This document discusses different types of computer networks. It defines a computer network as a system that connects multiple computers to share information and resources. It describes local area networks (LANs) that connect devices within a residence, building or campus, wide area networks (WANs) that span cities and countries, and metropolitan area networks (MANs) that connect multiple LANs within a city. It also defines personal area networks (PANs) for connecting devices around an individual and campus area networks (CANs) within a limited geographic area. The document concludes by describing different network topologies including bus, ring, star, tree and mesh.


![INTRODUCTION
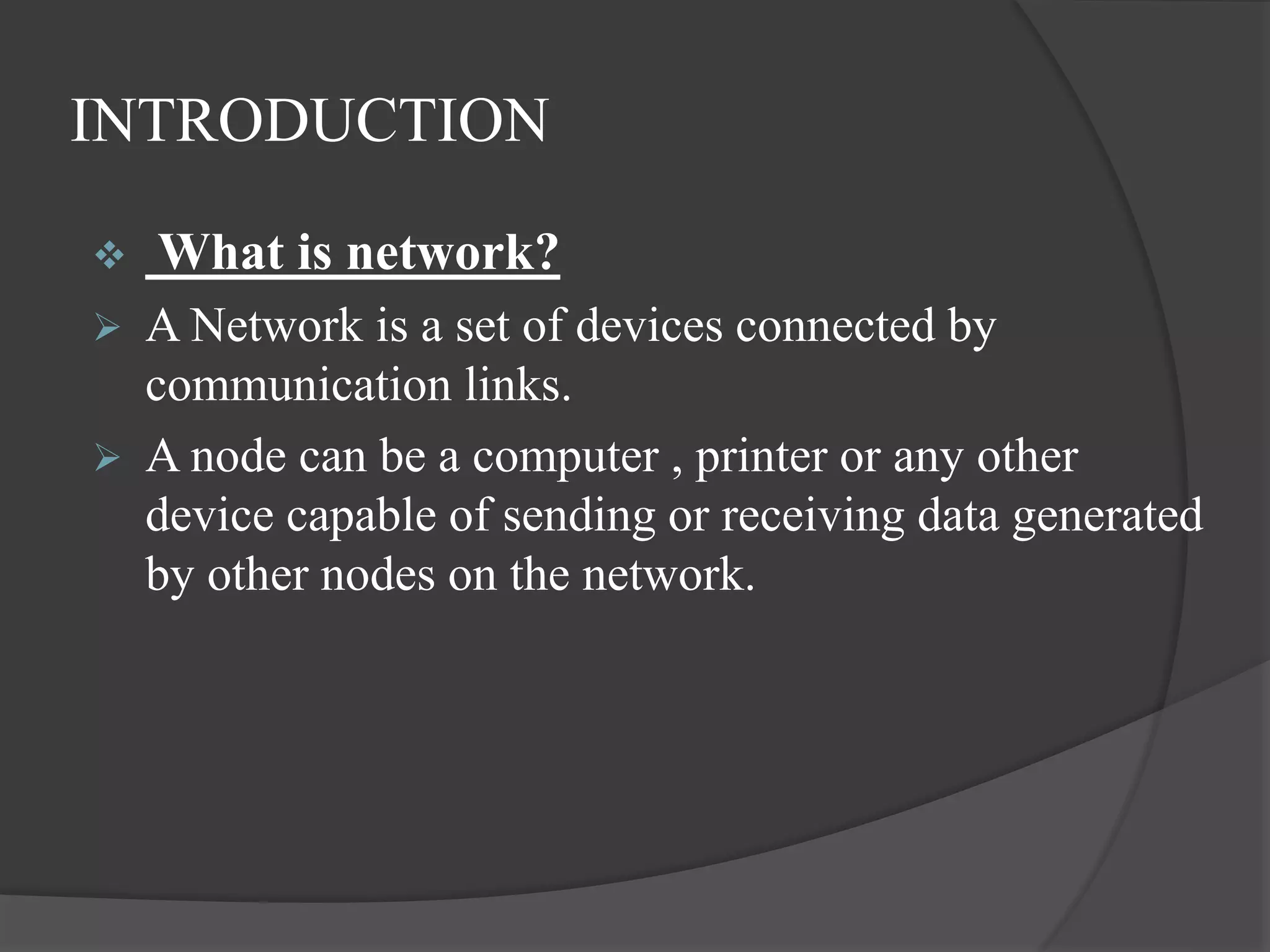
What is computer networks?
A computer network is a system in which multiple
computers are connected to each other to share
information and resources.
[Computer network]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computernetworks-180829165544/75/Computer-networks-4-2048.jpg)

![TYPES OF NETWORKS
LAN(Local Area Network):
LAN is a computer network that interconnects
computers within a limited area such as a
residence, school, laboratory, university campus
or office building.
[Local area network]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computernetworks-180829165544/75/Computer-networks-7-2048.jpg)
![TYPES OF NETWORKS
WAN (Wide Area Network):
WAN is a communications network that spans a
large geographic area such as across cities, states,
or countries.
[Wide area network]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computernetworks-180829165544/75/Computer-networks-8-2048.jpg)
![TYPES OF NETWORKS
MAN (Metropolitan Area Network):
MAN is similar to a LAN but spans an entire city or
campus. MANs are formed by connecting multiple
LANs. Thus, MANs are larger than LANs but smaller
than WAN.
[metropolitan area network]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computernetworks-180829165544/75/Computer-networks-9-2048.jpg)
![TYPES OF NETWORKS
PAN (Personal Area Network):
PAN is a computer network for interconnecting
devices centered on an individual person's workspace.
A PAN provides data transmission amongst devices
such as computers, smartphones , tablets and personal
digital assistants.
[personal area network]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computernetworks-180829165544/75/Computer-networks-10-2048.jpg)
![TYPES OF NETWORKS
CAN (Campus Area Network):
CAN is a computer network made up of an
interconnection of local area networks within a
limited geographical area.
[campus area network]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computernetworks-180829165544/75/Computer-networks-11-2048.jpg)


![REFERENCES
[1]https://tse4.mm.bing.net/th?id=OIP.4C_cvJOnrUCEkVZ
gMYwyyAHaE8&pid=15.1&P=0&w=240&h=161
[2]LAN:http://static.ccm2.net/ccm.net/faq/images/2761-lan-
s-.png
[3]Can:http://www.learnabhi.com/wp-
content/uploads/2018/02/can.jpg
[4]Wan:http://www.learnabhi.com/wp-
content/uploads/2018/02/can.jpg
[5]MAN:https://learnonit.files.wordpress.com/2014/03/metr
opolitan-area-network.jpg
[6]PAN:https://ictlounge.com/Images/pan_large.jpg](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computernetworks-180829165544/75/Computer-networks-20-2048.jpg)