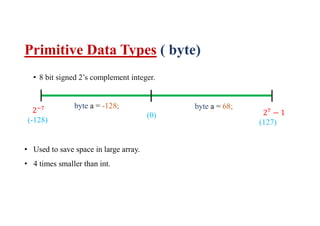
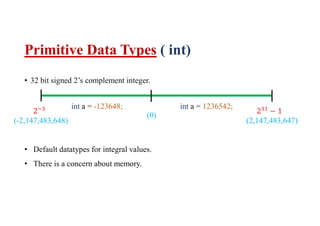
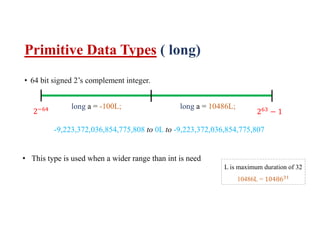
This document discusses basic Java datatypes. It explains that datatypes are used to create variables which reserve memory locations to store values. There are two main categories of datatypes - primitive and reference/object. The 8 primitive datatypes are byte, short, int, long, float, double, boolean and char. Reference datatypes refer to class objects and arrays. The document provides details on the typical size, range and usage of each primitive datatype. It also covers notation characters used to represent special characters in strings and chars.