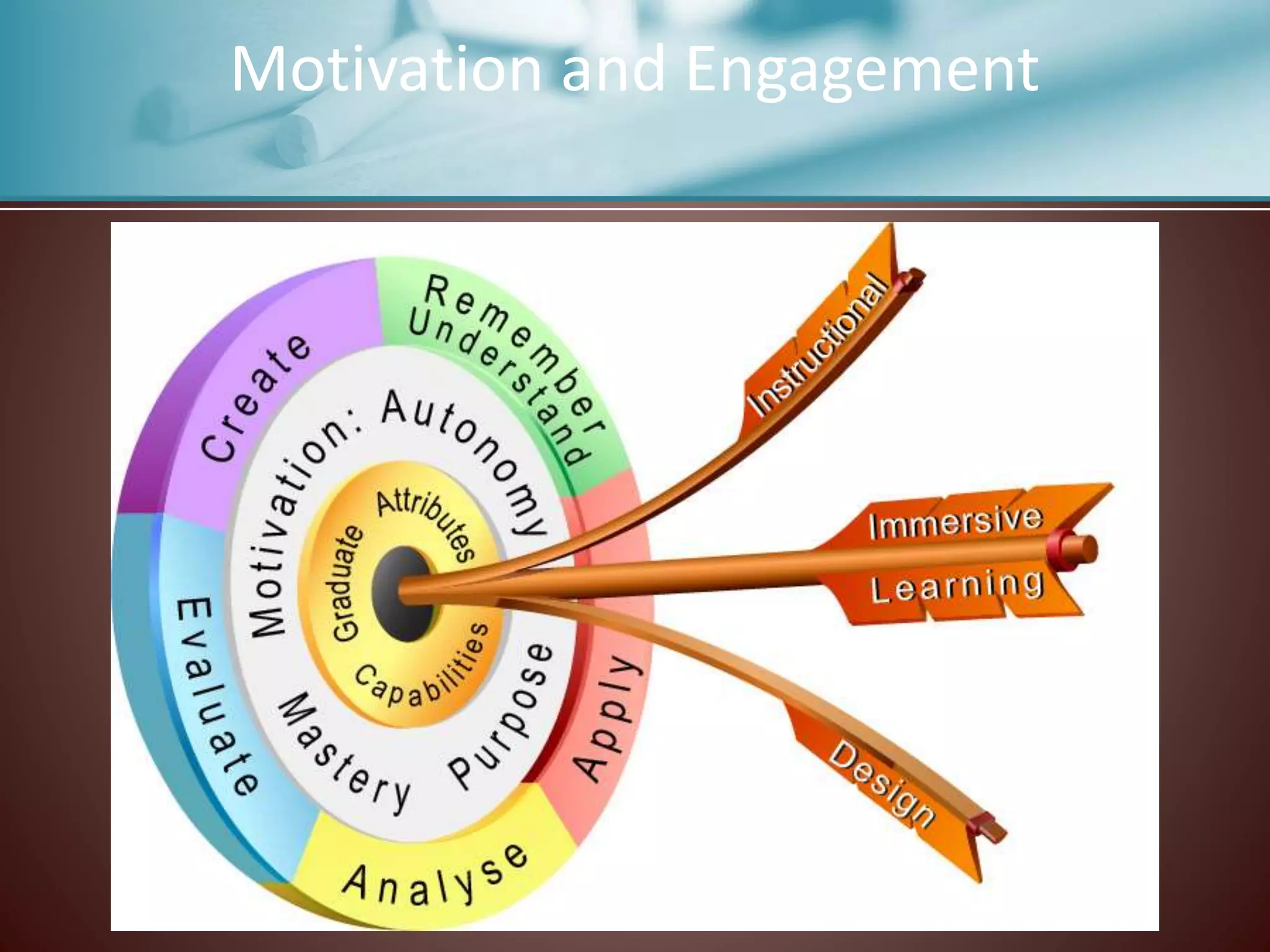
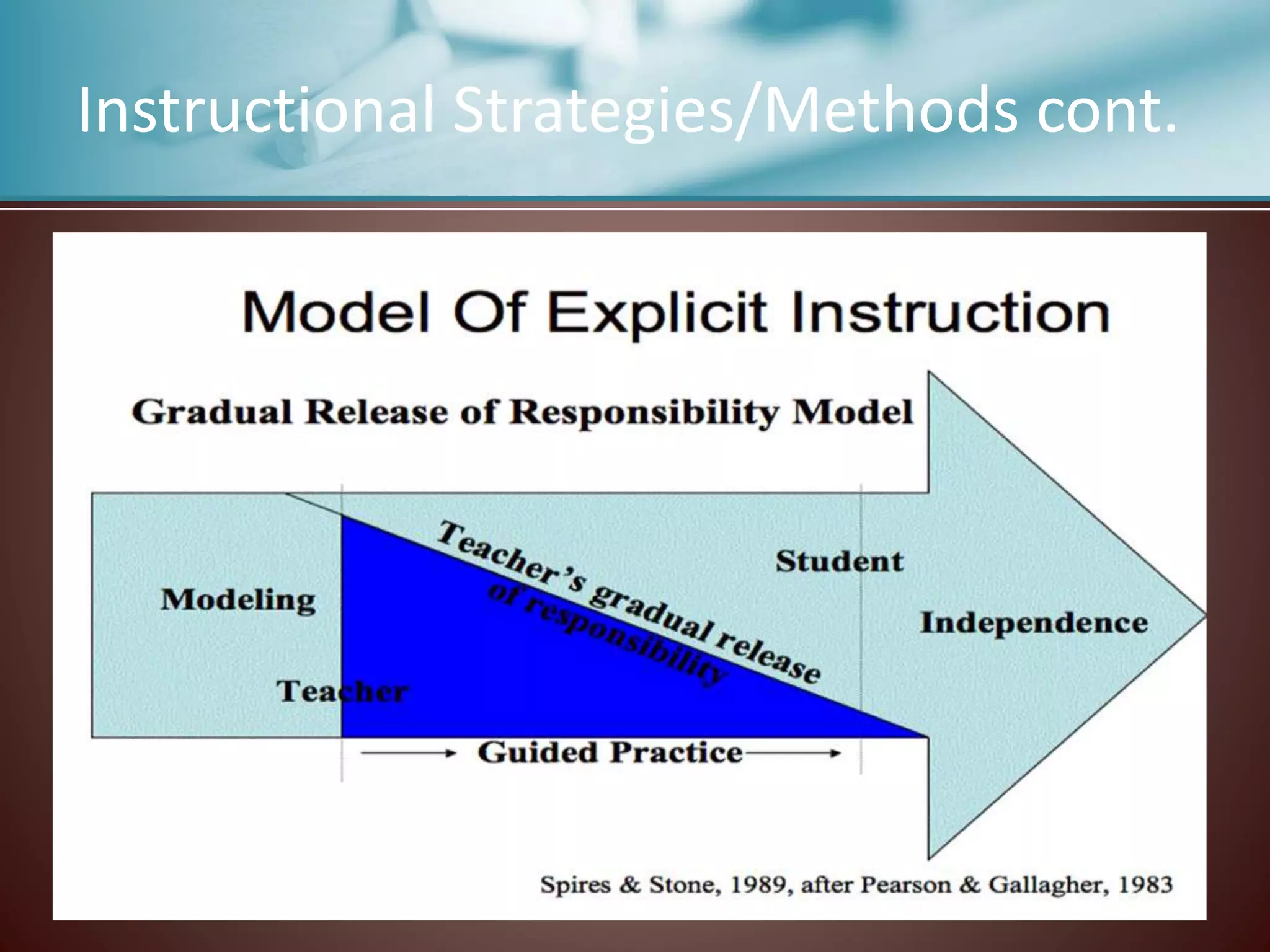
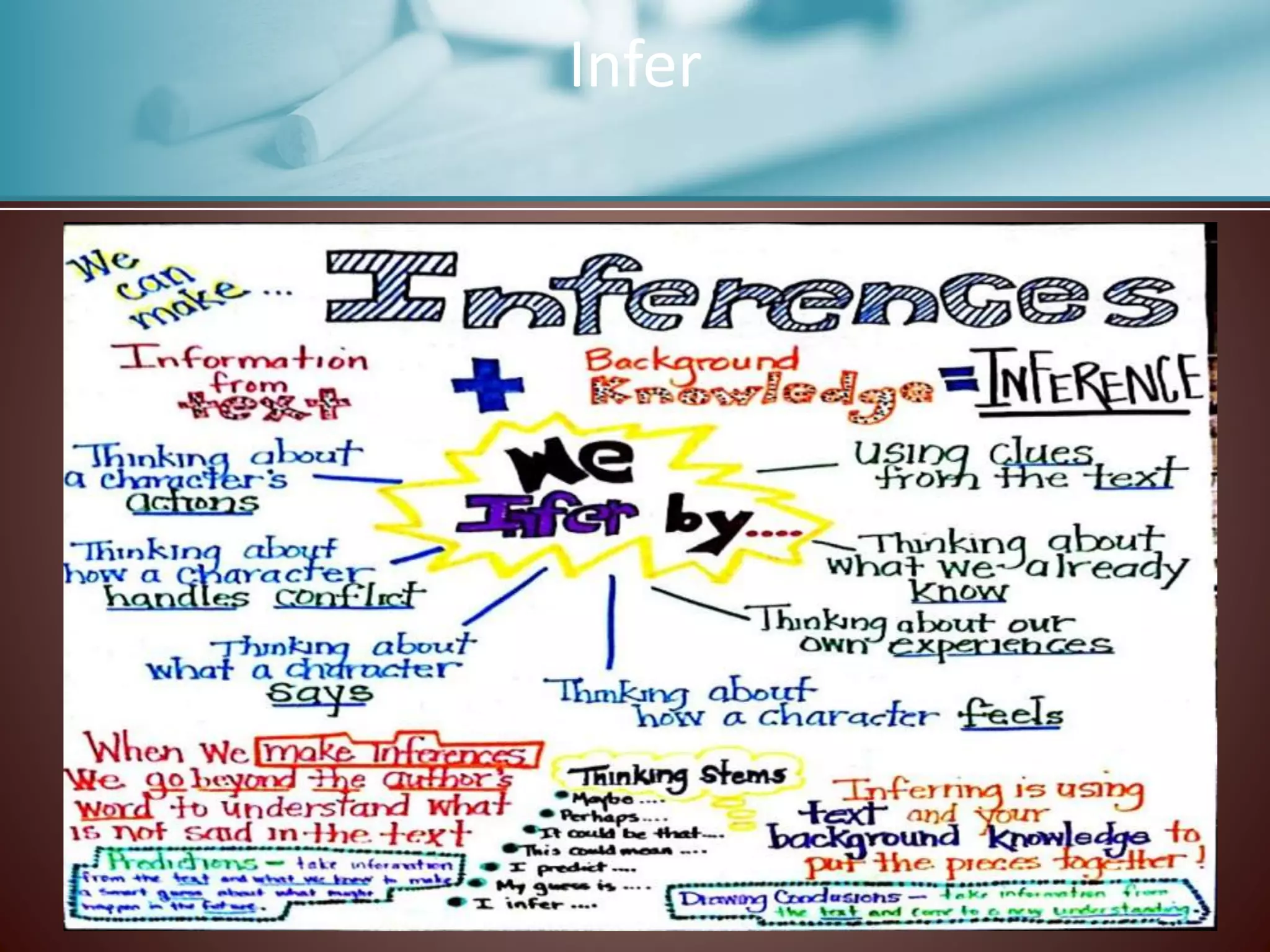
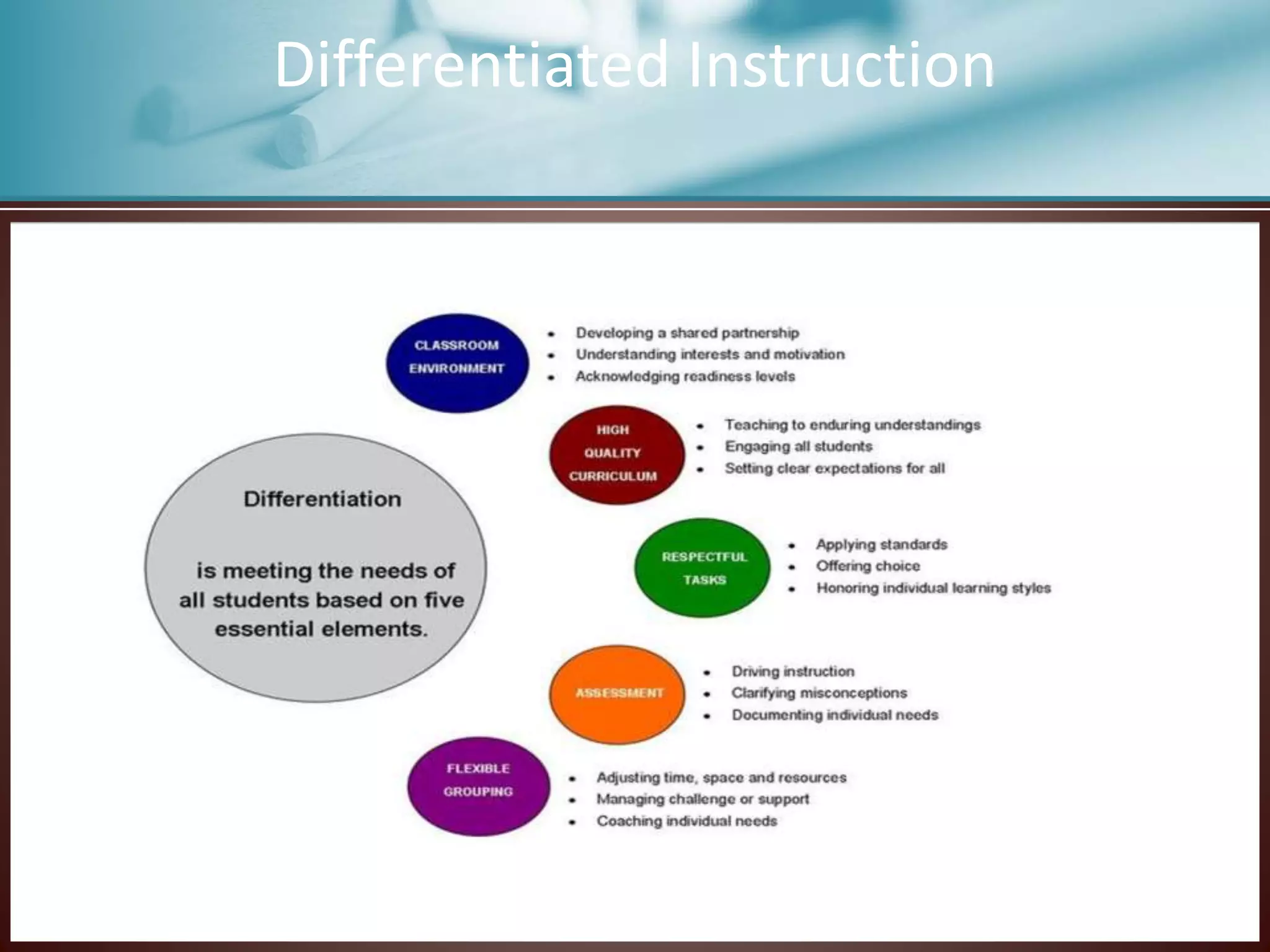
This document discusses strategies for supporting reading comprehension. It explains that comprehension is an active process that involves cognitive effort on the part of the reader. Teachers must provide explicit instruction in comprehension strategies and ensure students have experience with a variety of texts. Affective factors like metacognition, motivation, beliefs, and