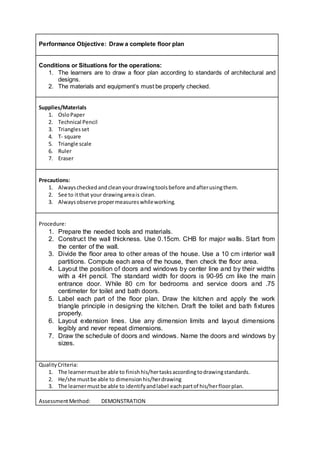
This document provides information on drafting floor plans, including technical terms and area planning considerations. It discusses the three main functional areas of a house: living areas, sleeping areas, and service/mechanical chore areas. For each area, it provides guidance on layout, sizes, and noise control considerations. Specific rooms discussed include the living room, bedrooms, kitchen, and bathroom. The document emphasizes the importance of logically dividing a building's functions into specific areas during the design process.