The document provides an overview of operating systems, including:
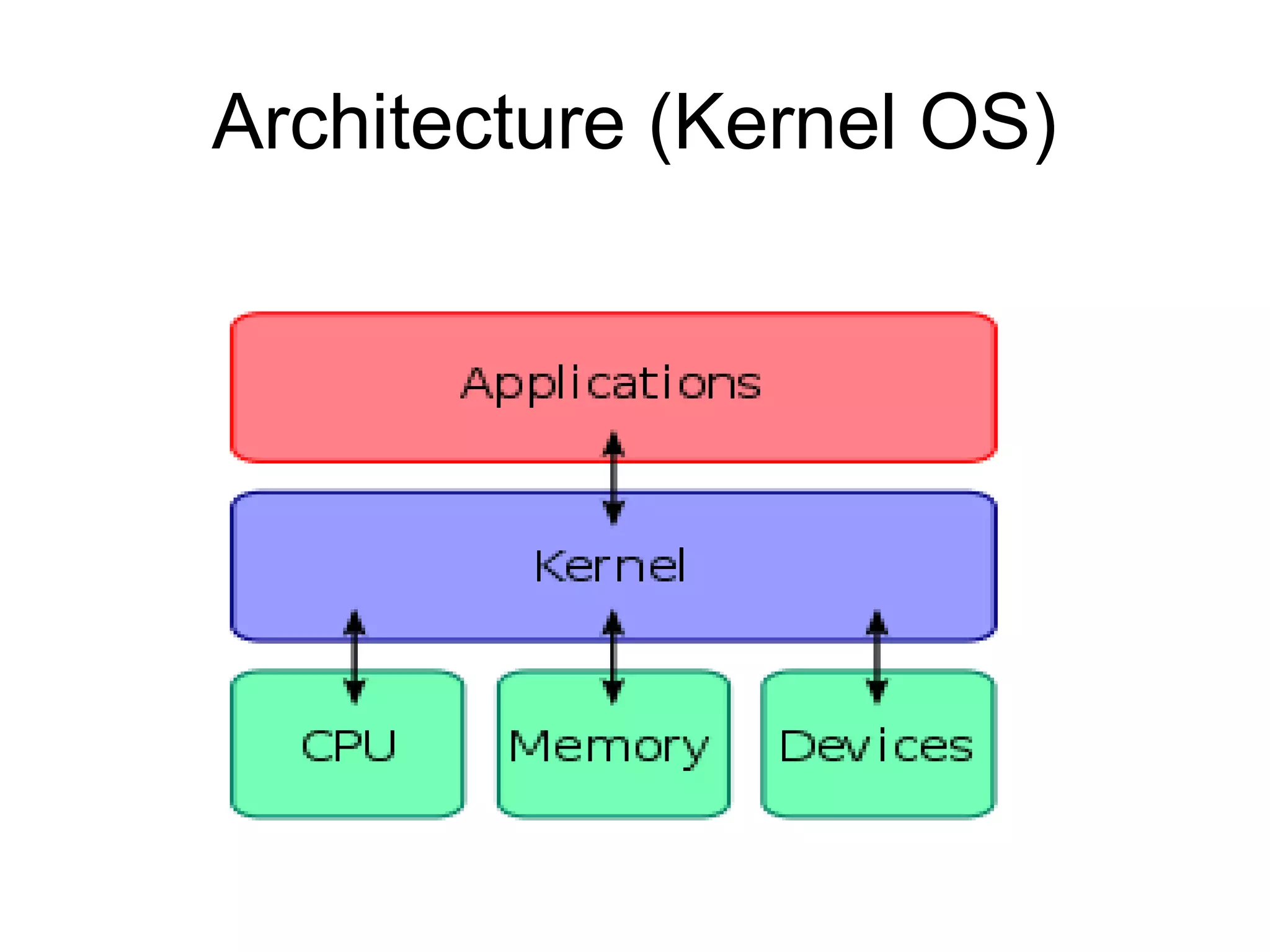
- An operating system manages hardware and provides services to computer programs through a cycle of hardware, OS, applications, and users. Real-time OS are for executing real-time applications with predictable responses to events.
- Common operating systems include Unix, Linux, Mac, Windows, Android, AIX, HP-UX, and Solaris. Distributed OS appear as one computer across many, and embedded OS are for embedded computer systems.
- Middleware provides services to software applications beyond the operating system to facilitate communication and data management between client and server. Development skills involve programming languages, software architecture, algorithms, and scripting.