self-efficacy also influence comprehension and must be considered in instructional plans. The document outlines specific comprehension strategies like inferring, summarizing, and think-alouds that teachers can model and students can practice. It stresses the importance of differentiation, scaffolded instruction, and incorporating collaborative learning activities to meet diverse student needs.





















![• Afflerbach, P., Cho, B.-Y., Kim, J.-Y., Crassas, M. E., & Doyle, B. (2013). Reading: What else matters besides strategies and skills?
The Reading Teacher, 66 (6), 440–448.
• Common Core State Standards Initiative. (2012b). English language arts standards: Reading: Foundational skills:
Kindergarten. Retrieved from http://www.corestandards.org/ELA-Literacy/RF/K
• Hollenbeck, A. F., & Saternus, K. (2013). Mind the comprehension iceberg: Avoiding titanic mistakes with the CCSS. The Reading
Teacher, 66(7), 558–568.
• International Reading Association (IRA) and National Council of Teachers of English. (2014a). ReadWriteThink. Retrieved from
http://www.readwritethink.org/search/?grade=13&resource_type=6&learning_objective=8
• Laureate Education (Producer). (2014). Conversations with Ray Reutzel: Supporting comprehension
[Audio file]. Baltimore, MD: Author.
• SEDL. (2013). Cognitive elements of reading. Retrieved from http://www.sedl.org/reading/framework/elements.html
References](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/comprehensionpresentation-150923102816-lva1-app6892/75/Comprehension-presentation-26-2048.jpg)