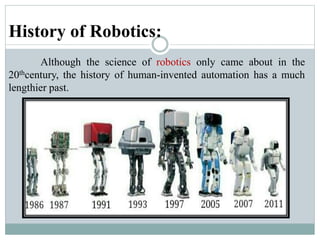
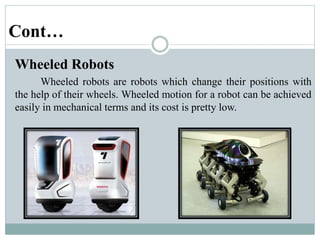
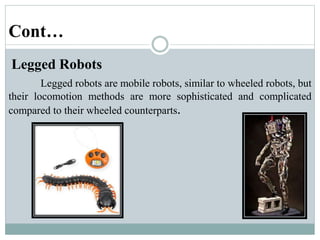
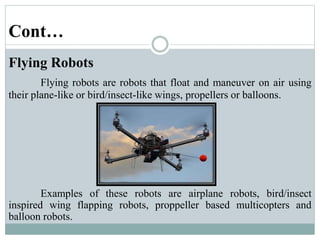
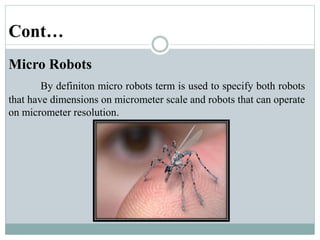
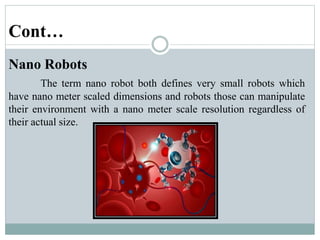
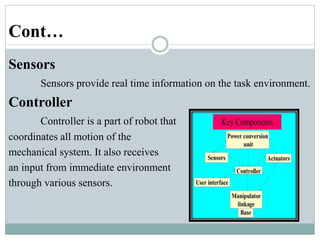
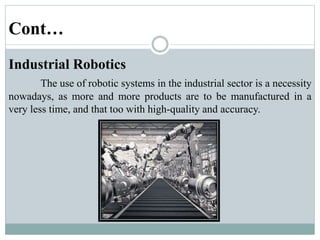
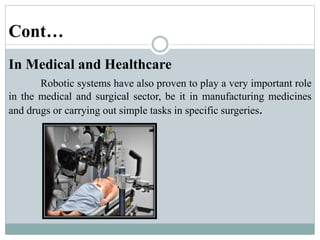
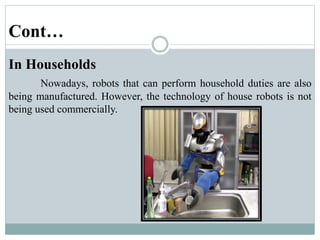
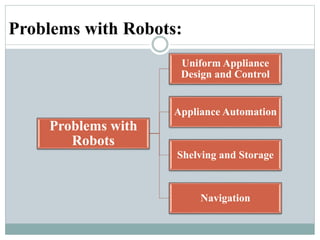
This presentation discusses robotics and was presented by 5 individuals supervised by Prof. Mubashir Tariq. It defines robots and covers the history of robotics. The main types of robots are described including industrial, wheeled, legged, swimming, flying, micro, and nano robots. The key components of robots and advantages like increased output are outlined. Disadvantages, laws of robotics, problems with robots, and the future of robotics are also examined. The conclusion discusses contributions to soft robotics modeling and control.